Abstract.
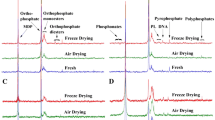
Soils of two climosequences in Russia were investigated by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. They comprised Dystric Podzoluvisols, Haplic Greyzems, Calcic Chernozems, and Gypsic Kastanozems, which are located along temperature and precipitation gradients of the Russian Plain. Another sequence of soils included forest Humic Cambisols and Umbric Leptosols of subalpine and alpine meadows, which are formed in different climatic conditions along a climosequence of the Mt. Malaya Khatipara (northern Caucasus). The results showed that accumulation of DNA was high in the cold, wet, and acid soils (Dystric Podzoluvisol, alpine Umbric Leptosol), while phospholipids and teichoic acids mainly accumulated in the more microbially active soils. We performed a laboratory incubation experiment to test the relationship between microbial biomass P and P species identified in soil extracts. The proportions of P compounds resonating at 0.5–3.0 ppm in the NaHCO3 and H2SO4 extracts from the incubated Humic Cambisol increased. The amounts of phosphate diesters resonating at 0 ppm in the same extracts and in the subsequent NaOH extracts decreased after incubation. Based on the results of 31P-NMR spectroscopy of native soils and of the laboratory incubation experiment we concluded that signals at 0 ppm in spectra of soil alkaline extracts belong to DNA P which is mainly stabilised in soil organic matter outside microbial cells (at least in soils with relatively low microbial activity). Phospholipids-teichoic acids P extracted with 0.5 M NaHCO3 seems to be derived from soil microbial biomass, and its proportion can reflect the microbial activity in the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makarov, .M., Haumaier, .L. & Zech, .W. The nature and origins of diester phosphates in soils: a 31P-NMR study. Biol Fertil Soils 35, 136–146 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0454-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0454-8