Abstract
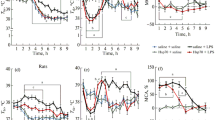
In adult mammals fever is associated with the reduction of blood plasma iron level. Immature mammals, however, show either a decrease (precocial animals such as guinea pig neonates) or a lack of reduction (altricial animals such as human neonates) of plasma iron in response to endotoxin. In order to determine whether this difference is connected with maturity just after delivery, plasma iron concentration, hematocrit, body temperature and body mass were measured in rat pups injected with E. coli endotoxin in doses of 50 or 200 μg kg−1. Rat pups, like human neonates, are altricial animals. In 7-day-old rats injection of LPS led to a dose-dependent decrease in plasma iron level. The fall in plasma iron was accompanied by changes in body temperature and body mass. The results showed that plasma iron response to endotoxin in altricial rat neonates is similar to that observed in precocial guinea pig pups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 4 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Te¸gowska, E., Wasilewska, E. & S´wie¸cka, E. Endotoxin-challenges precocial neonates and iron changes. J Comp Physiol B 167, 193–196 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050064
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050064