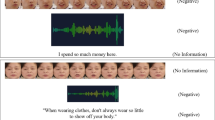
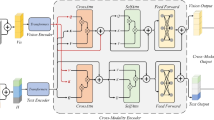
Abstract
Multimodal sentiment analysis is a challenging research area that aims to investigate the use of complementary multimodal information to analyze the sentiment tendencies of a character. In order to effectively fuse multimodal heterogeneous data from different information sources, the current advanced models have developed a variety of fusion strategies mainly based on text modality, and research in the field of audio–visual bimodal fusion is relatively scarce. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a framework for sentiment analysis based on audio and video bimodality, CCMA. Initially, we preprocess the raw data and retain modality-specific temporal information through positional embedding. On the one hand, in order to solve the issue of modal contribution unbalance, we use capsule network and 1D convolution at the video modality side and audio modality side, respectively, to better represent the modal features. On the other hand, we believe that inter-modal explicit interaction is the best way to fuse cross-modal information, and design a cross-modal attentional interaction module for explicit interaction of modal information to enhance the fusion quality. Experiments on two popular sentiment analysis datasets RAVDESS and CMU-MOSEI show that the accuracy of our model performs better that the competing methods, which illustrates the effectiveness of our method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
The datasets that support the findings of our study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The corresponding code for our research is available on GitHub at https://github.com/aodiguo/CCMA.
References
Zhu, L., Zhu, Z., Zhang, C., Xu, Y., Kong, X.: Multimodal sentiment analysis based on fusion methods: a survey. Inf. Fusion 95, 306–325 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.02.028
Xing, F.Z., Cambria, E., Welsch, R.E.: Natural language based financial forecasting: a survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 50(1), 49–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9588-9
Dang, C.N., Moreno-García, M.N., Prieta, F.D.L.: An approach to integrating sentiment analysis into recommender systems. Sensors 21(16), 5666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165666
Madhu, S.: An approach to analyze suicidal tendency in blogs and tweets using sentiment analysis. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng; 6(4):34–36. (2018). https://doi.org/10.26438/ijsrcse/v6i4.3436
Langlet, C., Clavel, C.: Grounding the detection of the user’s likes and dislikes on the topic structure of human-agent interactions. Knowl.-Based Syst. 106, 116–124 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.05.038
Pozzi, F.A., Fersini, E., Messina, E., Liu, B.: Challenges of sentiment analysis in social networks: an overview. Sentim. Anal. Soc. Netw. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804412-4.00001-2
Lee, C.M., Narayanan, S.S.: Toward detecting emotions in spoken dialogs. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 13(2), 293–303 (2005)
Zeng, Z., Pantic, M., Roisman, G. I., Huang, T. S.: A survey of affect recognition methods: audio, visual and spontaneous expressions. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, pp. 126–133 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1145/1322192.1322216
Noroozi, F., Corneanu, C.A., Kamińska, D., Sapiński, T., Escalera, S., Anbarjafari, G.: Survey on emotional body gesture recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 12(2), 505–523 (2018)
Hsu, Y.L., Wang, J.S., Chiang, W.C., Hung, C.H.: Automatic ECG-based emotion recognition in music listening. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 11(1), 85–99 (2017)
Gandhi, A., Adhvaryu, K., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Hussain, A.: Multimodal sentiment analysis: a systematic review of history, datasets, multimodal fusion methods, applications, challenges and future directions. Inf. Fusion 91, 424–444 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.09.025
Lin, X., Sun, S., Huang, W., Sheng, B., Li, P., Feng, D.D.: EAPT: efficient attention pyramid transformer for image processing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 50–61 (2021)
Han, W., Chen, H., Gelbukh, A., Zadeh, A., Morency, L. P., Poria, S.: Bi-bimodal modality fusion for correlation-controlled multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, pp. 6–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3462244.3479919
Yang, B., Shao, B., Wu, L., Lin, X.: Multimodal sentiment analysis with unidirectional modality translation. Neurocomputing 467, 130–137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.041
Wang, F., Tian, S., Yu, L., Liu, J., Wang, J., Li, K., Wang, Y.: TEDT: transformer-based encoding–decoding translation network for multimodal sentiment analysis. Cogn. Comput. 15(1), 289–303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-022-10073-9
Yang, B., Wu, L., Zhu, J., Shao, B., Lin, X., Liu, T.Y.: Multimodal sentiment analysis with two-phase multi-task learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 30, 2015–2024 (2022)
Wang, D., Guo, X., Tian, Y., Liu, J., He, L., Luo, X.: TETFN: A text enhanced transformer fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. Pattern Recogn. 136, 109259 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109259
Krishna, D. N., Patil, A.: Multimodal emotion recognition using cross-modal attention and 1D convolutional neural networks. In: Interspeech, pp. 4243–4247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2020-1190
Tsai, Y. H. H., Ma, M. Q., Yang, M., Salakhutdinov, R., Morency, L. P.: Multimodal routing: Improving local and global interpretability of multimodal language analysis. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. NIH Public Access, Vol. 2020, p. 1823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.143
Kim, D., Kang, P.: Cross-modal distillation with audio–text fusion for fine-grained emotion classification using BERT and Wav2vec 2.0. Neurocomputing 506, 168–183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.035
Cai, J., Meng, Z., Khan, A. S., Li, Z., O’Reilly, J., Han, S., et al.: Feature-level and model-level audiovisual fusion for emotion recognition in the wild. In: 2019 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR) (2019), pp. 443–448. IEEE
Kumar, P., Malik, S., Raman, B.: Interpretable multimodal emotion recognition using hybrid fusion of speech and image data. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16443-1
Majumder, N., Hazarika, D., Gelbukh, A., Cambria, E., Poria, S.: Multimodal sentiment analysis using hierarchical fusion with context modeling. Knowl.-Based Syst. 161, 124–133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.07.041
Ghosal, D., Akhtar, M. S., Chauhan, D., Poria, S., Ekbal, A., Bhattacharyya, P.: Contextual inter-modal attention for multi-modal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 3454–3466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D18-1382
Le, H.D., Lee, G.S., Kim, S.H., Kim, S., Yang, H.J.: Multi-label multimodal emotion recognition with transformer-based fusion and emotion-level representation learning. IEEE Access 11, 14742–14751 (2023)
Wei, Q., Huang, X., Zhang, Y.: FV2ES: a fully End2End multimodal system for fast yet effective video emotion recognition inference. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 69(1), 10–20 (2022)
Lin, Y. B., Li, Y. J., Wang, Y. C. F.: Dual-modality seq2seq network for audio-visual event localization. In: ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2002–2006. IEEE (2019)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., et al.: Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30 (2017)
Huang, J., Tao, J., Liu, B., Lian, Z., Niu, M.: Multimodal transformer fusion for continuous emotion recognition. In ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp. 3507–3511 (2020)
Wang, Z., Wan, Z., Wan, X.: Transmodality: An end2end fusion method with transformer for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of The Web Conference 2020, pp. 2514–2520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3366423.3380000
Tsai, Y. H. H., Bai, S., Liang, P. P., Kolter, J. Z., Morency, L. P., Salakhutdinov, R.: Multimodal transformer for unaligned multimodal language sequences. In: Proceedings of the conference. Association for Computational Linguistics. Meeting. NIH Public Access, Vol. 2019, p. 6558 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/p19-1656
Tang, J., Li, K., Jin, X., Cichocki, A., Zhao, Q., Kong, W.: Ctfn: Hierarchical learning for multimodal sentiment analysis using coupled-translation fusion network. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 5301–5311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.412
Hazarika, D., Zimmermann, R., Poria, S.: Misa: modality-invariant and-specific representations for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia, pp. 1122–1131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3394171.3413678
Zhang, Y., Chen, M., Shen, J., Wang, C.: Tailor versatile multi-modal learning for multi-label emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 36, No. 8, pp. 9100–9108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i8.20895
Lin, H., Zhang, P., Ling, J., Yang, Z., Lee, L.K., Liu, W.: PS-mixer: a polar-vector and strength-vector mixer model for multimodal sentiment analysis. Inf. Process. Manage. 60(2), 103229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2022.103229
Paraskevopoulos, G., Georgiou, E., Potamianos, A.: Mmlatch: bottom-up top-down fusion for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp. 4573–4577 (2022)
Sheng, B., Li, P., Ali, R., Chen, C.P.: Improving video temporal consistency via broad learning system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 52(7), 6662–6675 (2021)
Sabour, S., Frosst, N., & Hinton, G. E. (2017). Dynamic routing between capsules. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30.
Shahin, I., Hindawi, N., Nassif, A.B., Alhudhaif, A., Polat, K.: Novel dual-channel long short-term memory compressed capsule networks for emotion recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 188, 116080 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116080
Gu, D., Wang, J., Cai, S., Yang, C., Song, Z., Zhao, H., et al.: Targeted aspect-based multimodal sentiment analysis: an attention capsule extraction and multi-head fusion network. IEEE Access 9, 157329–157336 (2021)
Liu, J., Chen, S., Wang, L., Liu, Z., Fu, Y., Guo, L., Dang, J.: Multimodal emotion recognition with capsule graph convolutional based representation fusion. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp. 6339–6343 (2021).
Wu, J., Mai, S., Hu, H.: Interpretable multimodal capsule fusion. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 30, 1815–1826 (2022)
Livingstone, S.R., Russo, F.A.: The Ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (RAVDESS): a dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 13(5), e0196391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196391
Zadeh, A. B., Liang, P. P., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L. P.: Multimodal language analysis in the wild: Cmu-mosei dataset and interpretable dynamic fusion graph. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 2236–2246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-1208
Luna-Jiménez, C., Griol, D., Callejas, Z., Kleinlein, R., Montero, J.M., Fernández-Martínez, F.: Multimodal emotion recognition on RAVDESS dataset using transfer learning. Sensors 21(22), 7665 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227665
Guo, P., Chen, Z., Li, Y., Liu, H.: Audio-visual fusion network based on conformer for multimodal emotion recognition. In: CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 315–326). Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20500-2_26
Chumachenko, K., Iosifidis, A., Gabbouj, M.: Self-attention fusion for audiovisual emotion recognition with incomplete data. In: 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). IEEE, pp. 2822–2828 (2022)
Middya, A.I., Nag, B., Roy, S.: Deep learning based multimodal emotion recognition using model-level fusion of audio–visual modalities. Knowl.-Based Syst. 244, 108580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108580
Wang, Y., Wu, J., Furumai, K., Wada, S., Kurihara, S.: VAE-based adversarial multimodal domain transfer for video-level sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 10, 51315–51324 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant 62106214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A, Y and H discussed the idea and details of the experiment. H supervised the experiment and gave suggestions for improvement. A wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Guo, A. & Li, Y. CCMA: CapsNet for audio–video sentiment analysis using cross-modal attention. Vis Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03453-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03453-9