Abstract
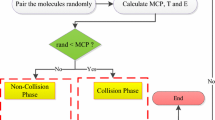
The present work introduces a new metaheuristic optimization method based on the ideal gas molecular movement (IGMM) to solve mathematical and engineering optimization problems. Ideal gas molecules scatter throughout the confined environment quickly. This is embedded in the high speed of molecules, collisions between them and with the surrounding barriers. In IGMM algorithm, the initial population of gas molecules is randomly generated and the governing equations related to the velocity of gas molecules and collisions between those are utilized to accomplish the optimal solutions. To verify the performance of the IGMM algorithm, some mathematical and engineering benchmark optimization problems, commonly used in the literature, are inspected. Comparison of results obtained by IGMM with other optimization algorithms show that the proposed method has a challenging capacity in finding the optimal solutions and exhibits significance both in terms of the accuracy and reduction on the number of function evaluations vital in reaching the global optimum.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2010) A novel heuristic optimization method: charged system search. Acta Mech 213:267–289. doi:10.1007/s00707-009-0270-4
Alberdi R, Khandelwal K (2015) Comparison of robustness of metaheuristic algorithms for steel frame optimization. Eng Struct 102:40–60. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.08.012
Mirjalili S (2015) Dragonfly algorithm : a new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1920-1
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2010) An improved ant colony optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng Comput 27:155–182. doi:10.1108/02644401011008577
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Tech Rep TR06, Erciyes Univ 10. doi:citeulike. Article-id: 6592152
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Lévy flights. In: 2009 World Congr. Nat. Biol. Inspired Comput. NABIC 2009—Proc, pp 210–214
Mirjalili S (2015) The ant lion optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 83:80–98. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.010
Wang G-G, Guo L, Gandomi AH et al (2014) Chaotic Krill Herd algorithm. Inf Sci (Ny) 274:17–34. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.123
Guo L, Wang G-G, Gandomi AH et al (2014) A new improved krill herd algorithm for global numerical optimization. Neurocomputing 138:392–402. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2014.01.023
Wang G-G, Deb S, Coelho LDS (2015) Earthworm optimization algorithm: a bioinspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Int J Bio Inspir Comput (in press)
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci (NY) 179:2232–2248. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2009.03.004
Wang G-G, Deb S, Cui Z (2015) Monarch butterfly optimization. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1923-y
Wang G-G, Deb S, Coelho LDS (2015) Elephant herding optimization. 3rd Int Symp Comput Bus Intell. doi:10.1109/ISCBI.2015.8
Wang G-G, Deb S, Gao X-Z, Coelho LDS (2016) A new metaheuristic optimization algorithm motivated by elephant herding behavior. Int J Bio Inspir Comput (in press)
Mirjalili SM, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Dizangian B, Ghasemi MR (2015) A fast decoupled reliability-based design optimization of structures using B-spline interpolation curves. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 1–13. doi:10.1007/s40430-015-0423-4
Dizangian B, Ghasemi MR (2015) Ranked-based sensitivity analysis for size optimization of structures. J Mech Des 137:121402-1–121402-10. doi:10.1115/1.4031295
Shobeiri V (2016) The optimal design of structures using ACO and EFG. Eng Comput. doi:10.1007/s00366-016-0443-4
Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Bahreininejad A, Kim JH (2015) Water cycle, mine blast and improved mine blast algorithms for discrete sizing optimization of truss structures. Comput Struct 149:1–16. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.12.003
Safaeian Hamzehkolaei N, Miri M, Rashki M (2015) An enhanced simulation-based design method coupled with meta-heuristic search algorithm for accurate reliability-based design optimization. Eng Comput 1–19. doi:10.1007/s00366-015-0427-9
Fabritius B, Tabor G (2015) Improving the quality of finite volume meshes through genetic optimisation. Eng Comput. doi:10.1007/s00366-015-0423-0
Ghasemi MR, Dizangian B (2010) Size, shape and topology optimization of composite steel box girders using PSO method. ASIAN J Civ Eng (BUILDING HOUSING) 11:699–715
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1:67–82. doi:10.1109/4235.585893
Sonntag RE, Borgnakke C, Van Wylen GJ (2009) Fundamentals of thermodynamics 7th edn. University of Michigan, Willey
Van Wylen GJ, Sonntag RE, Dybbs A (1975) Fundamentals of classical thermodynamics (2nd edition). J Appl Mech 42:522. doi:10.1115/1.3423632
Laurendeau NM (2005) Statistical thermodynamics fundamentals and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Harsha PS (2006) Principles of vapor deposition of thin films. The Boulevard, Oxford
Moore FL (1963) Kinetic theory of gases. Am J Phys 31:213. doi:10.1119/1.1969378
Mirjalili S, Zaiton S, Hashim M et al (2010) A new hybrid PSOGSA algorithm for function optimization. Proc ICCIA 2010 Int Conf Comput Inf Appl 374–377. doi:10.1109/ICCIA.2010.6141614
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison Wesley, Boston. doi:10.1007/s10589-009-9261-6
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Neural Networks, 1995. Proceedings, IEEE Int. Conf, vol 4, pp 1942–1948
Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76:60–68. doi:10.1177/003754970107600201
Simon D, Member S (2008) Biogeography-based optimization. Evol Comput IEEE Trans 12:702–713. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2008.919004
Wang G-G, Guo L, Wang H et al (2014) Incorporating mutation scheme into krill herd algorithm for global numerical optimization. Neural Comput Appl 24:853–871. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1304-8
Patel VK, Savsani VJ (2015) Heat transfer search (HTS): a novel optimization algorithm. Inf Sci (NY) 324:217–246. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2015.06.044
Clerc M, Kennedy J (2002) The particle swarm-explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. Evol Comput IEEE Trans 6:58–73
Coello CAC, Montes EM (2002) Constraint-handling in genetic algorithms through the use of dominance-based tournament selection. Adv Eng Inform 16:193–203
Parsopoulos KE, Vrahatis MN et al (2002) Particle swarm optimization method for constrained optimization problems. Intell Technol Appl New Trends Intell Technol 76:214–220
Joines J, Houck CR, others (1994) On the use of non-stationary penalty functions to solve nonlinear constrained optimization problems with GA’s. In: Evol. Comput. 1994. IEEE World Congr. Comput. Intell. Proc. First IEEE Conf., pp 579–584
Ahmadi-Nedushan B, Varaee H (2009) Optimal design of reinforced concrete retaining walls using a swarm intelligence technique. In: first Int. Conf. Soft Comput. Technol. Civil, Struct. Environ. Eng. UK, pp 1–12
Rao SS (2009) Engineering optimization: theory and practice. Wiley, New York. doi:10.1002/9780470549124
Ragsdell KM, Phillips DT (1976) Optimal design of a class of welded structures using geometric programming. J Eng Ind 98:1021–1025
Deb K (1991) Optimal design of a welded beam via genetic algorithms. AIAA J 29:2013–2015. doi:10.2514/3.10834
Coello CAC (2000) Constraint-handling using an evolutionary multiobjective optimization technique. Civ Eng Syst 17:319–346
Mezura-Montes E, Coello CAC (2008) An empirical study about the usefulness of evolution strategies to solve constrained optimization problems. Int J Gen Syst 37:443–473
He Q, Wang L (2007) An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 20:89–99
Mirjalili SM, Mirjalili SM, Hatamlou A (2015) Multi-verse optimizer: a nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput Appl 1–19. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1870-7
Coello CAC (2000) Use of a self-adaptive penalty approach for engineering optimization problems. Comput Ind 41:113–127
Eskandar H, Sadollah A, Bahreininejad A, Hamdi M (2012) Water cycle algorithm—a novel metaheuristic optimization method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Comput Struct 110:151–166
Coello CAC, Becerra RL (2004) Efficient evolutionary optimization through the use of a cultural algorithm. Eng Optim 36:219–236
Liu H, Cai Z, Wang Y (2010) Hybridizing particle swarm optimization with differential evolution for constrained numerical and engineering optimization. Appl Soft Comput 10:629–640
Zahara E, Kao Y-T (2009) Hybrid Nelder-Mead simplex search and particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst Appl 36:3880–3886
Lampinen J (2002) A constraint handling approach for the differential evolution algorithm. In: wcci, pp 1468–1473
Coello CAC (2012) Constraint-handling techniques used with evolutionary algorithms. In: Proc. 14th Annu. Conf. companion Genet. Evol. Comput, pp 849–872
Coello CAC, Montes EM (2001) Use of dominance-based tournament selection to handle constraints in genetic algorithms. Intell Eng Syst through Artif Neural Netw 11:177–182
Gao L, Hailu A (2010) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for constrained mixed-variable optimization problems. Int J Comput Intell Syst 3:832–842
Lee KS, Geem ZW (2004) A new structural optimization method based on the harmony search algorithm. Comput Struct 82:781–798. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2004.01.002
Sandgren E (1990) Nonlinear integer and discrete programming in mechanical design optimization. J Mech Des 112:223–229
Kannan BK, Kramer SN (1994) An augmented Lagrange multiplier based method for mixed integer discrete continuous optimization and its applications to mechanical design. J Mech Des 116:405–411
Akhtar S, Tai K, Ray T (2002) A socio-behavioural simulation model for engineering design optimization. Eng Optim 34:341–354. doi:10.1080/03052150212723
Yun YS (2005) Study on Adaptive hybrid genetic algorithm and its applications to engineering design problems. MSc Thesis, Waseda University
Tsai J-F, Li H-L, Hu N-Z (2002) Global optimization for signomial discrete programming problems in engineering design. Eng Optim 34:613–622
Coelho LDS (2010) Gaussian quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization approaches for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst Appl 37:1676–1683
Cao YJ, Wu QH (1997) Evolutionary programming. In: Evol. Comput. 1997., IEEE Int. Conf., pp 443–446
Deb K (1997) Geneas: A robust optimal design technique for mechanical component design. In: Evol. algorithms Eng. Appl. Springer, Berlin, pp 497–514
Coello CAC (1999) Self-adaptive penalties for GA-based optimization. Evol. Comput. 1999. CEC 99. Proc. 1999 Congr., p 1
Sandgren E (1988) Nonlinear integer and discrete programming in mechanical design. In: Proc. ASME Des. Technol. Conf., pp 95–105
Zhang C, Wang H-P (1993) Mixed-discrete nonlinear optimization with simulated annealing. Eng Optim 21:277–291
Coello CAC, Cortés NC (2004) Hybridizing a genetic algorithm with an artificial immune system for global optimization. Eng Optim 36:607–634
Homaifar A, Qi CX, Lai SH (1994) Constrained optimization via genetic algorithms. Simulation 62:242–253
Gandomi AH (2014) Interior search algorithm (ISA): a novel approach for global optimization. ISA Trans 53:1168–1183
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm : a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2015.07.006
Michalewicz Z, Attia N (1994) Evolutionary optimization of constrained problems. In: Proc. 3rd Annu. Conf. Evol. Program, pp 98–108
Gandomi AH, Yang X-S, Alavi AH, Talatahari S (2013) Bat algorithm for constrained optimization tasks. Neural Comput Appl 22:1239–1255
Ben Hadj-Alouane A, Bean JC (1997) A genetic algorithm for the multiple-choice integer program. Oper Res 45:92–101
Fu J-F, Fenton RG, Cleghorn WL (1991) A mixed integer-discrete-continuous programming method and its application to engineering design optimization. Eng Optim 17:263–280
Li H-L, Chou C-T (1993) A global approach for nonlinear mixed discrete programming in design optimization. Eng Optim 22:109–122
Sadollah A, Bahreininejad A, Eskandar H, Hamdi M (2013) Mine blast algorithm: a new population based algorithm for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput J 13:2592–2612. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2012.11.026
Cai J, Thierauf G (1997) Evolution strategies in engineering optimization. Eng Optim 29:177–199
He S, Prempain E, Wu QH (2004) An improved particle swarm optimizer for mechanical design optimization problems. Eng Optim 36:585–605
Cao YJ, Wu QH (1999) A mixed variable evolutionary programming for optimisation of mechanical design. Eng Intell Syst Electr Eng Commun 7:77–82
Hu X, Eberhart RC, Shi Y (2003) Engineering optimization with particle swarm. In: Swarm Intell. Symp. 2003. SIS’03. Proc. 2003 IEEE, pp 53–57
Huang F, Wang L, He Q (2007) An effective co-evolutionary differential evolution for constrained optimization. Appl Math Comput 186:340–356
Litinetski VV, Abramzon BM (1998) MARS-A multistart adaptive random search method for global constrained optimization in engineering applications. Eng Optim 30:125–154
Wu S-J, Chow P-T (1995) Genetic algorithms for nonlinear mixed discrete-integer optimization problems via meta-genetic parameter optimization. Eng Optim A35(24):137–159
Lee KS, Geem ZW (2005) A new meta-heuristic algorithm for continuous engineering optimization: harmony search theory and practice. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:3902–3933. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2004.09.007
Cagnina LC, Esquivel SC, Coello CAC (2008) Solving engineering optimization problems with the simple constrained particle swarm optimizer. Informatica 32:319–326
Hossein A, Yang GX, Gandomi AH et al (2013) Cuckoo search algorithm: a metaheuristic approach to solve structural optimization problems. Eng Comput 29:17–35. doi:10.1007/s00366-011-0241-y
Ray T, Liew KM (2003) Society and civilization: an optimization algorithm based on the simulation of social behavior. Evol Comput IEEE Trans 7:386–396
Mezura-Montes E, Coello CAC, Velázquez-Reyes J, Muñoz-Dávila L (2007) Multiple trial vectors in differential evolution for engineering design. Eng Optim 39:567–589
Parsopoulos KE, Vrahatis MN (2005) Unified particle swarm optimization for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. In: Adv. Nat. Comput. Springer, Berlin, pp 582–591
Shih CJ, Lai TK (1995) Mixed-discrete fuzzy programming for nonlinear engineering optimization. Eng Optim 23:187–199
Li H-L, Chang C-T (1998) An approximate approach of global optimization for polynomial programming problems. Eur J Oper Res 107:625–632
Belegundu AD, Arora JS (1985) A study of mathematical programming methods for structural optimization. Part I: theory. Int J Numer Methods Eng 21:1583–1599
Arora J (2004) Introduction to optimum design. Academic Press, Cambridge
Krohling R, dos Santos Coelho LDS et al (2006) Coevolutionary particle swarm optimization using Gaussian distribution for solving constrained optimization problems. Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern IEEE Trans 36:1407–1416
Mahdavi M, Fesanghary M, Damangir E (2007) An improved harmony search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 188:1567–1579. doi:10.1016/j.amc.2006.11.033
Kaveh A, Mahdavi VRR (2014) Colliding bodies optimization: a novel meta-heuristic method. Comput Struct 139:18–27. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.04.005
He Q, Wang L (2007) A hybrid particle swarm optimization with a feasibility-based rule for constrained optimization. Appl Math Comput 186:1407–1422
Wang L, Li L (2010) An effective differential evolution with level comparison for constrained engineering design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:947–963
Zhang M, Luo W, Wang X (2008) Differential evolution with dynamic stochastic selection for constrained optimization. Inf Sci (NY) 178:3043–3074
Wang Y, Cai Z, Zhou Y, Fan Z (2009) Constrained optimization based on hybrid evolutionary algorithm and adaptive constraint-handling technique. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37:395–413
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) Artificial bee colony (ABC) optimization algorithm for solving constrained optimization. In: Probl. LNCS Adv. Soft Comput. Found. Fuzzy Log. Soft Comput. Springer, IFSA (2007). Citeseer, pp 789–798
Mezura-Montes E, Coello CAC (2005) Useful infeasible solutions in engineering optimization with evolutionary algorithms. In: MICAI 2005 Adv. Artif. Intell. Springer, Berlin, pp 652–662
Chickermane H, Gea HC (1996) Structural optimization using a new local approximation method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39:829–846
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes- a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Cheng M-Y, Prayogo D (2014) Symbiotic organisms search: a new metaheuristic optimization algorithm. Comput Struct 139:98–112
Deb K, Goyal M (1996) A combined genetic adaptive search (GeneAS) for engineering design. Comput Sci Inform 26:30–45
Sharma TK, Pant M, Singh VP (2012) Improved local search in artificial bee colony using golden section search. arXiv:1210.6128 (arXiv Prepr)
Schmit LA, Farshi B (1974) Some approximation concepts for structural synthesis. AIAA J 12:692–699
Schmit LA, Miura H (1976) Approximation concepts for efficient structural synthesis. US National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Li LJ, Huang ZB, Liu F (2009) A heuristic particle swarm optimization method for truss structures with discrete variables. Comput Struct 87:435–443. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.01.004
Kaveh A, Rahami H (2006) Analysis, design and optimization of structures using force method and genetic algorithm. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65:1570–1584
Camp C, Pezeshk S, Cao G (1998) Optimized design of two-dimensional structures using a genetic algorithm. J Struct Eng 124:551–559. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1998)124:5(551)
Farshi B, Alinia-Ziazi A (2010) Sizing optimization of truss structures by method of centers and force formulation. Int J Solids Struct 47:2508–2524. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.05.009
Rizzi P (1976) Optimization of multi-constrained structures based on optimality criteria. Conf. AIAA/ASME/SAE 17th Struct. Struct. Dyn. Mater., King Prussia, PA
John KV, Ramakrishnan CV, Sharma KG (1987) Minimum weight design of trusses using improved move limit method of sequential linear programming. Comput Struct 27:583–591
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2009) Particle swarm optimizer, ant colony strategy and harmony search scheme hybridized for optimization of truss structures. Comput Struct 87:267–283. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.01.003
Camp CV, Bichon BJ (2004) Design of space trusses using ant colony optimization. J Struct Eng 130:741–751
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2009) Size optimization of space trusses using Big Bang-Big Crunch algorithm. Comput Struct 87:1129–1140. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.04.011
Schutte JF, Groenwold AA (2003) Sizing design of truss structures using particle swarms. Struct Multidiscip Optim 25:261–269
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2010) Optimal design of skeletal structures via the charged system search algorithm. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:893–911
Kaveh A, Sheikholeslami R, Talatahari S, Keshvari-Ilkhichi M (2014) Chaotic swarming of particles: a new method for size optimization of truss structures. Adv Eng Softw 67:136–147. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.09.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varaee, H., Ghasemi, M.R. Engineering optimization based on ideal gas molecular movement algorithm. Engineering with Computers 33, 71–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0457-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0457-y