Abstract
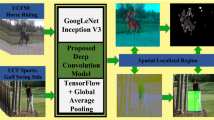
Human action localization in any long, untrimmed video can be determined from where and what action takes place in a given video segment. The main hurdles in human action localization are the spatiotemporal randomnesses of their happening in a parallel mode which means the location (a particular set of frames containing action instances) and duration of any particular action in real-life video sequences generally are not fixed. At another end, the uncontrolled conditions such as occlusions, viewpoints and motions at the crisp boundary of the action sequences demand to develop a fast deep network which can be easily trained from unlabeled samples of complex video sequences. Motivated from the facts, we proposed a weakly supervised deep network model for human action localization. The model is trained from unlabeled action samples from UCF50 action benchmark. The five-channel data obtained from the concatenation of RGB (three-channel) and optical flow vectors (two-channel) are fed to the proposed convolutional neural network. LSTM network is used to yield the region of action happening area. The performance of the model is tested on UCF-sports dataset. The observation and comparative results reflect that our model can localize any action from annotation-free data samples captured in uncontrolled conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parameswaran, V., Chellappa, R.: View invariance for human action recognition. IJCV 66(1), 83–101 (2006)
Liu, J., Ali, S., Shah, M.: Recognizing human actions using multiple features. In: CVPR (2008)
Mosabbeb, E.A., Cabral, R., De la Torre, F., Fathy, M.: Multi-label discriminative weakly-supervised human activity recognition and localization. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 241–258. Springer, Cham (2014)
Singh, B., Shao, M.: A multi-stream bi-directional recurrent neural network for fine-grained action detection. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Tu, Z., Xie, W., Qin, Q., Poppe, R., Veltkamp, R.C., Li, B., Yuan, J.: Multi-stream CNN: learning representations based on human-related regions for action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 79, 32–43 (2018)
Vishwakarma, S., Agrawal, A.: A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 29(10), 983–1009 (2013)
Singh, V.K., Nevatia, R.: Simultaneous tracking and action recognition for single actor human actions. Vis. Comput. 27(12), 1115–1123 (2011)
Laptev, I., Perez, P.: Retrieving actions in movies. In: 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision ICCV, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2007)
Lan, T., Wang, Y., Mori, G.: Discriminative figure-centric models for joint action localization and recognition. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2003–2010. IEEE (2011)
Sultani, W., Shah, M.: Automatic action annotation in weakly labeled videos. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 161, 77–86 (2017)
Agahian, S., Negin, F., Köse, C.: Improving bag-of-poses with semi-temporal pose descriptors for skeleton-based action recognition. Vis. Comput., 1–17 (2018)
Dawn, D.D., Shaikh, S.H.: A comprehensive survey of human action recognition with spatiotemporal interest point (STIP) detector. Vis. Comput. 32(3), 289–306 (2016)
Yi, Y., Wang, H.: Motion keypoint trajectory and covariance descriptor for human action recognition. Vis. Comput. 34(3), 391–403 (2018)
Qin, Y., Mo, L., Li, C., Luo, J.: Skeleton-based action recognition by part-aware graph convolutional networks. Vis. Comput., 1–11 (2019)
Chao, Y.W., Vijayanarasimhan, S., Seybold, B., Ross, D.A., Deng, J., Sukthankar, R.: Rethinking the faster R-CNN architecture for temporal action localization. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 38, 1130–1139 (2018)
Dong, X., Shen, J.: Triplet loss in siamese network for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 459–474 (2018)
Wang, W., Shen, J.: Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(5), 2368–2378 (2017)
Dong, X., Shen, J., Wang, W., Liu, Y., Shao, L., Porikli, F.: Hyperparameter optimization for tracking with continuous deep q-learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 518–527 (2018)
Dong, Xingping, Shen, Jianbing, Dongming, Wu, Guo, Kan, Jin, Xiaogang, Porikli, Fatih: Quadruplet network with one-shot learning for fast visual object tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(7), 3516–3527 (2019)
Mettes, P., van Gemert, J.C., Snoek, C.G.: Spot on: action localization from pointly-supervised proposals. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 437–453. Springer, Cham (2016)
Singh, K.K., Lee, Y.J.: Hide-and-seek: forcing a network to be meticulous for weakly-supervised object and action localization. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2017)
Savarese, S., DelPozo, A., Niebles, J.C., Fei-Fei, L.: Spatial-temporal correlatons for unsupervised action classification. In: 2008 IEEE Workshop on Motion and Video Computing WMVC, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Soomro, K., Shah, M.: Unsupervised action discovery and localization in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 696–705 (2017)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Ling, H.: A deep network solution for attention and aesthetics aware photo cropping. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(7), 1531–1544 (2018)
Oikonomopoulos, A., Patras, I., Pantic, M.: Spatiotemporal localization and categorization of human actions in unsegmented image sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(4), 1126–1140 (2011)
Shou, Z., Wang, D., Chang, S.F.: Temporal action localization in untrimmed videos via multi-stage CNNs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1049–1058 (2016)
Wu, J., Hu, D., Chen, F.: Action recognition by hidden temporal models. Vis. Comput. 30(12), 1395–1404 (2014)
Kalogeiton, V., Weinzaepfel, P., Ferrari, V., Schmid, C.: Action tubelet detector for spatio-temporal action localization. In: ICCV, Oct, 2 (2017)
Dai, X., Singh, B., Zhang, G., Davis, L.S., Chen, Y.Q.: Temporal context network for activity localization in videos. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5727–5736. IEEE (2017)
Duan, X., Wang, L., Zhai, C., Zhang, Q., Niu, Z., Zheng, N., Hua, G.: Joint spatiotemporal action localization in untrimmed videos with per frame segmentation. In: ICIP, Athens, Greece (2018)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 39(6), 91–99 (2015)
Hui, T.W., Tang, X., Change Loy, C.: Liteflownet: a lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE CVPR, pp. 8981–8989 (2018)
Ranjan, A., Black, M.J.: Optical flow estimation using a spatial pyramid network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4161–4170 (2017)
Kangwei, L., Jianhua, W., Zhongzhi, H.: Abnormal event detection and localization using level set based on hybrid features. Signal Image Video Process. 12(2), 255–261 (2018)
Jiang, Z., Lin, Z., Davis, L.S.: A tree-based approach to integrated action localization, recognition and segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 114–127. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2010)
Ma, S., Zhang, J., Ikizler-Cinbis, N., Sclaroff, S.: Action recognition and localization by hierarchical space-time segments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2744–2751 (2013)
Megrhi, S., Jmal, M., Souidene, W., Beghdadi, A.: Spatio-temporal action localization and detection for human action recognition in big dataset. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 41, 375–390 (2016)
Shen, J., Peng, J., Shao, L.: Submodular trajectories for better motion segmentation in videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(6), 2688–2700 (2018)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Video salient object detection via fully convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(1), 38–49 (2017)
Sivic, J., Russell, B., Zisserman, A., Freeman, W.: Discovering objects and their location in images. In: ICCV (2005)
Klaser, A., Marszaiek, M., Schmid, C., Zisserman, A.: Human focused action localization in video. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 219–233. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2010)
Tian, Y., Sukthankar, R., Shah, M.: Spatiotemporal deformable part models for action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2642–2649 (2013)
Gaidon, A., Harchaoui, Z., Schmid, C.: Temporal localization of actions with actoms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(11), 2782–2795 (2013)
Jain, M., Van Gemert, J., Jégou, H., Bouthemy, P., Snoek, C.G.: Action localization with tubelets from motion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 740–747 (2014)
Oneata, D., Verbeek, J., Schmid, C.: Efficient action localization with approximately normalized fisher vectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2545–2552 (2014)
Shao, L., Jones, S., Li, X.: Efficient search and localization of human actions in video databases. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 24(3), 504–512 (2014)
Van Gemert, J.C., Jain, M., Gati, E., Snoek, C.G.: APT: action localization proposals from dense trajectories. In: BMVC, vol. 2, p. 4 (2015)
Weinzaepfel, P., Harchaoui, Z., Schmid, C.: Learning to track for spatio-temporal action localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 28, pp. 3164–3172 (2015)
Sultani, W., Shah, M.: What if we do not have multiple videos of the same action?—Video action localization using web images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1077–1085 (2016)
Stoian, A., Ferecatu, M., Benois-Pineau, J., Crucianu, M.: Fast action localization in large-scale video archives. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 26(10), 1917–1930 (2016)
Soomro, K., Idrees, H., Shah, M.: Predicting the where and what of actors and actions through online action localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2648–2657 (2016)
Shou, Z., Chan, J., Zareian, A., Miyazawa, K., Chang, S.F.: CDC: convolutional-de-convolutional networks for precise temporal action localization in untrimmed videos. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1417–1426. IEEE (2017)
Singh, G., Saha, S., Sapienza, M., Torr, P.H., Cuzzolin, F.: Online real-time multiple spatiotemporal action localisation and prediction. In: ICCV, pp. 3657–3666 (2017)
Yuan, Z.H., Stroud, J.C., Lu, T., Deng, J.: Temporal action localization by structured maximal sums. In: CVPR, vol. 2, p. 7 (2017)
Hou, R., Sukthankar, R., Shah, M.: Real-time temporal action localization in untrimmed videos by sub-action discovery. In: BMVC, vol. 2, p. 7 (2017)
Soomro, K., Idrees, H., Shah, M.: Online localization and prediction of actions and interactions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41, 459–472 (2018)
Jiang, X., Zhong, F., Peng, Q., Qin, X.: Online robust action recognition based on a hierarchical model. Vis. Comput. 30(9), 1021–1033 (2014)
Yang, H., He, X., Porikli, F.: One-shot action localization by learning sequence matching network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1450–1459 (2018)
Ilg, E., Mayer, N., Saikia, T., Keuper, M., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T.: Flownet 2.0: evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), vol. 2, p. 6 (2017)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Greff, K., Srivastava, R.K., Koutnik, J., Steunebrink, B.R., Schmidhuber, J.: LSTM: a search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(10), 2222–2232 (2017)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167
Li, X., Chen, S., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Understanding the disharmony between dropout and batch normalization by variance shift (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.05134
Reddy, K.K., Shah, M.: Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. Mach. Vis. Appl. 24(5), 971–981 (2013)
Soomro, K., Zamir, A.R.: Action recognition in realistic sports videos. In: Moeslund, T.B., Thomas, G., Hilton, A. (eds.) Computer Vision in Sports, pp. 181–208. Springer, Cham (2014)
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to have joint financial support from our academic institute (IIT Roorkee) and MHRD, a body under the ages of Indian government for research associations. I would like to acknowledge with special thanks to Prof. R.S. Anand (Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Roorkee) for providing me background motivation to complete this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Sukavanam, N. Weakly supervised deep network for spatiotemporal localization and detection of human actions in wild conditions. Vis Comput 36, 1809–1821 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01777-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01777-5