Abstract
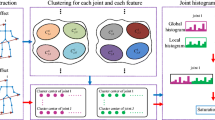
Over the last few decades, human action recognition has become one of the most challenging tasks in the field of computer vision. Effortless and accurate extraction of 3D skeleton information has been recently achieved by means of economical depth sensors and state-of-the-art deep learning approaches. In this study, we introduce a novel bag-of-poses framework for action recognition using 3D skeleton data. Our assumption is that any action can be represented by a set of predefined spatiotemporal poses. The pose descriptor is composed of three parts. The first part is concatenation of the normalized coordinate of the skeleton joints. The second part is consisted of temporal displacement of the joints constructed with predefined temporal offset, and the third part is temporal displacement with the previous frame in the sequence. In order to generate the key poses, we apply K-means clustering over all the training pose descriptors of the dataset. SVM classifier is trained with the generated key poses to classify an action pose. Accordingly, every action in the dataset is encoded with key pose histograms. ELM classifier is used for action recognition due to its fast, accurate and reliable performance compared to the other classifiers. The proposed framework is validated with five publicly available benchmark 3D action datasets and achieved state-of-the-art results on three of the datasets and competitive results on the other two datasets compared to the other methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, J., Xia, L.: Human activity recognition from 3d data: a review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 48, 70–80 (2014)
Aggarwal, J.K., Ryoo, M.S.: Human activity analysis: a review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 43(3), 16 (2011)
Amor, B.B., Su, J., Srivastava, A.: Action recognition using rate-invariant analysis of skeletal shape trajectories. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(1), 1–13 (2016)
Cao, Z., Simon, T., Wei, S.E., Sheikh, Y.: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.08050 (2016)
Chaaraoui, A.A., Padilla-Lpez, J.R., Climent-Prez, P., Flrez-Revuelta, F.: Evolutionary joint selection to improve human action recognition with rgb-d devices. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(3), 786–794 (2014)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: Libsvm: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2(3), 27 (2011)
Chen, C., Jafari, R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Utd-mhad: A multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 168–172. IEEE (2015)
Chen, C., Jafari, R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: A real-time human action recognition system using depth and inertial sensor fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 16(3), 773–781 (2016)
Chen, X., Koskela, M.: Skeleton-based action recognition with extreme learning machines. Neurocomputing 149, 387–396 (2015)
Chron, G., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: P-cnn: Pose-based cnn features for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3218–3226
Dawn, D.D., Shaikh, S.H.: A comprehensive survey of human action recognition with spatio-temporal interest point (stip) detector. Vis. Comput. 32(3), 289–306 (2016)
Du, Y., Fu, Y., Wang, L.: Skeleton based action recognition with convolutional neural network. In: 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), pp. 579–583. IEEE (2015)
Du, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L.: Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1110–1118
Eweiwi, A., Cheema, M.S., Bauckhage, C., Gall, J.: Efficient pose-based action recognition. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 428–443. Springer
Fothergill, S., Mentis, H., Kohli, P., Nowozin, S.: Instructing people for training gestural interactive systems. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1737–1746. ACM
Gaglio, S., Re, G.L., Morana, M.: Human activity recognition process using 3-d posture data. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 45(5), 586–597 (2015)
Guo, Y., Li, Y., Shao, Z.: Rrv: A spatiotemporal descriptor for rigid body motion recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 99, 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2705227
Han, F., Reily, B., Hoff, W., Zhang, H.: Space-time representation of people based on 3d skeletal data: a review. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 158, 85–105 (2017)
Han, J., Shao, L., Xu, D., Shotton, J.: Enhanced computer vision with microsoft kinect sensor: a review. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 43(5), 1318–1334 (2013)
Hou, Y., Li, Z., Wang, P., Li, W.: Skeleton optical spectra based action recognition using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 99, 1–1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2628339
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1), 489–501 (2006)
Hussein, M.E., Torki, M., Gowayyed, M.A., El-Saban, M.: Human action recognition using a temporal hierarchy of covariance descriptors on 3d joint locations. In: Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Ibaez, R., Soria, I., Teyseyre, A., Rodrguez, G., Campo, M.: Approximate string matching: a lightweight approach to recognize gestures with kinect. Pattern Recognit. 62, 73–86 (2017)
Jiang, X., Zhong, F., Peng, Q., Qin, X.: Online robust action recognition based on a hierarchical model. Vis. Comput. 30(9), 1021–1033 (2014)
Johansson, G.: Visual Motion Perception. Scientific American, New York (1975)
Kapsouras, I., Nikolaidis, N.: Action recognition on motion capture data using a dynemes and forward differences representation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 25(6), 1432–1445 (2014)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Lee, I., Kim, D., Kang, S., Lee, S.: Ensemble deep learning for skeleton-based action recognition using temporal sliding lstm networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1012–1020
Li, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, Z.: Action recognition based on a bag of 3d points. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 9–14. IEEE (2010)
Lillo, I., Niebles, J.C., Soto, A.: Sparse composition of body poses and atomic actions for human activity recognition in rgb-d videos. Image Vis. Comput. 59, 63–75 (2017)
Liu, J., Shahroudy, A., Xu, D., Chichung, A.K., Wang, G.: Skeleton-based action recognition using spatio-temporal lstm network with trust gates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 99, 1–1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2771306
Liu, M., Chen, C., Liu, H.: Learning informative pairwise joints with energy-based temporal pyramid for 3d action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 901–906. IEEE (2017)
Liu, M., Liu, H., Chen, C.: Enhanced skeleton visualization for view invariant human action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 68, 346–362 (2017)
Lu, G., Zhou, Y., Li, X., Kudo, M.: Efficient action recognition via local position offset of 3d skeletal body joints. Multimed. Tools Appl. 75(6), 3479–3494 (2016)
Luvizon, D.C., Tabia, H., Picard, D.: Learning features combination for human action recognition from skeleton sequences. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 99, 13–20 (2017)
Minhas, R., Baradarani, A., Seifzadeh, S., Wu, Q.J.: Human action recognition using extreme learning machine based on visual vocabularies. Neurocomputing 73(10), 1906–1917 (2010)
Negin, F., Akgl, C.B., Yksel, K.A., Eril, A.: An rdf-based action recognition framework with feature selection capability, considering therapy exercises utilizing depth cameras. J. Theor. Appl. Comput. Sci. 8(3), 3–22 (2014)
Negin, F., zdemir, F., Akgl, C.B., Yksel, K.A., Eril, A.: A decision forest based feature selection framework for action recognition from rgb-depth cameras. In: International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, pp. 648–657. Springer
Nunes, U.M., Faria, D.R., Peixoto, P.: A human activity recognition framework using max–min features and key poses with differential evolution random forests classifier. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 99, 21–31 (2017)
Parisi, G.I., Weber, C., Wermter, S.: Self-organizing neural integration of pose–motion features for human action recognition. Front. Neurorobot. 9, 3 (2015)
Peng, X., Wang, L., Wang, X., Qiao, Y.: Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: comprehensive study and good practice. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 150, 109–125 (2016)
Poppe, R.: A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 28(6), 976–990 (2010)
Presti, L.L., La Cascia, M.: 3d skeleton-based human action classification: a survey. Pattern Recognit. 53, 130–147 (2016)
Qiao, R., Liu, L., Shen, C., van den Hengel, A.: Learning discriminative trajectorylet detector sets for accurate skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 66, 202–212 (2017)
Ramanathan, M., Yau, W.Y., Teoh, E.K.: Human action recognition with video data: research and evaluation challenges. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 44(5), 650–663 (2014)
Sadanand, S., Corso, J.J.: Action bank: a high-level representation of activity in video. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1234–1241. IEEE (2012)
Shan, J., Akella, S.: 3d human action segmentation and recognition using pose kinetic energy. In: IEEE Workshop on Advanced Robotics and its Social Impacts (ARSO), pp. 69–75. IEEE (2014)
Shotton, J., Sharp, T., Kipman, A., Fitzgibbon, A., Finocchio, M., Blake, A., Cook, M., Moore, R.: Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. Commun. ACM 56(1), 116–124 (2013)
Sung, J., Ponce, C., Selman, B., Saxena, A.: Unstructured human activity detection from rgbd images. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 842–849. IEEE (2012)
Tao, L., Vidal, R.: Moving poselets: a discriminative and interpretable skeletal motion representation for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 61–69
Tran, D., Torresani, L.: Exmoves: mid-level features for efficient action recognition and video analysis. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 119(3), 239–253 (2016)
Varol, G., Salah, A.A.: Efficient large-scale action recognition in videos using extreme learning machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(21), 8274–8282 (2015)
Veeriah, V., Zhuang, N., Qi, G.J.: Differential recurrent neural networks for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4041–4049
Vemulapalli, R., Arrate, F., Chellappa, R.: Human action recognition by representing 3d skeletons as points in a lie group. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 588–595
Vemulapalli, R., Arrate, F., Chellappa, R.: R3dg features: relative 3d geometry-based skeletal representations for human action recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 152, 155–166 (2016)
Vishwakarma, S., Agrawal, A.: A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 29(10), 983–1009 (2013)
Wang, C., Wang, Y., Yuille, A.L.: An approach to pose-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 915–922
Wang, C., Wang, Y., Yuille, A.L.: Mining 3d key-pose-motifs for action recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2639–2647. IEEE (2016)
Wang, J., Liu, Z., Wu, Y.: Learning Actionlet Ensemble for 3D Human Action Recognition, pp. 11–40. Springer, New York (2014)
Wang, J., Liu, Z., Wu, Y., Yuan, J.: Mining actionlet ensemble for action recognition with depth cameras. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1290–1297. IEEE (2012)
Wang, P., Li, Z., Hou, Y., Li, W.: Action recognition based on joint trajectory maps using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Multimedia Conference, pp. 102–106. ACM
Xia, L., Chen, C.C., Aggarwal, J.: View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3d joints. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 20–27. IEEE (2012 )
Yang, Y., Deng, C., Tao, D., Zhang, S., Liu, W., Gao, X.: Latent max-margin multitask learning with skelets for 3-d action recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(2), 439–448 (2017)
Yao, A., Gall, J., Fanelli, G., Van Gool, L.: Does human action recognition benefit from pose estimation? In: Proceedings of the 22nd British Machine Vision Conference-BMVC (2011)
Youssef, C.: Spatiotemporal representation of 3d skeleton joints-based action recognition using modified spherical harmonics. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 83, 32–41 (2016)
Zanfir, M., Leordeanu, M., Sminchisescu, C.: The moving pose: an efficient 3d kinematics descriptor for low-latency action recognition and detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2752–2759
Zelnik-Manor, L., Irani, M.: Event-based analysis of video. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2001, vol. 2, pp. II–II. IEEE (2001)
Zhang, J., Li, W., Ogunbona, P.O., Wang, P., Tang, C.: Rgb-d-based action recognition datasets: a survey. Pattern Recognit. 60, 86–105 (2016)
Zhang, S., Liu, X., Xiao, J.: On geometric features for skeleton-based action recognition using multilayer lstm networks. In: IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 148–157. IEEE (2017)
Zhou, L., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Ogunbona, P., Nguyen, D.T., Zhang, H.: Discriminative key pose extraction using extended lc-ksvd for action recognition. In: International Conference on Digital lmage Computing: Techniques and Applications (DlCTA), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2014 )
Zhu, F., Shao, L., Xie, J., Fang, Y.: From handcrafted to learned representations for human action recognition: a survey. Image Vis. Comput. 55, 42–52 (2016)
Zhu, G., Zhang, L., Shen, P., Song, J.: Human action recognition using multi-layer codebooks of key poses and atomic motions. Signal Process. Image Commun. 42, 19–30 (2016)
Zhu, W., Lan, C., Xing, J., Zeng, W., Li, Y., Shen, L., Xie, X.: Co-occurrence feature learning for skeleton based action recognition using regularized deep lstm networks. AAAI 2, 8 (2016)
Zhu, Y., Chen, W., Guo, G.: Fusing multiple features for depth-based action recognition. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 6(2), 18 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agahian, S., Negin, F. & Köse, C. Improving bag-of-poses with semi-temporal pose descriptors for skeleton-based action recognition. Vis Comput 35, 591–607 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1489-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1489-7