Abstract
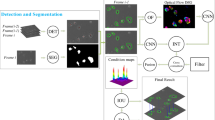
This paper presents a method for detecting and tracking large number of arbitrary-oriented and densely aggregated microbes from image sequences captured under microscope. We first propose an integral channel feature (ICF)-based detector which is able to localize the dense and arbitrarily oriented targets with low false positive rate. Then instead of treating target detection and tracking as two separated problems as many previous works did, we propose to refine the detection results in the data association process. The kinematic pattern of microbes is well modeled with the proposed integral sliding energy (ISE), which is combined with detection response in a hybrid cost function. Minimizing the cost function allows us to simultaneously select the true targets from the detections and to match the targets across two consecutive frames. Systematical experiments have been conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.F., Vedaldi, A., Torr, P.H.: Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 850–865. Springer (2016)
Betke, M., Wu, Z.: Data association for multi-object visual tracking. Synth. Lectures Computer Vis. 6(2), 1–120 (2016)
Bise, R., Sato, Y.: Cell detection from redundant candidate regions under nonoverlapping constraints. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(7), 1417–1427 (2015)
Butt, A.A., Collins, R.T.: Multi-target tracking by lagrangian relaxation to min-cost network flow. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2013)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2005)
Dollár, P., Tu, Z., Perona, P., Belongie, S.: Integral channel features. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2009)
Dong, X., Shen, J.: Triplet loss in siamese network for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 459–474 (2018)
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A., Vineet, V., Cheng, M.M., Hicks, S.L., Torr, P.H.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 38(10), 2096–2109 (2015)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 583–596 (2014)
Hu, H., Ma, B., Shen, J., Sun, H., Shao, L., Porikli, F.: Robust object tracking using manifold regularized convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 21(2), 510–521 (2018)
Kanade, T., Yin, Z., Bise, R., Huh, S., Eom, S., Sandbothe, M.F., Chen, M.: Cell image analysis: algorithms, system and applications. In: 2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 374–381. IEEE (2011)
Khan, Z., Balch, T., Dellaert, F.: An mcmc-based particle filter for tracking multiple interacting targets. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 279–290. Springer (2004)
Kuanar, S., Athitsos, V., Mahapatra, D., Rao, K., Akhtar, Z., Dasgupta, D.: Low dose abdominal ct image reconstruction: an unsupervised learning based approach. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1351–1355. IEEE (2019)
Kuanar, S., Athitsos, V., Pradhan, N., Mishra, A., Rao, K.R.: Cognitive analysis of working memory load from eeg, by a deep recurrent neural network. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2576–2580. IEEE (2018)
Kuanar, S., Rao, K., Bilas, M., Bredow, J.: Adaptive cu mode selection in hevc intra prediction: a deep learning approach. Circuits, Syst., Signal Process. 38(11), 5081–5102 (2019)
Liang, Z., Shen, J.: Local semantic siamese networks for fast tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 3351–3364 (2019)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C.Y., Berg, A.C.: Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21–37. Springer (2016)
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Chen, Y.Q.: Automatic 3d tracking system for large swarm of moving objects. Pattern Recognit. 52, 384–396 (2016)
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Gao, H., Wang, B.: Detecting dense crowds of microbes from microscope images in a global optimization framework. Optik 127(1), 76–80 (2016)
Luo, W., Xing, J., Milan, A., Zhang, X., Liu, W., Zhao, X., Kim, T.K.: Multiple object tracking: A literature review. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.7618 (2014)
Ma, B., Hu, H., Shen, J., Liu, Y., Shao, L.: Generalized pooling for robust object tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(9), 4199–4208 (2016)
Mei, X., Ling, H.: Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(11), 2259–2272 (2011)
Ming, Q., Zhou, Z., Miao, L., Zhang, H., Li, L.: Dynamic anchor learning for arbitrary-oriented object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.04150 (2020)
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 779–788 (2016)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767 (2018)
Rehman, B., Ong, W.H., Tan, A.C.H., Ngo, T.D.: Face detection and tracking using hybrid margin-based roi techniques. Vis Computer 36(3), 633–647 (2020)
Reilly, V., Idrees, H., Shah, M.: Detection and tracking of large number of targets in wide area surveillance. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 186–199. Springer (2010)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2016)
Ross, D.A., Lim, J., Lin, R.S., Yang, M.H.: Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Computer Vis. 77(1–3), 125–141 (2008)
Viola, P., Jones, M.J.: Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Computer Vis. 57(2), 137–154 (2004)
Wang, S.H., Cheng, X.E., Qian, Z.M., Liu, Y., Chen, Y.Q.: Automated planar tracking the waving bodies of multiple zebrafish swimming in shallow water. PloS One 11(4), e0154714 (2016)
Wojke, N., Bewley, A., Paulus, D.: Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3645–3649. IEEE (2017)
Wu, Z., Hristov, N.I., Hedrick, T.L., Kunz, T.H., Betke, M.: Tracking a large number of objects from multiple views. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1546–1553. IEEE (2009)
Yang, X., Yan, J.: Arbitrary-oriented object detection with circular smooth label. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 677–694. Springer (2020)
Zhao, J., Wang, S.H., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Chen, Y.Q.: Early diagnosis of cirrhosis via automatic location and geometric description of liver capsule. Vis. Computer 34(12), 1677–1689 (2017)
Zou, D., Zhao, Q., Wu, H.S., Chen, Y.Q.: Reconstructing 3d motion trajectories of particle swarms by global correspondence selection. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1578–1585. IEEE (2009)
Acknowledgements
The research work of this paper is sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61602255 and 61931012. The authors would like to thank Prof. T. Vicsek and his group for providing the research data of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Nie, J. et al. Localizing and tracking dense crowd of microbes by joint association and detection refinement. Vis Comput 38, 2373–2382 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02118-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02118-1