Abstract
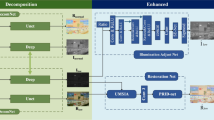
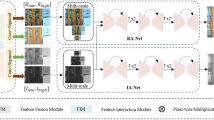
Low-light image enhancement (LLIE) is mainly used to restore image degradation caused by environmental noise, lighting effects, and other factors. Despite many relevant works combating environmental interference, LLIE currently still faces multiple limitations, such as noise, unnatural color recovery, and severe loss of details, etc. To effectively overcome these limitations, we propose a DICNet based on the Retinex theory. DICNet consists of three components: image decomposition, illumination enhancement, and color restoration. To avoid the influence of noise during the enhancement process, we use feature maps after the image high-frequency component denoising process to guide image decomposition and suppress noise interference. For illumination enhancement, we propose a feature separation method that considering the influence of different lighting intensities and preserves details. In addition, to address the insufficient high-low-level feature fusion of the U-Net used in color restoration, we design a Feature Cross-Fusion Module and propose a feature fusion connection plug-in to ensure natural and realistic color restoration. Based on a large number of experiments on publicly available datasets, our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both performance and visual quality.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The LOL, LOL-v2-Real, and LSRW datasets used in this paper are publicly available. The LOL, LOL-v2-Real, and LSRW datasets can be acquired from the following links. All data used in this paper, including images and codes are available by contacting the corresponding author by reasonable request. LOL: https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=ABMrDjBTeHIJGlOFIeP1IQ, LOL-v2-Real: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1U9ePTfeLlnEbr5dtI1tm5g, LSRW: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1XHWQAS0ZNrnCyZ-bq7MKvA.
References
Pisano, E.D., Zong, S., Hemminger, B.M., DeLuca, M., Johnston, R.E., Muller, K., Braeuning, M.P., Pizer, S.M.: Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms. J. Digit. Imaging 11, 193–200 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178082
Farid, H.: Blind inverse gamma correction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(10), 1428–1433 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.951529
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z.-U., Woodell, G.A.: Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(3), 451–462 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.557356
Rahman, Z., Jobson, D.J., Woodell, G.A.: Multi-scale Retinex for color image enhancement. In: Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 3, pp. 1003–1006. IEEE (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.1996.560995
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z.-U., Woodell, G.A.: A multiscale Retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(7), 965–976 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.597272
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., Liu, J.: Deep Retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement (2018). arXiv:1808.04560. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1808.04560
Guo, C., Li, C., Guo, J., Loy, C.C., Hou, J., Kwong, S., Cong, R.: Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1780–1789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.06826
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, X.: Kindling the darkness: a practical low-light image enhancer. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1632–1640 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3343031.3350926
Land, E.H.: The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 237(6), 108–129 (1977). arXiv:jstor:2495.3876
Guo, X., Li, Y., Ling, H.: Lime: low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(2), 982–993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450
Fu, X., Zeng, D., Huang, Y., Zhang, X.-P., Ding, X.: A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2782–2790 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.304
Cai, J., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(4), 2049–2062 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2794218
Lore, K.G., Akintayo, A., Sarkar, S.: Llnet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. 61, 650–662 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.008
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Xu, J., Koltun, V.: Learning to see in the dark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3291–3300 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1805.01934
Jiang, Y., Gong, X., Liu, D., Cheng, Y., Fang, C., Shen, X., Yang, J., Zhou, P., Wang, Z.: Enlightengan: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2340–2349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
Ibrahim, H., Kong, N.S.P.: Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 53(4), 1752–1758 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2007.4429280
Wang, C., Ye, Z.: Brightness preserving histogram equalization with maximum entropy: a variational perspective. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 51(4), 1326–1334 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2005.1561863
Chen, S.-D., Ramli, A.R.: Minimum mean brightness error bi-histogram equalization in contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(4), 1310–1319 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2003.1261234
Reza, A.M.: Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (clahe) for real-time image enhancement. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 38, 35–44 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VLSI.0000028532.53893.82
Beghdadi, A., Le Negrate, A.: Contrast enhancement technique based on local detection of edges. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 46(2), 162–174 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0734-189X(89)90166-7
Peli, E.: Contrast in complex images. JOSA A 7(10), 2032–2040 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.7.002032
Wang, C., Zhang, H., Liu, L.: Total generalized variation-based Retinex image decomposition. Vis. Comput. 37(1), 77–93 (2021)
Shen, L., Yue, Z., Feng, F., Chen, Q., Liu, S., Ma, J.: Msr-net: low-light image enhancement using deep convolutional network (2017). arXiv:1711.02488. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1711.02488
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.901238
Wang, R., Zhang, Q., Fu, C.-W., Shen, X., Zheng, W.-S., Jia, J.: Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6849–6857 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00701
Wu, W., Weng, J., Zhang, P., Wang, X., Yang, W., Jiang, J.: Uretinex-net: Retinex-based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5901–5910 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00581
Yu, X., Li, H., Yang, H.: Two-stage image decomposition and color regulator for low-light image enhancement. Vis. Comput. 39(9), 4165–4175 (2023)
Guo, S., Wang, W., Wang, X., Xu, X.: Low-light image enhancement with joint illumination and noise data distribution transformation. Vis. Comput. 39(4), 1363–1374 (2023)
Zhang, Z., Zheng, H., Hong, R., Xu, M., Yan, S., Wang, M.: Deep color consistent network for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1899–1908 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00194
Kim, H., Choi, S.-M., Kim, C.-S., Koh, Y.J.: Representative color transform for image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4459–4468 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00442
Hai, J., Xuan, Z., Yang, R., Hao, Y., Zou, F., Lin, F., Han, S.: R2rnet: low-light image enhancement via real-low to real-normal network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 90, 103712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103712
Zhou, F., Sun, X., Dong, J., Zhu, X.X.: Surroundnet: towards effective low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2110.05098
Hinton, G.E., Salakhutdinov, R.R.: Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786), 504–507 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127647
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., Manzagol, P.-A., Bottou, L.: Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. (2010). https://doi.org/10.5555/1756006.1953039
Hek, M., Sunj, T.X.O.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2341 (2011)
Li, C., Guo, C., Han, L., Jiang, J., Cheng, M.-M., Gu, J., Loy, C.C.: Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(12), 9396–9416 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3126387
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1512.03385
Maas, A.L., Hannun, A.Y., Ng, A.Y., et al.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings of Icml, vol. 30, p. 3. Atlanta, Georgia, USA (2013)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 14, pp. 694–711. Springer (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_43
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5–9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pp. 234–241. Springer (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Colorful image colorization. In: Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part III 14, pp. 649–666. Springer (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_40
Baldassarre, F., Morín, D.G., Rodés-Guirao, L.: Deep koalarization: image colorization using cnns and inception-resnet-v2 (2017). arXiv:1712.03400. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1712.03400
Dudhane, A., Zamir, S.W., Khan, S., Khan, F.S., Yang, M.-H.: Burst image restoration and enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5759–5768 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00567
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization (2014). arXiv:1412.6980
Liu, R., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10561–10570 (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2012.05609
Jin, Y., Yang, W., Tan, R.T.: Unsupervised night image enhancement: when layer decomposition meets light-effects suppression. In: Computer Vision—ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XXXVII, pp. 404–421. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19836-6_23
Ma, L., Ma, T., Liu, R., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5637–5646 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00555
Wang, H., Xu, K., Lau, R.W.: Local color distributions prior for image enhancement. In: Computer Vision—ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XVIII, pp. 343–359. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19797-0_20
Wen, J., Wu, C., Zhang, T., Yu, Y., Swierczynski, P.: Self-reference deep adaptive curve estimation for low-light image enhancement (2023). arXiv:2308.08197
Wang, C., Wu, H., Jin, Z.: Fourllie: Boosting low-light image enhancement by Fourier frequency information. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 7459–7469 (2023)
Fu, Z., Yang, Y., Tu, X., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Ma, K.-K.: Learning a simple low-light image enhancer from paired low-light instances. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22252–22261 (2023)
Nguyen, H., Tran, D., Nguyen, K., Nguyen, R.: Psenet: progressive self-enhancement network for unsupervised extreme-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 1756–1765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00180
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A.C.: Making a completely blind image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(3), 209–212 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 586–595 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00068
Yang, W., Wang, W., Huang, H., Wang, S., Liu, J.: Sparse gradient regularized deep Retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2072–2086 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3050850
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province under Grant LH2022E024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Heng Pan: Conceptualization, Software, Methodology, Visualization, Validation, Writing-Original Draft, Resources. Bingkun Gao: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing-Review & Editing, Supervision. Xiufang Wang: Funding Acquisition, Writing-Review & Editing, Supervision. Chunlei Jiang: Investigation, Resources, Writing-Original Draft. Peng Chen: Data Curation, Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests regarding the content of this paper.
Ethics approval
This paper does not address the ethics of data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Gao, B., Wang, X. et al. DICNet: achieve low-light image enhancement with image decomposition, illumination enhancement, and color restoration. Vis Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03262-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03262-0