Abstract
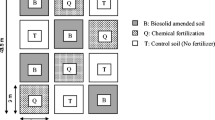
Accurate prediction of plant-available N release from sewage sludge is necessary to optimize crop yields and minimize NO3− leaching to groundwater. We conducted a 1.5-year study with three maize crops to determine N mineralization from an urban sewage sludge from Barueri, State of São Paulo, Brazil, and its potential to contaminate groundwater with NO3−. The soil at the experimental site was a loamy/clayey-textured Dark Red Dystroferric Oxisol. The treatments consisted of: plots without chemical fertilization or sludge, plots with complete chemical fertilization, and plots receiving four different doses of sewage sludge. Dose 1 was calculated at the agronomic N rate, while doses 2, 3 and 4 were, respectively, two, four, and eight times dose 1. The inorganic N addition increased with the rate of biosolid application. The high NO3− concentrations in relation to NH4+ were associated with intense soil nitrification. High N losses occurred for the first 27 days after soil sludge incorporation, even at the lowest dose, suggesting that land application of sewage sludge based on the N requirement of the crop may be overestimating the amount of sewage sludge to be applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee MR, Burton DL, Depoe S (1997) Impact of sewage sludge application on soil biological characteristics. Agric Ecosyst Environ 66:241–249
Barbarick KA, Ipplito JA, Westfall DG (1996) Distribution and mineralisation of biosolids nitrogen applied to dryland wheat. J Environ Qual 25:796–801
Boeira RC, Ligo MAV, Dynia JF (2002) Mineralização de nitrogênio em solo tropical tratado com lodos de esgoto. Pesq Agropec Bras 37:1639–1647
CETESB (1999) Aplicação de lodos de sistemas de tratamento biológico em áreas agrícolas—critérios para projeto e operação (manual técnico). Norma P 4230. CETESB, São Paulo
Craswell ET (1978) Some factors influencing denitrification and nitrogen immobilization in a clay soil. Soil Biol Biochem 10:214–245
Dou H, Alva AK, Khakural BR (1997) Nitrogen mineralization from citrus tree residues under different production conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 61:1226–1232
Hernández T, Moral R, Perez-Espinosa A, Moreno-Caselles J, Perez-Murcia MD, Garcia C (2002) Nitrogen mineralisation potential in calcareous soils amended with sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 83:213–219
Jorge JA, Camargo AO, Valadares JMAS (1991) Condições físicas de um latossolo Vermelho-Escuro quatro anos após aplicação de lodo esgoto e calcário. R Bras Ci Solo 15:237–240
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-inorganics forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wis., pp 643–698
Linderman WC, Cardenas M (1984) Nitrogen mineralization potential and nitrogen transformations of sludge-amended soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1072–1077
Lindsay BJ, Logan TJ (1998) Field response of soil physical properties to sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 27:534–542
Melfi AJ, Montes CR (2001) Impactos dos biossólidos sobre o solo. In: Tsutiya MT, Comparini JB, Sobrinho PA, Hespanhol I, Carvalho PCT, Melfi AJ, de Melo WJ, Marques MO (eds) Biossólidos na agricultura. Sabesp, São Paulo, pp 243–271
Melo WJ, Marques MO, Melo VP de (2001) O uso agrícola do biossólido e as propriedades do solo. In: Tsutiya MT, Comparini JB, Sobrinho PA, Hespanhol I, Carvalho PCT, Melfi AJ, Melo WJ de, Marques MO (eds) Biossólidos na agricultura. Sabesp, São Paulo, pp 289–363
Navarro Pedreño J, Moral R, Gómez I, Mataix J (1996) Reducing nitrogen losses by decreasing mineral fertilization in horticultural crops in eastern Spain. Agric Ecosyst Environ 59:217–221
Oliveira FC, Marques MO, Bellingieri PA, Perecin D (1995) Lodo de esgoto como fonte de macronutrientes para a cultura do sorgo granífero. Sci Agric 52:360–367
Olness A, Clapp CE, Liu R, Palazzo AJ (1998) Biosolids and their effects on soil properties. In: Wallace A, Terry RE (eds) Handbook of soil conditioners. Dekker, New York, pp 141–166
Paul EA, Clark FE (1989) Soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic, San Diego, Calif.
Raison RJ, Connele MJ, Khanna PK (1987) Methodology for studying fluxes of soil mineral N in situ. Soil Biol Biochem 19:521–530
Recous S, Mary B (1990) Microbial immobilization of ammonium and nitrate in cultivated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 22:913–922
Rice CW, Tiedje, JM (1989) Regulation of nitrate assimilation by ammonium in soils and in isolated soil microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 21:597–602
SAS Institute (1998) SAS/STAT users guide version 6.12. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Scott A, Ball BC, Crichton IJ, Aitken MN (2000) Nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions from grassland amended with sewage sludge. Soil Use Manage 16:36–41
Simarmata T, Benckiser G, Ottow JCG (1993) Effect of an increasing carbon:nitrate-N ratio on the reliability of acetylene in blocking the N2O-reductase activity of denitrifying bacteria in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 15:107–112
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 9:703–707
Verhagen FJM, Laanbroek HJ (1991) Competition for ammonium between nitrifying and heterotrophic bacteria in dual energy-limited chemostats. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3255–3263
Vieira RF (2001) Sewage sludge effects on soybean growth and nitrogen fixation. Biol Fertil Soils 34:196–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, R.F., Maia, A.H.N. & Teixeira, M.A. Inorganic nitrogen in a tropical soil with frequent amendments of sewage sludge. Biol Fertil Soils 41, 273–279 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0803-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0803-x