Abstract
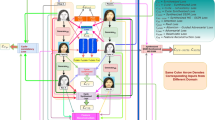
Facial image synthesis using delineated face images is a complex task associated with computer vision. The delineated face image synthesis such as sketch to face generation or thermal to visual face generation using generative adversarial networks (GANs) is a widely accepted task due to its generative capability. The accurate and realistic sample generation by using GAN with an attention network shows a more realistic sample generation. Attention-based network improves the network’s learning by prioritizing the learning over a specific region. Motivated by the success of attention mechanism in recent literature, we develop a new inception-based encoder–decoder self-attentive generative adversarial network (ISA-GAN) by incorporating an inception network with self-attention-based learning. The proposed network is embedded with parallel self-attention, which helps to generate high-quality images and converges faster in terms of training epochs. The proposed scenario has been experimented for face synthesis using delineated face images of sketch images over the CUHK dataset. We also test it over thermal to visual face synthesis using WHU-IIP and CVBL-CHILD datasets. The proposed ISA-GAN outperforms the state-of-the-art generative models for face synthesis. The proposed ISA-GAN shows on an average improvement of \(9.95\%\) in SSIM score over CUHK dataset while \(10.38\%,12.58\% \) for WHU-IIP and CVBL-CHILD datasets, respectively.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen, Y., Luo, P., Yan, J., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Faceid-gan: Learning a symmetry three-player gan for identity-preserving face synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 821–830 (2018)
Zhao, S., Liu, W., Liu, S., Ge, J., Liang, X.: A hybrid-supervision learning algorithm for real-time uncompleted face recognition. Comput. Electr. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108090
Yadav, N.K., Singh, S.K., Dubey, S.R.: TVA-GAN: attention guided generative adversarial network for thermal to visible image transformations. Neural Comput. Appl. 35(27), 19729–19749 (2023)
Wang, L., Sindagi, V., Patel, V.: High-quality facial photo-sketch synthesis using multi-adversarial networks. In: 2018 13th IEEE international conference on automatic face & gesture recognition (FG 2018), pp. 83–90. IEEE (2018)
Mao, X., Shen, C., Yang, Y.B.: Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with symmetric skip connections. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2802–2810 (2016)
Asif, M., Chen, L., Song, H., Yang, J., Frangi, A.F.: An automatic framework for endoscopic image restoration and enhancement. Appl. Intell. 51(4), 1959–1971 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01923-w
Peng, C., Wang, N., Li, J., Gao, X.: Face sketch synthesis in the wild via deep patch representation-based probabilistic graphical model. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 172–183 (2020)
Kera, S.B., Tadepalli, A., Ranjani, J.J.: A paced multi-stage block-wise approach for object detection in thermal images. The Visual Computer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02445-x.
Liang, S., Chu, G., Xie, C., Wang, J.: Joint relation based human pose estimation. Vis. Comput. 38(4), 1369–1381 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02282-4
Leng, L., Zhang, J., Xu, J., Khan, M.K., Alghathbar, K.: Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis in DCT domain for face and palmprint recognition. In: 2010 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), pp. 467–471 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTC.2010.5674791
Leng, L., Teoh, A.B.J., Li, M., Khan, M.K.: Analysis of correlation of 2dpalmhash code and orientation range suitable for transposition. Neurocomputing 131, 377–387 (2014)
Isola, P., Zhu, J.Y., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1125–1134 (2017)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Yi, Z., Zhang, H., Tan, P., Gong, M.: Dualgan: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2849–2857 (2017)
Liao, B., Chen, Y.: An image quality assessment algorithm based on dual-scale edge structure similarity. In: Second International Conference on Innovative Computing, Informatio and Control (ICICIC 2007), pp. 56–56. IEEE (2007)
Cho, K., van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1724–1734 (2014)
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham, A., Acosta, A., Aitken, A., Tejani, A., Totz, J., Wang, Z., et al.: Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4681–4690 (2017)
Mousa, A., Badran, Y., Salama, G., Mahmoud, T.: Regression layer-based convolution neural network for synthetic aperture radar images: de-noising and super-resolution. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02405-5
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Colorful image colorization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 649–666. Springer (2016)
Sun, Q., Chen, Y., Tao, W., Jiang, H., Zhang, M., Chen, K., Erdt, M.: A GAN-based approach toward architectural line drawing colorization prototyping. Vis. Comput. 38(4), 1283–1300 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02219-x
Abdal, R., Qin, Y., Wonka, P.: Image2stylegan: How to embed images into the stylegan latent space? In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4432–4441 (2019)
Souly, N., Spampinato, C., Shah, M.: Semi supervised semantic segmentation using generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5688–5696 (2017)
Fang, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, T., Hung, C.C., Xiao, J., Feng, G.: Facial expression GAN for voice-driven face generation. Vis. Comput. 38(3), 1151–1164 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02074-w
Zhang, S., Ji, R., Hu, J., Lu, X., Li, X.: Face sketch synthesis by multidomain adversarial learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(5), 1419–1428 (2018)
Zhang, X.Y., Huang, Y.P., Mi, Y., Pei, Y.T., Zou, Q., Wang, S.: Video sketch: a middle-level representation for action recognition. Appl. Intell. 51(4), 2589–2608 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01905-y
Goodfellow, I., Pouget Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Mirza, M., Osindero, S.: Conditional generative adversarial nets. Preprint at arXiv:1411.1784 (2014)
Liu, M.Y., Tuzel, O.: Coupled generative adversarial networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 469–477 (2016)
Babu, K.K., Dubey, S.R.: Csgan: Cyclic-synthesized generative adversarial networks for image-to-image transformation. arXiv:1901.03554 (2019)
Babu, K.K., Dubey, S.R.: Pcsgan: perceptual cyclic-synthesized generative adversarial networks for thermal and NIR to visible image transformation. Neurocomputing 413, 41–50 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.104
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I.J., Metaxas, D.N., Odena, A.: Self-attention generative adversarial networks. Preprint at abs/1805.08318 (2018)
Lejbølle, A.R., Nasrollahi, K., Krogh, B., Moeslund, T.B.: Person re-identification using spatial and layer-wise attention. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 1216–1231 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2019.2938870
Mejjati, Y.A., Richardt, C., Tompkin, J., Cosker, D., Kim, K.I.: Unsupervised attention-guided image-to-image translation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3693–3703 (2018)
Tang, H., Xu, D., Sebe, N., Yan, Y.: Attention-guided generative adversarial networks for unsupervised image-to-image translation. In: 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2019)
Chen, H., Hu, G., Lei, Z., Chen, Y., Robertson, N.M., Li, S.Z.: Attention-based two-stream convolutional networks for face spoofing detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 578–593 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2019.2922241
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I., Metaxas, D., Odena, A.: Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 7354–7363 (2019)
Mejjati, Y.A., Richardt, C., Tompkin, J., Cosker, D., Kim, K.I.: Unsupervised attention-guided image-to-image translation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3693–3703 (2018)
Yadav, N.K., Singh, S.K., Dubey, S.R.: CSA-GAN: cyclic synthesized attention guided generative adversarial network for face synthesis. Appl. Intell. (2022)
Tang, H., Xu, D., Sebe, N., Wang, Y., Corso, J.J., Yan, Y.: Multi-channel attention selection GAN with cascaded semantic guidance for cross-view image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2417–2426 (2019)
Zheng, W., Yue, M., Zhao, S., Liu, S.: Attention-based spatial-temporal multi-scale network for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Biomet. Behav. Identity Sci. 3(3), 296–307 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tbiom.2021.3066983
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018)
Üzen, H., Turkoglu, M., Aslan, M., Hanbay, D.: Depth-wise squeeze and excitation block-based efficient-unet model for surface defect detection. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02442-0
Lauriola, I., Lavelli, A., Aiolli, F.: An introduction to deep learning in natural language processing: models, techniques, and tools. Neurocomputing 470, 443–456 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.05.103
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’17, p. 6000-6010. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook (2017)
Liu, H., Liu, F., Fan, X., Huang, D.: Polarized self-attention: Towards high-quality pixel-wise regression. Preprint at arXiv:2107.00782 (2021)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Preprint at arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Kniaz, V.V., Knyaz, V.A., Hladůvka, J., Kropatsch, W.G., Mizginov, V.A.: ThermalGAN: multimodal color-to-thermal image translation for person re-identification in multispectral dataset. In: Computer Vision—ECCV 2018 workshops. Springer (2018)
Kumar, S., Singh, S.K.: A comparative analysis on the performance of different handcrafted descriptors over thermal and low resolution visible image dataset. In: 2018 5th IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (UPCON), pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/UPCON.2018.8596897
Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Wu, F.: Thermal to visible facial image translation using generative adversarial networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25, 1161–1165 (2018)
Dubey, S.R., Chakraborty, S., Roy, S.K., Mukherjee, S., Singh, S.K., Chaudhuri, B.B.: diffgrad: an optimization method for convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 31 (2020)
Hore, A., Ziou, D.: Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In: 2010 20th international conference on pattern recognition, pp. 2366–2369. IEEE (2010)
Sheikh, H., Bovik, A.: Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(2), 430–444 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2005.859378
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 586–595. IEEE (2018)
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., Hochreiter, S.: Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30 (2017)
Simon, L., Webster, R., Rabin, J.: Revisiting precision and recall definition for generative model evaluation. Preprint at arXiv:1905.05441 (2019)
Sajjadi, M.S.M., Bachem, O., Lucic, M., Bousquet, O., Gelly, S.: Assessing generative models via precision and recall. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5234–5243 (2018)
Serengil, S.I., Ozpinar, A.: Hyperextended lightface: A facial attribute analysis framework. In: 2021 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEET53442.2021.9659697
Tang, X., Wang, X.: Face photo recognition using sketch. In: Proceedings. International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 1, pp. I–I. IEEE (2002)
Funding
I gratefully acknowledge the Ministry Of Education and Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India for providing me with the necessary funding and fellowship to pursue research work. I would also like to acknowledge the CCF facility of IIIT Allahabad for providing me with GPU resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests:
We declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, N.K., Singh, S.K. & Dubey, S.R. ISA-GAN: inception-based self-attentive encoder–decoder network for face synthesis using delineated facial images. Vis Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03233-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03233-x