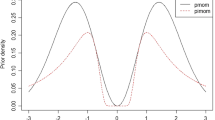
Abstract
In many applications, variables can be naturally partitioned into different groups. We consider a hierarchical model with nonlocal priors over group-structured covariates to perform group selection in high-dimensional linear regression. While several frequentist and Bayesian approaches have been proposed for group selection, theoretical properties of Bayesian approaches using nonlocal priors have not been studied. Under mild conditions, we establish strong group selection consistency of the induced posterior when the number of covariates grows at nearly exponential rate with sample size. An efficient shotgun stochastic search algorithm tailored for the group selection is adopted for implementing our proposed approach and simulation studies are conducted to demonstrate its superior empirical performance. We further apply the proposed method to an fMRI dataset for identifying brain regions with altered functional activities to predict disease progression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abós A, Baggio HC, Segura B, García-Díaz AI, Compta Y, Martí MJ, Valldeoriola F, Junqué C (2017) Discriminating cognitive status in Parkinson’s disease through functional connectomics and machine learning. Sci Rep 7(1):45347
Bai R, Moran GE, Antonelli JL, Chen Y, Boland MR (2020) Spike-and-slab group lassos for grouped regression and sparse generalized additive models. J Am Stat Assoc 0(0):1–14
Breheny P (2015) The group exponential lasso for bi-level variable selection. Biometrics 71(3):731–740
Breheny P, Huang J (2009) Penalized methods for bi-level variable selection. Stat Interface 2(3):369
Cao X, Lee K (2021) Joint Bayesisan variable and DAG selection consistency for high-dimensional regression models with network-structured covariates. Stat Sin 31(3):1509–1530
Cao X, Khare K, Ghosh M (2019) Posterior graph selection and estimation consistency for high-dimensional Bayesian DAG models. Ann Stat 47(1):319–348
Cao X, Khare K, Ghosh M (2020) High-dimensional posterior consistency for hierarchical non-local priors in regression. Bayesian Anal 15(1):241–262
Cao X, Wang X, Xue C, Zhang S, Huang Q, Liu W (2020) A radiomics approach to predicting Parkinson’s disease by incorporating whole-brain functional activity and gray matter structure. Front Neurosci 14:751
Castillo I, Schmidt-Hieber J, Van der Vaart A et al (2015) Bayesian linear regression with sparse priors. Ann Stat 43(5):1986–2018
Chagas MHN, Linares IMP, Garcia GJ, Hallak JEC, Tumas V, Crippa JAS (2013) Neuroimaging of depression in Parkinson’s disease: a review. Int Psychogeriatr 25(12):1953–1961
Deng L, Sun J, Cheng L, Tong S (2016) Characterizing dynamic local functional connectivity in the human brain. Sci Rep 6(1):26976
Hans C, Dobra A, West M (2007) Shotgun stochastic search for large \(p\) regression. J Am Stat Assoc 102(478):507–516
Huang J, Breheny P, Ma S (2012) A selective review of group selection in high-dimensional models. Stat Sci 27(4):481–499
Ishwaran H, Rao JS (2005) Spike and slab variable selection: frequentist and Bayesian strategies. Ann Stat 33(2):730–773
Ishwaran H, Rao JS (2005) Spike and slab variable selection: frequentist and Bayesian strategies. Ann Stat 33(2):730–773
Johnson V, Rossell D (2010) On the use of non-local prior densities in bayesian hypothesis tests hypothesis. J. R. Statist. Soc. B 72:143–170
Johnson VE, Rossell D (2012) Bayesian model selection in high-dimensional settings. J Am Stat Assoc 107(498):649–660
Lee K, Cao X (2021) Bayesian group selection in logistic regression with application to MRI data analysis. Biometrics 77(2):391–400
Lee K, Lee JL, Lin L (2019) Minimax posterior convergence rates and model selection consistency in high-dimensional DAG models based on sparse cholesky factors. Ann Stat 47(6):3413–3437
Li W, Chekouo T (2022) Bayesian group selection with non-local priors. Comput Stat 37(1):287–302
Liao H, Cai S, Shen Q, Fan J, Wang T, Zi Y, Mao Z, Situ W, Liu J, Zou T, Yi J, Zhu X, Tan C (2021) Networks are associated with depression in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a resting-state imaging study. Front Neurosci 14:573538
Lin H, Cai X, Zhang D, Liu J, Na P, Li W (2020) Functional connectivity markers of depression in advanced Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 25:102130
Martin R, Mess R, Walker SG et al (2017) Empirical Bayes posterior concentration in sparse high-dimensional linear models. Bernoulli 23(3):1822–1847
Meinshausen N, Bühlmann P (2006) High-dimensional graphs and variable selection with the lasso. Ann Stat 34(3):1436–1462
Narisetty NN, He X (2014) Bayesian variable selection with shrinking and diffusing priors. Ann Stat 42(2):789–817
Narisetty NN, Shen J, He X (2019) Skinny Gibbs: a consistent and scalable Gibbs sampler for model selection. J Am Stat Assoc 114(527):1205–1217
Pandya M, Altinay M, Malone DA, Anand A (2012) Where in the brain is depression? Curr Psychiatry Rep 14(6):634–642
Ročková V, George EI (2018) The spike-and-slab lasso. J Am Stat Assoc 113(521):431–444
Rossell D, Telesca D (2017) Nonlocal priors for high-dimensional estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 112(517):254–265
Shearer J, Green C, Counsell CE, Zajicek JP (2012) The impact of motor and non motor symptoms on health state values in newly diagnosed idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 259(3):462–468
Shi G, Lim CY, Maiti T (2019) Bayesian model selection for generalized linear models using non-local priors. Comput Stat Data Anal 133:285–296
Shin M, Bhattacharya A, Johnson VE (2018) Scalable Bayesian variable selection using nonlocal prior densities in ultrahigh-dimensional settings. Stat Sin 28:1053–1078
Song Q, Liang F (2017) Nearly optimal Bayesian shrinkage for high dimensional regression. arXiv:1712.08964
Song X-W, Dong Z-Y, Long X-Y, Li S-F, Zuo X-N, Zhu C-Z, He Y, Yan C-G, Zang Y-F (2011) Rest: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS ONE 6(9):1–12
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodol) 58(1):267–288
Wang L, Chen G, Li H (2007) Group SCAD regression analysis for microarray time course gene expression data. Bioinformatics 23(12):1486–1494
Wang M, Liao H, Shen Q, Cai S, Zhang H, Xiang Y, Liu S, Wang T, Zi Y, Mao Z, Tan C (2020) Changed resting-state brain signal in Parkinson’s patients with mild depression. Front Neurol 11:28
Wei L, Hu X, Zhu Y, Yuan Y, Liu W, Chen H (2017) Aberrant intra-and internetwork functional connectivity in depressed Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Xu X, Ghosh M (2015) Bayesian variable selection and estimation for group lasso. Bayesian Anal 10(4):909–936
Xu Z, Lai J, Zhang H, Ng CH, Zhang P, Xu D, Hu S (2019) Regional homogeneity and functional connectivity analysis of resting-state magnetic resonance in patients with bipolar II disorder. Medicine 98:47
Yang X, Narisetty NN (2020) Consistent group selection with Bayesian high dimensional modeling. Bayesian Anal 15(3):909–935
Yang Y, Wainwright MJ, Jordan MI et al (2016) On the computational complexity of high-dimensional Bayesian variable selection. Ann Stat 44(6):2497–2532
Yuan M, Lin Y (2006) Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. J R Stat Soc Series B (Statistical Methodology) 68(1):49–67
Yue Y, Jiang Y, Shen T, Pu J, Lai H-Y, Zhang B (2020) Alff and REHO mapping reveals different functional patterns in early- and late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci 14:141
Zang Y, Jiang T, Lu Y, He Y, Tian L (2004) Regional homogeneity approach to FMRI data analysis. Neuroimage 22(1):394–400
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Editor and reviewers for their valuable comments which have significantly improved the quality of presentation and technical content of our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Zhang, L., Zheng, J. et al. Consistent group selection using nonlocal priors in regression. Stat Papers 65, 989–1019 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-023-01441-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-023-01441-0