Abstract
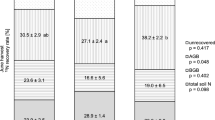
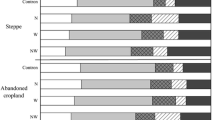
At four sites across Denmark with varying medium- and long-term histories of annual slurry applications, N turnover rates and crop N use efficiencies were measured in 2000. No significant effect of medium-term (in this study, 3 years) annual slurry applications on gross N turnover was observed. However, a significant effect of long-term (in this study, >25 years) annual slurry applications was observed. At one site in Denmark with short-term (4 days before measurement) slurry application, N turnover was measured in 2001. Gross N turnover was 4–5 times higher in the slurry-amended soil compared to the unamended soil. In both years, net N turnover was unaffected by the slurry application. Generally, the crops had higher use efficiency of slurry NH4 +-N than of mineral fertilizer-N, indicating that the crops were able to extract slurry organic-N, independently of the net mineralization. The measured net N mineralization rate was generally higher than the difference between gross rates. The application of 15NH4 + to soil (a prerequisite for the determination of N mineralization and N immobilization turnover), probably stimulated the gross N immobilization rate in soil with little native NH4 +, since NH4 + is the substrate for immobilization. The results suggest that gross immobilization estimates should be interpreted with caution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen MK, Jensen LS (2001) Low soil temperature effects on short-term gross N mineralisation-immobilisation turnover after incorporation of a green manure. Soil Biol Biochem 33:511–521
Barrett JE, Burke IC (2000) Potential nitrogen immobilization in grassland soils across a soil organic matter gradient. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1707–1716
Brooks PD, Stark JM, McInteer BB, Preston T (1989) Diffusion method to prepare soil extracts for automated nitrogen-15 analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1707–1711
Chang C, Sommerfeldt TG, Entz T (1991) Soil chemistry after eleven annual applications of cattle feedlot manure. J Environ Qual 20:474–480
DAAS (2000). Danish Agricultural Advisory Service. http://www.lr.dk/applikationer/kate/viskategori.asp?ID=ka00400012000080000200
Dawes EA (1976) Endogenous metabolism and the survival of starved prokaryotes. In: Gray TRG and Postgate JR (eds) The survival of vegetative microbes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 19–53
Jamieson N, Monaghan R, Barraclough D (1999) Seasonal trends of gross N mineralization in a natural calcareous grassland. Global Change Biol 5:423–431
Jensen LS, Pedersen IS, Hansen TB, Nielsen NE (2000) Turnover and fate of 15N-labelled cattle slurry ammonium-N applied in the autumn to winter wheat. Eur J Agron 12:23–35
Kirkham D, Bartholomew WV (1954) Equations for following nutrients transformantions in soil, utilizing tracer data. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 18:33–34
Ledgard SF, Jarvis SC, Hatch DJ (1998) Short-term nitrogen fluxes in grassland soils under different long-term nitrogen management regimes. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1233–1241
Limaux F, Recous S, Meynard JM, Guckert A (1999) Relationship between rate of crop growth at date of fertiliser N application and fate of fertiliser N applied to winter wheat. Plant Soil 214:49–59
Manlay RJ, Chotte JL, Masse D, Laurent JY, Feller C (2002) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus allocation in agro-ecosystems of a West African savanna. III. Plant and soil components under continuous cultivation. Agric Ecosyst Environ 88:249–269
Mary B, Recous S, Robin D (1998) A model for calculating nitrogen fluxes in soil using 15N tracing. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1963–1979
Murphy DV, Recous S, Stockdale EA, Fillery IRP, Jensen LS, Hatch DJ, Goulding KWT (2003) Gross nitrogen fluxes in soil: theory, measurement and application of 15N pool dilution techniques. Adv Agron 79:69–118
Nielsen NE, Schorring JK, Jensen HE (1988) Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen uptake by spring barley. In: Jenkinson DS and Smith KA (eds) Nitrogen effeciency in agricultural soils. Elsevier, London, pp 62–72
Norton JM, Firestone MK (1996) N dynamics in the rhizosphere of Pinus ponderosa seedlings. Soil Biol Biochem 28:351–362
Recous S, Machet JM (1998) Short-term immobilisation and crop uptake of fertiliser nitrogen applied to winter wheat: effect of date of application in spring. Plant Soil 206:137–149
Recous S, Robin D, Darwis D, Mary B (1995) Soil inorganic N availability: Effect on maize residue decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1529–1538
Recous S, Aita C, Mary B (1999) In situ changes in gross N transformations in bare soil after addition of straw. Soil Biol Biochem 31:119–133
SAS Institute (1988) SAS/STAT user’s guide, Release 6.03. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Sommerfeldt TG, Chang C, Entz T (1988) Long-term annual manure applications increase soil organic matter and nitrogen, and decrease carbon to nitrogen ratio. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1668–1672
Sørensen P, Amato M (2002) Remineralisation and residual effects of N after application of pig slurry to soil. Eur J Agron 16:81–95
Sørensen P, Jensen ES (1995) Mineralization-immobilization and plant uptake of nitrogen as influenced by the spatial distribution of cattle slurry in soils of different texture. Plant Soil 173:283–291
Sparling GP, Murphy DV, Thompson RB, Fillery IRP (1995) Short-term net N mineralization from plant residues and gross and net N mineralisation from soil organic matter after rewetting of a seasonally dry soil. Aust J Soil Res 33:961–973
Stockdale EA, Hatch DJ, Murphy DV, Ledgard SF, Watson CJ (2002) Vertifying the nitrification to immobilization ratio ( N/I) as a key determinant of potential nitrate loss in grassland and arable soils. Agronomie 22:831–838
Thomsen IK, Kjellerup V, Jensen B (1997) Crop uptake and leaching of 15N applied in ruminant slurry with selectively labelled faeces and urine fractions. Plant Soil 197:233–239
Tlustos P, Willison TW, Baker JC, Murphy DV, Pavlikova D, Goulding K-WT, Powlson DS (1998) Short-term effects of nitrogen on methane oxidation in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 28:64–70
Wang J, Bakken LR (1997) Competition for nitrogen during decomposition of plant residues in soil: effect of spatial placement of N-rich and N-poor plant residues. Soil Biol Biochem 29:153–162
Whalen JK, Chang C, Olson BM (2001) Nitrogen and phosphorus mineralization potentials of soils receving repeated annial cattle manure application. Biol Fertil Soils 34:334–341
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Danish Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries for funding this study. The authors also thank the Danish Agricultural Advisory Service for collaboration and guidance. Finally the authors thank Birthe K. Nielse and Anja H. Ivø for their supreme laboratory skills.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luxhøi, J., Debosz, K., Elsgard, L. et al. Mineralization of nitrogen in Danish soils, as affected by short-, medium- and long-term annual inputs of animal slurries. Biol Fertil Soils 39, 352–359 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0705-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0705-3