Abstract.
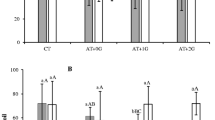
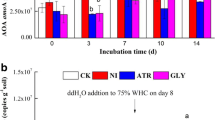
Atrazine alone and atrazine plus glyphosate were added to soil to determine their effect on soil microbial activity as measured by C and N mineralization (Cmin, Nmin) and soil extractable atrazine without the use of radiolabelled isotopes. Atrazine alone was added to soils as a formulated product (Aatrex 4L) at a field rate of 2× (94 mg kg–1), 4× (188 mg kg–1), and 6× (282 mg kg–1) with an assumed soil penetration depth of 58 mm. Glyphosate, as Roundup Ultra, was added along with atrazine to soil in equal amounts bringing the total cumulative herbicide amount to 2× (188 mg kg–1), 4× (376 mg kg–1) and 6× (564 mg kg–1) assuming a 2-mm soil penetration depth for glyphosate. Atrazine plus glyphosate stimulated microbial activity more than atrazine alone. During 56 days of incubation, mineralized C and N were highly correlated (r 2 =0.93). In addition, the C and N added from the herbicides were correlated with the amounts of C and N mineralized above the controls and were highly correlated (r 2 =0.93 for Cmin and r 2 =0.97 for Nmin). Cmin was greatest during the first 7 days of incubation after herbicide application while Nmin was greatest during the day 14 to day 28 period indicating a possible substrate shift from glyphosate to atrazine since atrazine has more N relative to C than glyphosate. Atrazine extracted from soil at four time periods (day 7, 14, 28, and 56) showed similar degradation curves (DT50 = 10.5 days) for the atrazine and atrazine-glyphosate treatments for all rates, with the exception of the 6× rate after 14 days and the 2× rate after 28 days of incubation where glyphosate appeared to slightly enhance the degradation of atrazine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haney, .R., Senseman, .S., Krutz, .L. et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization as affected by atrazine and glyphosate. Biol Fertil Soils 35, 35–40 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0437-1
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0437-1