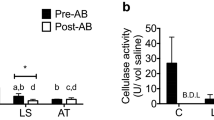
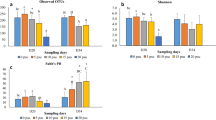
Abstract
In both underwater and semi-aquatic environments, the gut microbiota is of particular physiological importance for amphibious animals, given that the gut tract is among those organs in direct communication with the external environment. In this study, we examined the effects of these contrasting environments on the dominant bacteria in the guts of the amphibious mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris. Compared with the guts of normal mudskippers, in which the dominant bacteria were identified as Vibrio and Faecalibacterium, we found that Acinetobacter, Shigella, and Bacillus predominated in their guts after exposure to the semi-aquatic environment, whereas Escherichia, Bacteroides, and Bacillus were more prevalent in the guts in the underwater environment. The total number of cultured gut bacteria decreased significantly in the semi-aquatic environment. In semi-aquatic mudskippers, we also detected reductions and increases in the length and width of gut villi, respectively, whereas the width of gut villi declined and the number of goblet cells increased significantly in mudskippers maintained underwater. The mRNA expression of multiple gut transporters for glucose, long-chain fatty acids, and amino acids was found to increase markedly in both underwater and semi-aquatic environments, with the expression of most transporters being significantly higher in those mudskippers exposed to an underwater environment. Furthermore, we detected significant increases in the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine transcripts in the guts of both underwater and semi-aquatic mudskippers on days 2, 4, and 6 of exposure, whereas the expression of IL-10 and TGFβ mRNA was more pronounced on days 4 and 8, respectively. Comparatively, we found that expression levels of cytokines in the guts of underwater mudskipper were substantially higher than those in the guts of semi-aquatic mudskippers. Collectively, our findings revealed notable differences in the gut microbiota and energy metabolism requirements of mudskippers exposed to underwater and semi-aquatic conditions, thereby providing a theoretical basis explaining the maintenance of a homeostatic state in mudskippers that constantly transition between these contrasting amphibious habitats.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aon MA, Bhatt N, Cortassa SC (2014) Mitochondrial and cellular mechanisms for managing lipid excess. Front Physiol 5:282
Apper E, Weissman D, Respondek F, Guyonvarch A, Baron F, Boisot P, Rodiles A, Merrifield DL (2016) Hydrolysed wheat gluten as part of a diet based on animal and plant proteins supports good growth performance of Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer), without impairing intestinal morphology or microbiota. Aquaculture 453:40–48
Bagchi S, Baomar HA, Al-Walai S, Al-Sadi S, Fredriksson R (2014) Histological analysis of SLC38A6 (SNAT6) expression in mouse brain shows selective expression in excitatory neurons with high expression in the synapses. PLoS ONE 9:e95438
Biolley C, Tretola M, Bee G, Jud C, Silacci P (2019) Punicalagin increases glutamate absorption in differentiated Caco-2 cells by a mechanism involving gene expression regulation of an EAAT3 transporter. Food Funct 10:5333–5338
Bray N (2020) A gut instinct for glucose. Nat Rev Neurosci 21:301–301
Dinh QM, Tran LT, Mihn Tran TT, To DK, Thi Kieu TN, Dinh Tran D (2020) Variation in diet composition of the mudskipper Periophthalmodon septemradiatus from Hau River, Vietnam. B Mar Sci 96:487–500
Dong HB, Sun YX, Duan YF, Li H, Li Y, Liu QS, Wang WH, Zhang JS (2020) The effect of teprenone on the intestinal morphology and microbial community of Chinese sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) under intermittent hypoxic stress. Fish Physiol Biochem 46:1873–1882
Ferraris RP, Choe JY, Patel CR (2018) Intestinal absorption of fructose. Annu Rev Nutr 38:41–67
Guan F, Lu XJ, Li CH, Chen J (2017) Molecular characterization of mudskipper (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and analysis of its function in monocytes/macrophages. PLoS ONE 12:e0177960
Hagberg CE, Falkevall A, Wang X, Larsson E, Huusko J, Nilsson I, van Meeteren LA, Samen E, Lu L, Vanwildemeersch M, Klar J, Genove G, Pietras K, Stone-Elander S, Claesson-Welsh L, Ylä-Herttuala S, Lindahl P, Eriksson U (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor B controls endothelial fatty acid uptake. Nature 464:917–921
Hägglund MGA, Sreedharan S, Nilsson VCO, Shaik JHA, Almkvist IM, Bäcklin S, Wrange O, Fredriksson R (2011) Identification of SLC38A7 (SNAT7) protein as a glutamine transporter expressed in neurons. J Biol Chem 286:20500–20511
Hamidian G, Zirak K, Sheikhzadeh N, Oushani AK, Divband B (2018) Intestinal histology and stereology in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) administrated with nanochitosan/zeolite and chitosan/zeolite composites. Aquacult Res 49:1803–1815
Houpt N, Borowiec BG, Bose APH, Brown NA, Scott GR, Balshine S (2020) Parental males of the plainfin midshipman are physiologically resilient to the challenges of the intertidal zone. Physiol Biochem Zool 93:111–128
Katayama Y, Saito K, Sakamoto T (2020) Introducing the amphibious mudskipper goby as a unique model to evaluate neuro/endocrine regulation of behaviors mediated by buccal sensation and corticosteroids. Int J Mol Sci 21:6748
Kishida K, Martinez G, Iida T, Yamada T, Ferraris RP, Toyoda Y (2019) D-Allulose is a substrate of glucose transporter type 5 (GLUT5) in the small intestine. Food Chem 277:604–608
Knöpfel EB, Vilches C, Camargo SMR, Errasti-Murugarren E, Stäubli A, Mayayo C, Munier FL, Miroshnikova N, Poncet N, Junza A, Bhattacharya SS, Prat E, Berry V, Berger W, Heon E, Moore AT, Yanes Ó, Nunes V, Palacín M, Verrey F, Kloeckener-Gruissem B (2019) Dysfunctional LAT2 amino acid transporter is associated with cataract in mouse and humans. Front Physiol 10:688
Li Y, Ran C, Wei K, Xie Y et al (2021) The effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on growth, gut and liver health, and anti-viral immunity of zebrafish. Aquaculture 540:736677
Lin R, Liu WT, Piao MY, Zhu H (2017) A review of the relationship between the gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism. Amino Acids 49:2083–2090
Liu HS, Fu SL, Zhang SS, Ding MM, Wang AL (2020) Lead induces structural damage, microbiota dysbiosis and cell apoptosis in the intestine of juvenile bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Aquaculture 528:735573
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Radka CD, Frank MW, Rock CO, Yao JW (2020) Fatty acid activation and utilization by Alistipes finegoldii, a representative Bacteroidetes resident of the human gut microbiome. Mol Microbiol 113:807–825
Rathinam VAK, Chan FK (2018) Inflammasome, inflammation, and tissue homeostasis. Trends Mol Med 24:304–318
Ravindran R, Loebbermann J, Nakaya HI, Khan N, Ma HL, Gama L, Machiah DK, Lawson B, Hakimpour P, Wang YC, Li SZ, Sharma P, Kaufman RJ, Martinez J, Pulendran B (2016) The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Nature 531:523–527
Rombout JHWM, Abelli L, Picchietti S, Scapigliati G, Kiron V (2011) Teleost intestinal immunology. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:616–626
Rotoli BM, Barilli A, Visigalli R, Ferrari F, Dall’Asta V (2020) y+LAT1 and y+LAT2 contribution to arginine uptake in different human cell models: implications in the pathophysiology of lysinuric protein intolerance. J Cell Mol Med 24:921–929
Ruiz-Rodríguez M, Scheifler M, Sanchez-Brosseau S, Magnanou E, West N, Suzuki M, Duperron S, Desdevises Y (2020) Host species and body site explain the variation in the microbiota associated to wild sympatric mediterranean teleost fishes. Microb Ecol 80:212–222
Schmitt CC, Aranias T, Viel T, Chateau D, Le Gall ML, Waligora-Dupriet AJ, Melchior C, Rouxel O, Kapel N, Gourcerol G, Tavitian B, Lehuen A, Brot-Laroche E, Leturque A, Serradas P, Grosfeld A (2017) Intestinal invalidation of the glucose transporter GLUT2 delays tissue distribution of glucose and reveals an unexpected role in gut homeostasis. Mol Metab 6:61–72
Shen HY, Zhou Y, Zhou QJ, Li MY, Chen J (2020) Mudskipper interleukin-34 modulates the functions of monocytes/macrophages via the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor 1. Zool Res 41:123–137
Shen L, Guan F, Yuan Y (2021) Fasting affects the intestine and bacterial flora in mudskippers (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris) in semiaquatic and underwater conditions. Aquaculture 533:736162
Skopec MM, Green AK, Karasov WH (2010) Flavonoids have differential effects on glucose absorption in rats (Rattus norvegicus) and American robins (Turdis migratorius). J Chem Ecol 36:236–243
Soares MC, Cable J, Lima-Maximino MG, Monica G, Maximino C, Xavier R (2019) Using fish models to investigate the links between microbiome and social behaviour: The next step for translational microbiome research? Fish Fish 20:640–652
Sunyer JO (2013) Fishing for mammalian paradigms in the teleost immune system. Nat Immunol 14:320–326
Tran-Ngoc KT, Dinh NT, Nguyen TH, Roem AJ, Schrama JW, Verreth JAJ (2016) Interaction between dissolved oxygen concentration and diet composition on growth, digestibility and intestinal health of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 462:101–108
Tran-Ngoc KT, Huynh ST, Sendão J, Nguyen TH, Roem AJ, Verreth JAJ, Schrama JW (2019) Environmental conditions alter the effect of organic acid salts on digestibility and intestinal morphology in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult Nutr 25:134–144
van der Wielen N, Moughan PJ, Mensink M (2017) Amino acid absorption in the large intestine of humans and porcine models. J Nutr 147:1493–1498
Wołczuk K, Ostrowski M, Ostrowska A, Napiórkowska T (2018) Structure of the alimentary tract in the Atlantic mudskipper Periophthalmus barbarus (Gobiidae: Oxudercinae): Anatomical, histological and ultrastructural studies. Zoology 128:38–45
Xu QQ, Xu P, Zhou JW, Pan TS, Tuo R, Ai K, Yang DQ (2016) Cloning and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and its receptor, IL-1R2, in the Asian swamp eel Monopterus albus. Mol Biol 50:760–774
Yi YH, Liang LF, Wang ZL, Ai P, You XX, Bian C, Shi Q, Dong B (2019) A comparative metagenomics study on gastrointestinal microbiota in amphibious mudskippers and other vertebrate animals. Animals 9:660
Yu HX, Wang CY, Tang M (2013) Fungal and bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of Pinus tabulaeformis related to the restoration of plantations and natural secondary forests in the Loess Plateau, northwest China. Sci World J 2013:606480
Yuan Y, Zhao G, Ji H, Peng B, Huang Z, Jin W, Chen X, Guan H, Tang G, Zhang H, Jiang Z (2019) Changes in the gut microbiota during and after commercial helium–oxygen saturation diving in China. Occup Environ Med 76:801–807
Zaccon G, Lauriano ER, Kuciel M, Capillo G, Pergolizzi S, Alesci A, Icardo JM (2017) Identification and distribution of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and neurochemical markers in the neuroepithelial cells of the gill and the skin in the giant mudskipper, Periophthalmodon schlosseri. Zoology 125:41–52
Zhao L, Huang YF, Lu L, Yang W, Huang T, Lin ZS, Lin CY, Kwan H, Wong HLX, Chen Y, Sun SL, Xie XF, Fang XD, Yang HM, Wang J, Zhu LX, Bian ZX (2018) Saturated long-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria contribute to enhanced colonic motility in rats. Microbiome 6:107
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (NO. LY17C010001); Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (NO. 2017A610287); Food Science and Engineering Key Discipline of Ningbo Higher Education (NO. 2019FSEKDNB001); Zhejiang Provincial Top Discipline of Biological Engineering (Level A) (NO. CX2019014); College Student Technological Creativity Program (NO. 2019R420015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.V. Carey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, F., Shen, L., Zhou, X. et al. Effects of underwater and semi-aquatic environments on gut tissue and microbiota of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris. J Comp Physiol B 191, 741–753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-021-01380-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-021-01380-y