Abstract
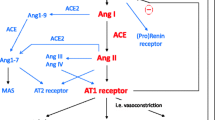
The vertebrate renin-angiotensin system controls cardiovascular, renal and osmoregulatory functions. Angiotensin II (ANG II) is the most potent hormone of the RAS but in some vertebrate animals angiotensin III (Val4-ANG III) may be a hormone. We studied the effects of some angiotensins and mammalian ANG II receptor antagonists on nasal salt gland function and arterial blood pressure in conscious white Pekin ducks. Nasal salt gland fluid secretion (NFS) was induced by a 10 ml · kg−1 bw i.v. injection of a NaCl solution (1000 mosmol · kg−1 H2O) and maintained by a continuous i.v. infusion of the same solution at a rate of 0.97 ml · min−1. There was a positive linear correlation between nasal fluid [Na+] and osmolality, between [Na+] and [K+], and also between the rate of NFS and [Na+] and [K+]. [Asp1,Val5]-ANG II (1 nmol · kg−1 i.v.) inhibited NFS but did not change ionic concentrations. Val4-ANG III (1 or 5 nmol · kg−1) and ANG I (1-7) (20 nmol · kg−1) had no effect on NFS. [Sar1, Ile8]-ANG II (SARILE) acted as an ANG II receptor agonist and resulted in a prolonged and complete inhibition of NFS. The AT1 receptor antagonist, losartan (DuP 753) and the AT2 receptor antagonist, PD 123319 both failed to block the inhibitory effect of [Asp1, Val5]-ANG II on the nasal salt glands.
[Asp1,Val5]-ANG II (2 nmol · kg−1 i.v.) increased mean arterial blood pressure (MABP), whereas the same dose of [Asn1,Val5]-ANG II (teleost) had only 30% of the pressor potency of the avian ANG II. Neither 1 nor 5 nmol · kg−1 of Val4-ANG III i.v. nor 20 nmol · kg−1 of ANG I (1-7) had any measurable effect on MABP. SARILE blocked completely the pressor response to [Asp1,Val5]-ANG II but the AT1 antagonists losartan and CGP 48933 and the AT2 antagonist PD 123319 all failed to block the pressor response to [Asp1,Val5]-ANG II. These results have substantiated an important role of the nasal salt gland in potassium regulation and highlighted a pharmacological dimorphism of saralasin, namely agonist and antagonist to angiotensin II-mediated inhibition of nasal salt gland function and pressor response, respectively. Using specific nonpeptidergic angiotensin II receptor antagonists, we have confirmed the distinct pharmacology of the avian angiotensin II receptors in a nongallinaceous species and the absence of significant angiotensin I (1-7) and angiotensin II effects on the cardiovascular system and nasal salt gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 6 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butler, D., Zandevakili, R. & Oudit, G. Effects of ANG II and III and angiotensin receptor blockers on nasal salt gland secretion and arterial blood pressure in conscious Pekin ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). J Comp Physiol B 168, 213–224 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050139