Abstract
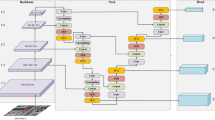
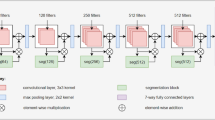
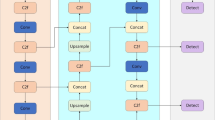
Mainstream RGB-T crowd counting methods use cross-modal complementary information to improve the counting accuracy. However, most of them neglect the effect of lighting variation on cross-modal data fusion. In this paper, we propose a Light-sensitive and Adaptive Fusion Network (LAFNet) for RGB-T crowd counting. Specifically, we present a Modality-specific Feature Extraction Module (MFEM) that fuses the lighting information, and a Light-sensitive and Adaptive Fusion Module (LAFM) that adjusts the fusion strategies of different modalities according to the lighting conditions of the input crowd images. Moreover, we propose an Improved Multi-scale Extraction Module (IMEM) to extract and fuse multi-modal at different scales. We evaluate our method on the RGBT-CC dataset and the experiment results show the validity of the model and its effectiveness in various scenarios.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gao, G., Gao, J., Liu, Q., Wang, Q., Wang, Y.: CNN-based density estimation and crowd counting: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.12783 (2020)
Fan, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Lu, G., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y.: A survey of crowd counting and density estimation based on convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 472, 224–251 (2022)
Kang, D., Ma, Z., Chan, A.B.: Beyond counting: comparisons of density maps for crowd analysis tasks-counting, detection, and tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 29(5), 1408–1422 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Zhou, D., Chen, S., Gao, S., Ma, Y.: Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 589–597 (2016)
Hashemzadeh, M., Farajzadeh, N.: Combining keypoint-based and segment-based features for counting people in crowded scenes. Inf. Sci. 345, 199–216 (2016)
Idrees, H., Tayyab, M., Athrey, K., Zhang, D., Al-Maadeed, S., Rajpoot, N., Shah, M.: Composition loss for counting, density map estimation and localization in dense crowds. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 532–546 (2018)
Alaska, Y.A., Aldawas, A.D., Aljerian, N.A., Memish, Z.A., Suner, S.: The impact of crowd control measures on the occurrence of stampedes during mass gatherings: the hajj experience. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 15, 67–70 (2017)
Shao, Y., Li, W., Chu, H., Chang, Z., Zhang, X., Zhan, H.: A multitask cascading CNN with multiscale infrared optical flow feature fusion-based abnormal crowd behavior monitoring uav. Sensors 20(19), 5550 (2020)
Zeng, X., Wu, Y., Hu, S., Wang, R., Ye, Y.: Dspnet: deep scale purifier network for dense crowd counting. Expert Syst. Appl. 141, 112977–112987 (2020)
Tripathi, G., Singh, K., Vishwakarma, D.K.: Convolutional neural networks for crowd behaviour analysis: a survey. Vis. Comput. 35, 753–776 (2019)
Khan, S.D., Salih, Y., Zafar, B., Noorwali, A.: A deep-fusion network for crowd counting in high-density crowded scenes. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 14(1), 168 (2021)
Zhang, S., Wu, G., Costeira, J.P., Moura, J.M.: Understanding traffic density from large-scale web camera data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5898–5907 (2017)
Liu, L., Zhen, J., Li, G., Zhan, G., He, Z., Du, B., Lin, L.: Dynamic spatial-temporal representation learning for traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(11), 7169–7183 (2021)
Sheng, B., Li, P., Ali, R., Chen, C.P.: Improving video temporal consistency via broad learning system. IEEE Trans. Cybernet. 52(7), 6662–6675 (2021)
Khan, S.D., Basalamah, S.: Sparse to dense scale prediction for crowd couting in high density crowds. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(4), 3051–3065 (2021)
Zhu, A., Zheng, Z., Huang, Y., Wang, T., Jin, J., Hu, F., Hua, G., Snoussi, H.: Cacrowdgan: cascaded attentional generative adversarial network for crowd counting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(7), 8090–8102 (2022)
Zhou, W., Liu, C., Lei, J., Yu, L., Luo, T.: Hfnet: hierarchical feedback network with multilevel atrous spatial pyramid pooling for RGB-D saliency detection. Neurocomputing 490, 347–357 (2022)
Deng, M., Zhao, H., Gao, M.: Clformer: a unified transformer-based framework for weakly supervised crowd counting and localization. Vis. Comput. 40(2), 1053–1067 (2023)
Basalamah, S., Khan, S.D., Ullah, H.: Scale driven convolutional neural network model for people counting and localization in crowd scenes. IEEE Access 7, 71576–71584 (2019)
Khan, S.D., Basalamah, S.: Scale and density invariant head detection deep model for crowd counting in pedestrian crowds. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2127–2137 (2021)
Bondi, E., Seidenari, L., Bagdanov, A.D., Del Bimbo, A.: Real-time people counting from depth imagery of crowded environments. In: 2014 11th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), pp. 337–342 (2014)
Hwang, S., Park, J., Kim, N., Choi, Y., So Kweon, I.: Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1037–1045 (2015)
Yu, T., Zheng, Z., Guo, K., Zhao, J., Dai, Q., Li, H., Pons-Moll, G., Liu, Y.: Doublefusion: real-time capture of human performances with inner body shapes from a single depth sensor. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7287–7296 (2018)
Fu, H., Ma, H., Xiao, H.: Real-time accurate crowd counting based on rgb-d information. In: 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 2685–2688 (2012)
Yang, S.-D., Su, H.-T., Hsu, W.H., Chen, W.-C.: Deccnet: Depth enhanced crowd counting. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), pp. 4521–4530 (2019)
Lian, D., Li, J., Zheng, J., Luo, W., Gao, S.: Density map regression guided detection network for RGB-D crowd counting and localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1821–1830 (2019)
Zhang, X., Yan, J., Feng, S., Lei, Z., Yi, D., Li, S.Z.: Water filling: Unsupervised people counting via vertical kinect sensor. In: 2012 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance, pp. 215–220 (2012)
Li, H., Zhang, S., Kong, W.: Rgb-d crowd counting with cross-modal cycle-attention fusion and fine-coarse supervision. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 19(1), 306–316 (2023)
Zhang, S., Li, H., Kong, W.: A cross-modal fusion based approach with scale-aware deep representation for RGB-D crowd counting and density estimation. Expert Syst. Appl. 180, 115071–115082 (2021)
Jiang, N., Sheng, B., Li, P., Lee, T.-Y.: Photohelper: portrait photographing guidance via deep feature retrieval and fusion. IEEE Transact. Multimed. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3144890
She, J., Liu, L., Liu, W.: Covid-19 epidemic: disease characteristics in children. J. Med. Virol. 92(7), 747–754 (2020)
Liu, L., Chen, J., Wu, H., Li, G., Li, C., Lin, L.: Cross-modal collaborative representation learning and a large-scale rgbt benchmark for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4823–4833 (2021)
Tang, H., Wang, Y., Chau, L.-P.: Tafnet: A three-stream adaptive fusion network for RGB-T crowd counting. In: 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 3299–3303 (2022)
Wu, Z., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Mao, M., Lin, L., Li, G.: Multimodal crowd counting with mutual attention transformers. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6 (2022)
Zhang, Y., Choi, S., Hong, S.: Spatio-channel attention blocks for cross-modal crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), pp. 90–107 (2022)
Chen, Z., Qiu, G., Li, P., Zhu, L., Yang, X., Sheng, B.: Mngnas: distilling adaptive combination of multiple searched networks for one-shot neural architecture search. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3293885
Lin, X., Sun, S., Huang, W., Sheng, B., Li, P., Feng, D.D.: Eapt: efficient attention pyramid transformer for image processing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 50–61 (2021)
Ma, Z., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Bayesian loss for crowd count estimation with point supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6142–6151 (2019)
Wu, B., Nevatia, R.: Detection of multiple, partially occluded humans in a single image by bayesian combination of edgelet part detectors. In: Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, vol. 1, pp. 90–971 (2005)
Sam, D.B., Peri, S.V., Sundararaman, M.N., Kamath, A., Babu, R.V.: Locate, size, and count: accurately resolving people in dense crowds via detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(8), 2739–2751 (2021)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) Computer Vision: ECCV 2020, pp. 213–229. Springer, Cham (2020)
Yu, R., Wang, S., Lu, Y., Di, H., Zhang, L., Lu, L.: Saf: Semantic attention fusion mechanism for pedestrian detection. In: Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 523–533 (2019)
Chen, D., Lu, L., Lu, Y., Yu, R., Wang, S., Zhang, L., Liu, T.: Cross-domain scene text detection via pixel and image-level adaptation. In: International Conference Neural Information Processing, pp. 135–143 (2019)
Idrees, H., Saleemi, I., Seibert, C., Shah, M.: Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2547–2554 (2013)
Chan, A.B., Vasconcelos, N.: Bayesian poisson regression for crowd counting. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 545–551 (2009)
Lowe, D.G.: Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1150–1157 (1999)
Zhang, C., Li, H., Wang, X., Yang, X.: Cross-scene crowd counting via deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 833–841 (2015)
Li, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, D.: Csrnet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1091–1100 (2018)
Shen, Z., Xu, Y., Ni, B., Wang, M., Hu, J., Yang, X.: Crowd counting via adversarial cross-scale consistency pursuit. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5245–5254 (2018)
Xie, Z., Zhang, W., Sheng, B., Li, P., Chen, C.P.: Bagfn: broad attentive graph fusion network for high-order feature interactions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34(8), 4499–4513 (2021)
Wang, S., Lu, Y., Zhou, T., Di, H., Lu, L., Zhang, L.: Sclnet: spatial context learning network for congested crowd counting. Neurocomputing 404, 227–239 (2020)
Xie, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, S.: Rsanet: Deep recurrent scale-aware network for crowd counting. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1531–1535 (2020)
Duan, Z., Wang, S., Di, H., Deng, J.: Distillation remote sensing object counting via multi-scale context feature aggregation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–12 (2021)
Chen, X., Yu, X., Di, H., Wang, S.: Sa-internet: scale-aware interaction network for joint crowd counting and localization. In: Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision, pp. 203–215 (2021)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Liu, L., Chen, J., Wu, H., Li, G., Li, C., Lin, L.: Cross-modal collaborative representation learning and a large-scale rgbt benchmark for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4823–4833 (2021)
Guerrero-Gómez-Olmedo, R., Torre-Jiménez, B., López-Sastre, R., Maldonado-Bascón, S., Oñoro-Rubio, D.: Extremely overlapping vehicle counting. In: Paredes, R., Cardoso, J.S., Pardo, X.M. (eds.) Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, pp. 423–431. Springer, Cham (2015)
Zhang, J., Fan, D.-P., Dai, Y., Anwar, S., Saleh, F.S., Zhang, T., Barnes, N.: Uc-net: Uncertainty inspired rgb-d saliency detection via conditional variational autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8582–8591 (2020)
Pang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., Lu, H.: Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) Computer Vision: ECCV 2020, pp. 235–252. Springer, Cham (2020)
Zhou, W., Zhu, Y., Lei, J., Wan, J., Yu, L.: Ccafnet: crossflow and cross-scale adaptive fusion network for detecting salient objects in RGB-D images. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 2192–2204 (2022)
Zhou, W., Zhu, Y., Lei, J., Wan, J., Yu, L.: Apnet: adversarial learning assistance and perceived importance fusion network for all-day RGB-t salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 6(4), 957–968 (2022)
Zhang, Q., Chan, A.B.: Wide-area crowd counting via ground-plane density maps and multi-view fusion cnns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8297–8306 (2019)
Fan, D.-P., Zhai, Y., Borji, A., Yang, J., Shao, L.: Bbs-net: Rgb-D salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) Computer Vision: ECCV 2020, pp. 275–292. Springer, Cham (2020)
Lin, H., Ma, Z., Ji, R., Wang, Y., Hong, X.: Boosting crowd counting via multifaceted attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 19628–19637 (2022)
Wang, B., Liu, H., Samaras, D., Nguyen, M.H.: Distribution matching for crowd counting. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M.F., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1595–1607 (2020)
Li, H., Zhang, S., Kong, W.: RGB-D crowd counting with cross-modal cycle-attention fusion and fine-coarse supervision. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 19(1), 306–316 (2023)
Yu, Y., Cai, Z., Miao, D., Qian, J., Tang, H.: An interactive network based on transformer for multimodal crowd counting. Appl. Intell. 53(19), 22602–22614 (2023)
Li, S., Hu, Z., Zhao, M., Bi, S., Sun, Z.: Cross-modal collaborative representation and multi-level supervision for crowd counting. SIViP 17(3), 601–608 (2023)
Thißen, M., Hergenröther, E.: Why existing multimodal crowd counting datasets can lead to unfulfilled expectations in real-world applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06401 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH Conceptualization of this study, methodology, software, validation, investigation, visualization. WK Conceptualization of this study, methodology, software, validation, data curation, writing, editing. GC Methodology, visualization, validation, review. QZ Formal analysis, funding acquisition, review. JZ Discussion, review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest
Ethical and informed consent statement for date used
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Kang, W., Chen, G. et al. Light-sensitive and adaptive fusion network for RGB-T crowd counting. Vis Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03388-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03388-1