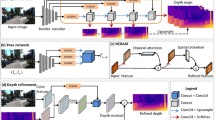
Abstract
Self-supervised monocular depth estimation takes advantage of adjacent frame images as supervision signals for training, which has made a significant improvement in recovering holistic scene geometry. However, owing to these methods do not pay attention to the details of images, and the predicted depth maps are imprecise, where some small objects are neglected, object boundaries are blurred, as well as the predictions lack global consistency. Inspired by the excellent ability of the attention scheme to focus on details, we address these issues by using multi-frames to construct 3D cost volume and taking into account attention awareness for the cost volume so that the network is more inclined to learn important information from the cost volume. In this paper, we propose two mechanisms of attention-aware cost volume: voxel-wise attention-aware (VAA) network and recurrent attention-aware (RAA) network. For the VAA network, 3D convolution is exploited to reweight the 3D cost volume so as to enhance essential areas of the cost volume while suppressing unimportant areas. Therefore, our proposed VAA network can autonomously select the required details. For the RAA network, 3D cost volume is sequentially refined along the depth dimension with 2D convolutions, thereby expanding the receptive field in the depth range and achieving better global consistency. Experiments demonstrate that our methods outperform other self-supervised methods on the KITTI and Cityscapes datasets.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We calculate computational complexity by https://github.com/sovrasov/flops-counter.pytorch.
References
Geiger, A., Lenz, P., Urtasun, R.: Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3354–3361. IEEE (2012)
Newcombe, R.A., Izadi, S., Hilliges, O., Molyneaux, D., Kim, D., Davison, A.J., Kohi, P., Shotton, J., Hodges, S., Fitzgibbon, A.: Kinectfusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, pp. 127–136). IEEE (2011
Luo, X., Huang, J.-B., Szeliski, R., Matzen, K., Kopf, J.: Consistent video depth estimation. ACM Trans. Gr. 39(4), 71–1 (2020)
Lienen, J., Hullermeier, E., Ewerth, R., Nommensen, N.: Monocular depth estimation via listwise ranking using the Plackett-Luce model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14595–14604 (2021)
Godard, C., Mac Aodha, O., Brostow, G.J.: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 270–279 (2017)
Zhou, T., Brown, M., Snavely, N., Lowe, D.G.: Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1851–1858 (2017)
Kuznietsov, Y., Stuckler, J., Leibe, B.: Semi-supervised deep learning for monocular depth map prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6647–6655 (2017)
Godard, C., Mac Aodha, O., Firman, M., Brostow, G.J.: Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3828–3838 (2019)
Casser, V., Pirk, S., Mahjourian, R., Angelova, A.: Depth prediction without the sensors: Leveraging structure for unsupervised learning from monocular videos. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 8001–8008 (2019)
Bozorgtabar, B., Rad, M.S., Mahapatra, D., Thiran, J.-P.: Syndemo: synergistic deep feature alignment for joint learning of depth and ego-motion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4210–4219 (2019)
Garg, R., Bg, V.K., Carneiro, G., Reid, I.: Unsupervised cnn for single view depth estimation: geometry to the rescue. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 740–756 (2016). Springer
Tonioni, A., Poggi, M., Mattoccia, S., Di Stefano, L.: Unsupervised domain adaptation for depth prediction from images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(10), 2396–2409 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Xu, C., Yang, J., Tai, Y., Chen, L.: Deep hierarchical guidance and regularization learning for end-to-end depth estimation. Pattern Recogn. 83, 430–442 (2018)
Lyu, X., Liu, L., Wang, M., Kong, X., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Chen, X., Yuan, Y.: Hr-depth: high resolution self-supervised monocular depth estimation. CoRR abs/2012.07356 (2020)
Watson, J., Mac Aodha, O., Prisacariu, V., Brostow, G., Firman, M.: The temporal opportunist: Self-supervised multi-frame monocular depth. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1164–1174 (2021)
Bello, I., Zoph, B., Vaswani, A., Shlens, J., Le, Q.V.: Attention augmented convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3286–3295 (2019)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A., et al.: Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 28, 2017–2025 (2015)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Yao, Y., Luo, Z., Li, S., Fang, T., Quan, L.: Mvsnet: Depth inference for unstructured multi-view stereo. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 767–783 (2018)
Yu, Z., Gao, S.: Fast-mvsnet: Sparse-to-dense multi-view stereo with learned propagation and gauss-newton refinement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1949–1958 (2020)
Yi, H., Wei, Z., Ding, M., Zhang, R., Chen, Y., Wang, G., Tai, Y.-W.: Pyramid multi-view stereo net with self-adaptive view aggregation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 766–782 (2020). Springer
Yao, Y., Luo, Z., Li, S., Shen, T., Fang, T., Quan, L.: Recurrent mvsnet for high-resolution multi-view stereo depth inference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5525–5534 (2019)
Eigen, D., Puhrsch, C., Fergus, R.: Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.2283 (2014)
Laina, I., Rupprecht, C., Belagiannis, V., Tombari, F., Navab, N.: Deeper depth prediction with fully convolutional residual networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 239–248 (2016). IEEE
Lee, J.H., Han, M.-K., Ko, D.W., Suh, I.H.: From big to small: Multi-scale local planar guidance for monocular depth estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.10326 (2019)
Bhat, S.F., Alhashim, I., Wonka, P.: Adabins: Depth estimation using adaptive bins. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4009–4018 (2021)
Liu, P., Zhang, Z., Meng, Z., Gao, N.: Monocular depth estimation with joint attention feature distillation and wavelet-based loss function. Sensors 21(1), 54 (2020)
Lai, Z., Tian, R., Wu, Z., Ding, N., Sun, L., Wang, Y.: Dcpnet: a densely connected pyramid network for monocular depth estimation. Sensors 21(20), 6780 (2021)
Eigen, D., Fergus, R.: Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2650–2658 (2015)
Mayer, N., Ilg, E., Hausser, P., Fischer, P., Cremers, D., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T.: A large dataset to train convolutional networks for disparity, optical flow, and scene flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4040–4048 (2016)
Liu, F., Shen, C., Lin, G., Reid, I.: Learning depth from single monocular images using deep convolutional neural fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2024–2039 (2015)
Zhao, T., Pan, S., Gao, W., Sheng, C., Sun, Y., Wei, J.: Attention unet++ for lightweight depth estimation from sparse depth samples and a single rgb image. Vis. Comput. 38(5), 1619–1630 (2022)
Shi, J., Sun, Y., Bai, S., Sun, Z., Tian, Z.: A self-supervised method of single-image depth estimation by feeding forward information using max-pooling layers. Vis. Comput. 37(4), 815–829 (2021)
Yang, N., Stumberg, L.v., Wang, R., Cremers, D.: D3vo: Deep depth, deep pose and deep uncertainty for monocular visual odometry. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1281–1292 (2020)
Yin, W., Liu, Y., Shen, C., Yan, Y.: Enforcing geometric constraints of virtual normal for depth prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5684–5693 (2019)
Yin, Z., Shi, J.: Geonet: Unsupervised learning of dense depth, optical flow and camera pose. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1983–1992 (2018)
Chen, P.-Y., Liu, A.H., Liu, Y.-C., Wang, Y.-C.F.: Towards scene understanding: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with semantic-aware representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2624–2632 (2019)
He, L., Lu, J., Wang, G., Song, S., Zhou, J.: Sosd-net: joint semantic object segmentation and depth estimation from monocular images. Neurocomputing 440, 251–263 (2021)
Fan, C., Yin, Z., Xu, F., Chai, A., Zhang, F.: Joint soft-hard attention for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. Sensors 21(21), 6956 (2021)
Zhao, B., Huang, Y., Ci, W., Hu, X.: Unsupervised learning of monocular depth and ego-motion with optical flow features and multiple constraints. Sensors 22(4), 1383 (2022)
Li, Y., Luo, F., Li, W., Zheng, S., Wu, H.-H., Xiao, C.: Self-supervised monocular depth estimation based on image texture detail enhancement. Vis. Comput. 37(9), 2567–2580 (2021)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Ranjan, A., Jampani, V., Balles, L., Kim, K., Sun, D., Wulff, J., Black, M.J.: Competitive collaboration: Joint unsupervised learning of depth, camera motion, optical flow and motion segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12240–12249 (2019)
Luo, C., Yang, Z., Wang, P., Wang, Y., Xu, W., Nevatia, R., Yuille, A.: Every pixel counts++: joint learning of geometry and motion with 3d holistic understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(10), 2624–2641 (2019)
Johnston, A., Carneiro, G.: Self-supervised monocular trained depth estimation using self-attention and discrete disparity volume. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4756–4765 (2020)
Chen, Y., Schmid, C., Sminchisescu, C.: Self-supervised learning with geometric constraints in monocular video: Connecting flow, depth, and camera. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7063–7072 (2019)
Guizilini, V., Ambrus, R., Pillai, S., Raventos, A., Gaidon, A.: 3d packing for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2485–2494 (2020)
Li, H., Gordon, A., Zhao, H., Casser, V., Angelova, A.: Unsupervised monocular depth learning in dynamic scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.16404 (2020)
Patil, V., Van Gansbeke, W., Dai, D., Van Gool, L.: Don’t forget the past: recurrent depth estimation from monocular video. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(4), 6813–6820 (2020)
Wang, J., Zhang, G., Wu, Z., Li, X., Liu, L.: Self-supervised joint learning framework of depth estimation via implicit cues. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.09876 (2020)
Zhou, H., Greenwood, D., Taylor, S.: Self-supervised monocular depth estimation with internal feature fusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.09482 (2021)
Gordon, A., Li, H., Jonschkowski, R., Angelova, A.: Depth from videos in the wild: Unsupervised monocular depth learning from unknown cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8977–8986 (2019)
Wang, R., Zou, J., Wen, J.Z.: Sfa-mden: Semantic-feature-aided monocular depth estimation network using dual branches. Sensors 21(16), 5476 (2021)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Pilzer, A., Xu, D., Puscas, M., Ricci, E., Sebe, N.: Unsupervised adversarial depth estimation using cycled generative networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 587–595. IEEE (2018)
Acknowledgements
The work presented in this paper is partially supported by Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61772225), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Nos. 2020A1515010558 and 2021A1515011972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Z., Wu, Q. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation via two mechanisms of attention-aware cost volume. Vis Comput 39, 5937–5951 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02704-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02704-x