Abstract
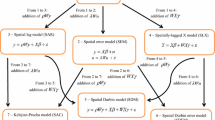
The accuracy of recent applications in small area statistics in many cases highly depends on the assumed properties of the underlying models and the availability of micro information. In finite population sampling, small sample sizes may increase the sensitivity of the modeling with respect to single units. In these cases, area-specific sample sizes tend to be small such that normal assumptions, even of area means, seem to be violated. Hence, applying robust estimation methods is expected to yield more reliable results. In general, two robust small area methods are applied, the robust EBLUP and the M-quantile method. Additionally, the use of adequate auxiliary information may further increase the accuracy of the estimates. In prediction based approaches where information is needed on universe level, in general, only few variables are available which can be used for modeling. In addition to variables from the dataset, in many cases further information may be available, e.g. geographical information which could indicate spatial dependencies between neighboring areas. This spatial information can be included in the modeling using spatially correlated area effects. Within the paper the classical robust EBLUP is extended to cover spatial area effects via a simultaneous autoregressive model. The performance of the different estimators are compared in a model-based simulation study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abberger K (1997) Quantile smoothing in financial time series. Stat Pap 38(2):125–148
Anselin L (1992) Spatial econometrics: methods and models. Kluwer, London
Banerjee S, Carlin B, Gelfand AE (2004) Hierarchical modeling and analysis for spatial data. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton
Battese GE, Harter RM, Fuller WA (1988) An error component model for prediction of county crop areas using survey and satellite data. J Am Stat Assoc 83(401):28–36
Besag J (1974) Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems (with discussion). J Royal Stat Soc Ser B 36:192–236
Breckling J, Chambers R (1988) M-quantiles. Biometrika 75(4):761–771
Chambers R (1986) Outlier robust finite population estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 81:1063–1069
Chambers R, Chandra H (2012) A random effect block bootstrap for clustered data. J Comput Graph Stat. doi:10.1080/10618600.2012.681216
Chambers R, Chandra H, Salvati N, Tzavidis N (2013) Outlier robust small area estimation. J Royal Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. doi:10.1111/rssb.12019
Chambers R, Tzavidis N (2006) M-quantile models for small area estimation. Biometrika 93(2):255–268
Chatterjee S, Lahiri P, Li H (2008) Parametric bootstrap approximation to the distribution of eblup and related predition intervals in linear mixed models. Ann Stat 36(3):1221–1245
Cressie N (1993) Statistics for spatial data. Wiley, New York
Dasiou D, Moyssiadis C (2001) The 50 % breakdown point in simultaneous m-estimation of location and scale. Stat Pap 42(2):243–252
Fellner WH (1986) Robust estimation of variance components. Technometrics 28(1):51–60
Hall P, Maiti T (2006) On parametric bootstrap methods for small area prediction. J Royal Stat Soc Ser B 68(2):221–238
Hampel FR, Ronchetti EM, Rousseeuw PJ, Stahel WA (1986) Robust statistics: the approach based on influence functions. Wiley, New York
Harville DA (1977) Maximum likelihood approaches to variance component estimation and to related problems. J Am Stat Assoc 72(358):320–340
Jiang J, Lahiri P (2006) Mixed model prediction and small area estimation. Test 15(1):1–96
Koenker R (2005) Quantile regression. Cambridge University Press, New York
Koenker R, Bassett G (1978) Regression quantiles. Econometrica 46:33–50
Koenker R, Hallock KF (2001) Quantile regression. J Econ Perspect 15(4):143–156
Landajo M, de Andrés J, Lorca P (2008) Measuring firm performance by using linear and non-parametric quantile regressions. J Royal Stat Soc Ser C 57(2):227–250
Molina I, Salvati N, Pratesi M (2009) Bootstrap for estimating the mean squared error of the spatial eblup. Comput Stat 24(3):441–458
Münnich R, Gabler S, Ganninger M (2007) Some remarks on the register-based census 2010/2011 in Germany. In: Proceedings of the workshop innovative methodologies for censuses in the new millennium, Southampton
Niemiro W, Wesolowski J (2010) Synthetic and composite estimation under a superpopulation model. Stat Pap 51(3):497–509
Petrucci A, Pratesi M, Salvati N (2005) Geographic information in small area estimation: small area models and spatially correlated random area effects. Stat Transit 7(3):609–623
Prasad NGN, Rao JNK (1990) The estimation of the mean squared error of small area estimators. J Am Stat Assoc 85(409):163–171
Pratesi M, Salvati N (2008) Small area estimation: the eblup estimator based on spatially correlated random area effects. Stat Methods & Appl 17:113–141
Rao JNK (2003) Small area estimation. Wiley, New York
Richardson AM (1997) Bounded influence estimation in the mixed linear model. J Am Stat Assoc 92(437):154–161
Richardson AM, Welsh AH (1994) Asymptotic properties of restricted maximum likelihood (reml) estimates for hierarchical mixed linear models. Aust J Stat 36:31–43
Richardson AM, Welsh AH (1995) Robust restricted maximum likelihood in mixed linear models. Biometrics 51(4):1429–1439
Salvati N (2004) Small area estimation by spatial models: the spatial empirical best linear unbiased prediction (spatial eblup). Technical report. University of Florence, Department of Statistics
Salvati N, Tzavidis N, Pratesi M, Chambers R (2012) Small area estimation via M-quantile geographically weighted regression. Test 21(1):1–28
Schmid T (2011) Spatial robust small area estimation applied on business data. Ph. D. thesis, University of Trier
Schmid T, Münnich R (2011) Parametric bootstrap mean squared error estimation for the spatial robust eblup. In: Proceedings of the second ITACOSM conference, survey research methods and applications, pp 211–214
Singh B, Shukla G, Kundu D (2005) Spatio-temporal models in small area estimation. Surv Methodol 31(2):183–195
Sinha SK, Rao JNK (2008) Robust small area estimation under unit level models. In: Proceedings of the survey research methods section, American statistical association, vol 82
Sinha SK, Rao JNK (2009) Robust small area estimation. Can J Stat 37(3):381–399
Särndal C-E, Swensson B, Wretman J (1992) Model assisted survey sampling. Springer, New York
Sun D, Tsutakawa RK, Speckman P (1999) Posterior distribution of hierarchical models using car(1) distributions. Technical report. National Institute of Statistical Sciences
Tzavidis N, Marchetti S, Chambers R (2010) Robust estimation of small area means and quantiles. Aust N Z J Stat 52(2):167–186
Tzavidis N, Salvati N, Pratesi M, Chambers R (2008) M-quantile models with application to poverty mapping. Stat Methods Appl 17(3):393–411
Vogt M (2010) Bayesian spatial modeling. Ph. D. thesis, University of Trier
Vogt M, Münnich R (2009) On the existence of a posterior distribution for spatial mixed models with binomial responses. Metron 67(2):199–207
Welsh A, Ronchetti E (1998) Bias-calibrated estimation from sample surveys containing outliers. J Royal Stat Soc Ser B 60:413–428
Zadlo T (2009) On mse of eblup. Stat Pap 50(1):101–118
Acknowledgments
The research was conducted within the BLUE-ETS research project which is funded by the European Commission within the 7th Framework Programme. For more information on the project, we refer to the project page http://www.blue-ets.eu. The first author was supported by the Foundation of German Economy. The authors are grateful to the SAMPLE project (http://www.sample-project.eu/) and Chambers et al. (2013) for providing R-code used in the simulations in this paper. The authors would like to thank the Editor-in-Chief and two anonymous referees for their very valuable comments which helped to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, T., Münnich, R.T. Spatial robust small area estimation. Stat Papers 55, 653–670 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-013-0517-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-013-0517-y