Abstract
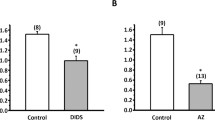
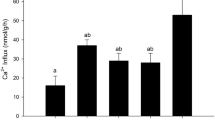
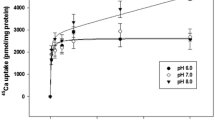
It is concluded that Ca2+ transport across the basolateral membranes of the ionocytes in killifish skin is mediated for the major part by a Na+/Ca2+-exchange mechanism that is driven by the (transmembrane) Na+ gradient established by Na+/K+-ATPase. The conclusion is based, firstly, on the biochemical evidence for the presence of a Na+/Ca2+-exchanger next to the Ca2+-ATPase in the basolateral membranes of killifish gill cells. Secondly, the transcellular Ca2+ uptake measured in an Ussing chamber setup was 85% and 80% reduced in freshwater (FW) and SW (SW) opercular membranes, respectively, as the Na+ gradient across the basolateral membrane was directly or indirectly (by ouabain) reduced. Thapsigargin or dibutyryl-cAMP/IBMX in SW opercular membranes reduced Ca2+ influx to 46%, comparable to the effects seen in FW membranes [reduction to 56%; Marshall et al. 1995a]. Basal Ca2+ influx across the opercular membrane was 48% lower in membranes from fish adapted to SW than in membranes from fish adaptated to FW. Branchial Na+/K+-ATPase activity was two times higher in SW adapted fish.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 29 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verbost, P., Bryson, S., Bonga, S. et al. Na+-dependent Ca2+ uptake in isolated opercular epithelium of Fundulus heteroclitus. J Comp Physiol B 167, 205–212 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050066