Abstract
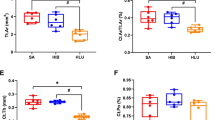
To determine that differential bone remodeling mechanism (especially Wnt signaling) in hindlimb unloaded rats and hibernating Daurian ground squirrels, the bone microstructure, mechanical properties, and expression levels of bone remodeling related proteins and key proteins of Wnt/β-catenin signaling were analyzed in this study. The thickness of cortical and trabecular bone was decreased in femur of hindlimb unloaded rats, while it was maintained in femur of hibernating ground squirrels. Interestingly, the ultimate bending energy and ultimate normalized displacement were reduced and the bending rigidity was increased in tibia of hibernating ground squirrels. Besides, the protein level of Runx2 was decreased in femur and tibia of unloaded rats, while it was maintained in tibia and even increased in femur of hibernating ground squirrels. The protein levels of RANKL and MMP-9 were increased in femur and tibia in unloaded rats, while they were maintained in both femur and tibia of hibernating ground squirrels. The protein level of GSK-3β was increased in femur and tibia of unloaded rats, while it was maintained in both femur and tibia of hibernating ground squirrels. The phospho-β-catenin expression was increased in both femur and tibia of unloaded rats, while it was only decreased in femur, but maintained in tibia of hibernating ground squirrels. In conclusion, the femur and tibia in hindlimb unloaded rats showed obvious bone loss, while they mitigated disuse-induced bone loss in hibernating ground squirrels, involving differential protein expression of key molecules in bone remodeling. In comparison with hindlimb unloaded rats, promoting osteoblast differentiation through activating canonical GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling involving Runx2 might be an adaptation to natural disuse in femur of hibernating Daurian ground squirrels. However, there was no statistical change in the protein levels of bone formation related proteins, GSK-3β and phospho-β-catenin in tibia of hibernating Daurian ground squirrels.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn HC, Lee SI, Choi MJ, Kim CH, Kim DW, Kim C (2005) Effect of hindlimb unloading of the mechanical properties of bone in mature adult male rats: with emphasis on the bone strength. Korean J Aerosp Environ Med 15(2):64–72
Andersen T, Ovejero M, Kirkegaard T, Lenhard T, Foged N, Delaissé J-M (2004) A scrutiny of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoclasts: evidence for heterogeneity and for the presence of MMPs synthesized by other cells. Bone 35:1107–1119
Andres-Mateos E, Mejias R, Soleimani A, Lin BM, Burks TN, Marx R, Lin B, Zellars RC, Zhang Y, Huso DL (2012) Impaired skeletal muscle regeneration in the absence of fibrosis during hibernation in 13-lined ground squirrels. PLoS ONE 7:e48884
Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Papapoulos SE (2016) Sclerostin inhibition in the management of osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 98:370–380
Apseloff G, Girten B, Weisbrode SE, Walker M, Stern LS, Krecic ME, Gerber N (1993) Effects of aminohydroxybutane bisphosphonate on bone growth when administered after hind-limb bone loss in tail-suspended rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:515–521
Badilatti SD, Christen P, Parkinson I, Müller R (2016) Load-adaptive bone remodeling simulations reveal osteoporotic microstructural and mechanical changes in whole human vertebrae. J Biomech 49:3770
Bandeira L, Lewiecki EM, Bilezikian JP (2017) Romosozumab for the treatment of osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 17:255–263
Bikle DD, Morey-Holton ER, Doty SB, Currier PA, Tanner SJ, Halloran BP (1994) Alendronate increases skeletal mass of growing rats during unloading by inhibiting resorption of calcified cartilage. J Bone Miner Res 9:1777–1787
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Müller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro–computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 25:1468–1486
Bradford R (2010) Exploration of the role of serum factors in maintaining bone mass during hibernation in black bears. Dissertation & Theses Gradworks, Michigan Technological University
Brodt MD, Ellis CB, Silva MJ (2010) Growing C57Bl/6 mice increase whole bone mechanical properties by increasing geometric and material properties. J Bone Miner Res 14:2159–2166
Bruderer M, Richards RG, Alini M, Stoddart MJ (2014) Role and regulation of runx2 in osteogenesis. Eur Cell Mater 28:269–286
Calvo MS, Eyre DR, Gundberg CM (1996) Molecular basis and clinical application of biological markers of bone turnover. Endocr Rev 17:333–368
Carvalho AAF, Louzada MJ, Nakamune ACMS (2009) Bone structure, strength and microhardness resulting after hindlimb unloading in rats. Braz J Morphol Sci 26:145–150
Chang H, Lei T, Ma X, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhang X, Gao YF (2018b) Muscle-specific activation of calpain system in hindlimb unloading rats and hibernating Daurian ground squirrels: a comparison between artificial and natural disuse. J Comp Physiol B 188:1–14
Chang H, Jiang S, Ma X, Peng X, Zhang J, Wang Z, Shenhui X, Wang H, Gao Y (2018a) Proteomic analysis reveals the distinct energy and protein metabolism characteristics involved in myofiber type conversion and resistance of atrophy in the extensor digitorum longus muscle of hibernating Daurian ground squirrels. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genom Proteom 26:20–31
Chang H, Peng X, Yan X, Zhang J, Xu S, Wang H, Wang Z, Ma X, Gao Y (2020) Autophagy and Akt-mTOR signaling display periodic oscillations during torpor-arousal cycles in oxidative skeletal muscle of Daurian ground squirrels (Spermophilus dauricus). J Comp Physiol B 190:113–123
Chatziravdeli V, Katsaras GN, Lambrou GI (2019) Gene expression in osteoblasts and osteoclasts under microgravity conditions: a systematic review. Curr Genom 20:184–198
Chen Z, Zhang Y, Zhao F, Yin C, Yang C, Wang X, Wu Z, Liang S, Li D, Lin X, Tian Y, Hu L, Li Y, Qian A (2020) Recombinant irisin prevents the reduction of osteoblast differentiation induced by stimulated microgravity through increasing β-catenin expression. Int J Mol Sci 21:1259
Cravens E, Kirkwood J, Wolfe L, Packer R, Whalen L, Wojda S, Prenni J, Florant G, Donahue S (2019) The effects of neurectomy and hibernation on bone properties and the endocannabinoid system in marmots (Marmota flaviventris). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 241:110621
David V, Lafage-Proust MH, Laroche N, Christian A, Ruegsegger P, Vico L (2006) Two-week longitudinal survey of bone architecture alteration in the hindlimb-unloaded rat model of bone loss: sex differences. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E440-447
Delaissé JM, Andersen TL, Engsig MT, Henriksen K, Troen T, Blavier L (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and cathepsin K contribute differently to osteoclastic activities. Microsc Res Tech 61:504–513
Doherty AH, Frampton JD, Vinyard CJ (2012) Hibernation does not reduce cortical bone density, area or second moments of inertia in woodchucks (Marmota monax). J Morphol 273:604–617
Doherty A, Roteliuk D, Gookin S, McGrew A, Broccardo C, Condon K, Prenni J, Wojda S, Florant G, Donahue S (2016) Exploring the bone proteome to help explain altered bone remodeling and preservation of bone architecture and strength in hibernating marmots. Physiol Biochem Zool 89:000–000
Donahue SW, Mcgee ME, Harvey KB, Vaughan MR, Robbins CT (2006) Hibernating bears as a model for preventing disuse osteoporosis. J Biomech 39:1480–1488
Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Herberth J, Browning SR, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Wirnsberger G, Holzer H, Dobnig H, Malluche HH (2008) Bone markers predict cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease. J Bone Miner Res 23:1850–1858
Globus RK, Bikle DD, Morey-Holton E (1986) The temporal response of bone to unloading. Endocrinology 118:733–742
Goichberg P, Shtutman M, Ben-Ze’ev A, Geiger B (2001) Recruitment of β-catenin to cadherin-mediated intercellular adhesions is involved in myogenic induction. J Cell Sci 114:1309–1319
Halloran BP, Bikle DD, Cone CM, Morey-Holton E (1988) Glucocorticoids and inhibition of bone formation induced by skeletal unloading. Am J Physiol 255:E875-879
Helen P (2002) Beta-catenin is essential and sufficient for skeletal myogenesis in P19 cells. J Biol Chem 18:15393–15399
Hickman DL, Johnson SW (2011) Evaluation of the aesthetics of physical methods of euthanasia of anesthetized rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci JAALAS 50:695–701
Huang DW, Wan YM, Shi ZZ, Huang ZM, Ying-Hui LI, Yong-Jie MA (2003) Effects of hindlimb unloading on bone histomorphometry and bone mass in rats. Space Med Med Eng 16(6):418–421
Ignacio AJ (2006) Osteocyte apoptosis is induced by weightlessness in mice and precedes osteoclast recruitment and bone loss. J Bone Miner Res 21(4):605–615
Ikeda K, Takeshita S (2015) The role of osteoclast differentiation and function in skeletal homeostasis. J Biochem 159:1–8
Ito T, Ohmori S, Kanda K, Kawano S, Seo H (1994) Changes in serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and mRNAs for osteocalcin and alkaline phosphatase in femur unloaded by tail suspension in rats. Environ Med 38:103–106
Jacon PUM, Tami SGC, Chacon CR, Tamura OGA, Hernandes CNAN, Menegati DRC, Quirino LMJ, Christopher GD (2017) Model of hindlimb unloading in adult female rats: characterizing bone physicochemical, microstructural, and biomechanical properties. PLoS ONE 12:e0189121
Jinhu X (2011) Matrix-embedded cells control osteoclast formation. Nat Med 17(10):1235–1241
Kobayashi Y, Maeda K, Takahashi N (2008) Roles of Wnt signaling in bone formation and resorption. Jpn Dent Sci Rev 44:76–82
Krishnan V (2006) Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Investig 116:1202–1209
Kwiecinski GG, Krook L, Wimsatt WA (1987) Annual skeletal changes in the little brown bat, Myotis lucifugus lucifugus, with particular reference to pregnancy and lactation. Am J Anat 178:410–420
Lam AP, Gottardi CJ (2011) β-catenin signaling: a novel mediator of fibrosis and potential therapeutic target. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:562–567
Lang DH, Sharkey NA, Arimantas L, Mack HA, Lars L, Vogler GP, Vandenbergh DJ, Blizard DA, Stout JT, Stitt JP (2010) Adjusting data to body size: a comparison of methods as applied to quantitative trait loci analysis of musculoskeletal phenotypes. J Bone Miner Res 20:748–757
Lau RY, Guo X (2011) A review on current osteoporosis research: with special focus on disuse bone loss. J Osteoporos 2011:293808
LeBlanc A, Schneider V, Spector E, Evans H, Rowe R, Lane H, Demers L, Lipton A (1995) Calcium absorption, endogenous excretion, and endocrine changes during and after long-term bed rest. Bone 16:301S-304S
Lee KS, Kim HJ, Li QL, Chi XZ, Ueta C, Komori T, Wozney JM, Kim EG, Choi JY, Ryoo HM, Bae SC (2000) Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast-specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol Cell Biol 20:8783–8792
Lilian IP (2015) Inhibition of osteocyte apoptosis prevents the increase in osteocytic receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) but does not stop bone resorption or the loss of bone induced by unloading. J Biol Chem 290(31):18934–18942
Lin C, Jiang X, Dai Z, Guo X, Weng T, Wang J, Li Y, Feng G, Gao X, He L (2009) Sclerostin mediates bone response to mechanical unloading through antagonizing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Bone Miner Res 24:1651–1661
Lloyd SA, Lewis GS, Yue Z, Paul EM, Donahue HJ (2012) Connexin 43 deficiency attenuates loss of trabecular bone and prevents suppression of cortical bone formation during unloading. J Bone Miner Res 27:2359–2372
Lloyd SA, Lang CH, Zhang Y, Paul EM, Laufenberg LJ, Lewis GS, Donahue HJ (2014) Interdependence of muscle atrophy and bone loss induced by mechanical unloading. J Bone Miner Res 29:1118–1130
Maeda K, Takahashi N, Kobayashi Y (2013) Roles of Wnt signals in bone resorption during physiological and pathological states. J Mol Med (Berl) 91:15–23
McGee-Lawrence ME, Carey HV, Donahue SW (2008) Mammalian hibernation as a model of disuse osteoporosis: the effects of physical inactivity on bone metabolism, structure, and strength. Am J Physiol 295:1999–2014
McGee-Lawrence M, Buckendahl P, Carpenter C, Henriksen K, Vaughan M, Donahue S (2015) Suppressed bone remodeling in black bears conserves energy and bone mass during hibernation. J Exp Biol 218:2067–2074
Mcgee-Lawrence ME, Wojda SJ, Barlow LN, Drummer TD, Castillo AB, Kennedy O, Condon KW, Auger J, Black HL, Nelson OL (2009b) Grizzly bears (Ursus arctos horribilis) and black bears (Ursus americanus) prevent trabecular bone loss during disuse (hibernation). Bone 45:1186–1191
Mcgee-Lawrence ME, Wojda SJ, Barlow LN, Drummer TD, Bunnell K, Auger J, Black HL, Donahue SW (2009a) Six months of disuse during hibernation does not increase intracortical porosity or decrease cortical bone geometry, strength, or mineralization in black bear (Ursus americanus) femurs. J Biomech 42:1378–1383
Mcgee-Lawrence ME, Stoll DM, Mantila ER, Fahrner BK, Carey HV, Donahue SW (2011) Thirteen-lined ground squirrels (Ictidomys tridecemlineatus) show microstructural bone loss during hibernation but preserve bone macrostructural geometry and strength. J Exp Biol 214:1240
Metzger CE, Brezicha JE, Elizondo JP, Anand NS, Hogan HA, Bloomfield SA (2017) Differential responses of mechanosensitive osteocyte proteins in forelimbs and hindlimbs in hindlimb unloaded rats. Bone 105:S8756328217302661
Morey-Holton ER, Globus RK (1998) Hindlimb unloading of growing rats: a model for predicting skeletal changes during space flight. Bone 22:83s–88s
Morey-Holton ER, Globus RK (2002) Hindlimb unloading rodent model: technical aspects. J Appl Physiol 92:1367
Moriishi T, Fukuyama R, Ito M, Miyazaki T, Maeno T, Kawai Y, Komori H, Komori T (2012) Osteocyte network; a negative regulatory system for bone mass augmented by the induction of Rankl in osteoblasts and Sost in osteocytes at unloading. PLoS ONE 7:e40143
Ono N, Nakashima K, Schipani E, Hayata T, Ezura Y, Soma K, Kronenberg HM, Noda M (2007) Constitutively active parathyroid hormone receptor signaling in cells in osteoblastic lineage suppresses mechanical unloading-induced bone resorption. J Biol Chem 282:25509–25516
Osako T, Ohira Y, Ito G, Iwashita Y, Maki E (1991) Structure and mineral content in weight-bearing bones following hindlimb suspension in young rats. Jpn J Physiol 41:923–932
Pan Z, Yang J, Guo C, Shi D, Shen D, Zheng Q, Chen R, Xu Y, Xi Y, Wang J (2008) Effects of hindlimb unloading on ex vivo growth and osteogenic/adipogenic potentials of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Stem Cells Dev 17:795–804
Park J, Lee N, Lee S (2017) Current understanding of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol Cells 40:706
Pineda N, Owen M, Tucker C, Wojda S, Kitchen S, Black H, Donahue S (2017) Hibernating little pocket mice show few seasonal changes in bone properties. Anat Rec 300:2175–2183
Rantakokko J, Uusitalo H, Jamsa T, Tuukkanen J, Aro HT, Vuorio E (1999) Expression profiles of mRNAs for osteoblast and osteoclast proteins as indicators of bone loss in mouse immobilization osteopenia model. J Bone Miner Res 14:1934–1942
Ruchanee S, Kunikazu T, Toshihisa K, Kazuhisa N, Yoichi E, Masaki N (2006) Runx2 is a target of mechanical unloading to alter osteoblastic activity and bone formation in vivo. Endocrinology 147(5):2296–2305
Shane AL (2012) Effect of proton irradiation followed by hindlimb unloading on bone in mature mice: a model of long-duration spaceflight. Bone 51(4):756–764
Silva MJ, Brodt MD, Lynch MA, Mckenzie JA, Tanouye KM, Nyman JS, Wang X (2010) Type 1 diabetes in young rats leads to progressive trabecular bone loss, cessation of cortical bone growth, and diminished whole bone strength and fatigue life. J Bone Miner Res 24:1618–1627
Simske SJ, Broz JJ, Fleet ML, Schmeister TA, Gayles EC, Luttges MW (1994) Contribution of dietary and loading changes to the effects of suspension on mouse femora. J Exp Zool 269:277–285
Soysa NS, Alles N, Aoki K, Ohya K (2012) Osteoclast formation and differentiation: an overview. J Med Dent Sci 59:65–74
Steinberg B, Singh I, Mitchell O (1981) The effects of cold-stress. Hibernation, and prolonged inactivity on bone dynamics in the golden hamster, Mesocricetus auratus. J Morphol 167:43–51
Utz JC, Nelson S, O’Toole BJ, van Breukelen F (2009) Bone strength is maintained after 8 months of inactivity in hibernating golden-mantled ground squirrels, Spermophilus lateralis. J Exp Biol 212:2746–2752
Vandamme K, Holy X, Bensidhoum M, Deschepper M, Logeart-Avramoglou D, Naert I, Duyck J, Petite H (2012) Impaired osteoblastogenesis potential of progenitor cells in skeletal unloading is associated with alterations in angiogenic and energy metabolism profile. Bio-Med Mater Eng 22:219–226
Vestergaard P, Støen OG, Swenson JE, Mosekilde L, Heickendorff L, Fröbert O (2011) Vitamin D status and bone and connective tissue turnover in brown bears (Ursus arctos) during hibernation and the active state. PLoS ONE 6:e21483
Vico L, Novikov VE, Very JM, Alexandre C (1991) Bone histomorphometric comparison of rat tibial metaphysis after 7-day tail suspension vs. 7-day spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med 62:26–31
Vigelsø A, Dybboe R, Hansen CN, Dela F, Helge JW, Guadalupe Grau A (2015) GAPDH and β-actin protein decreases with aging, making stain-free technology a superior loading control in Western blotting of human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda, Md: 1985) 118:386–394
Warden SJ, Hassett SM, Bond JL, Rydberg J, Grogg JD, Hilles EL, Bogenschutz ED, Smith HD, Fuchs RK, Bliziotes MM, Turner CH (2010) Psychotropic drugs have contrasting skeletal effects that are independent of their effects on physical activity levels. Bone 46:985–992
Whalen J, Krook L, Nunez E (1972) A radiographic and histologic study of bone in the active and hibernating bat (Myotis lucifugus). Anat Rec 172:97–108
Wise J, Sena K, Vranizan K, Pollock J, Healy K, Hughes W, Sumner D, Virdi A (2010) Temporal gene expression profiling during rat femoral marrow ablation-induced intramembranous bone regeneration. PLoS ONE 5:e12987
Wojda SJ, Mcgeelawrence ME, Gridley RA, Auger J, Black HL, Donahue SW (2012) Yellow-bellied marmots (Marmota flaviventris) preserve bone strength and microstructure during hibernation. Bone 50:182–188
Wojda S, Gridley R, McGee-Lawrence M, Drummer T, Hess A, Kohl F, Barnes B, Donahue S (2015) Arctic ground squirrels limit bone loss during the prolonged physical inactivity associated with hibernation. Physiol Biochem Zool 89:000–000
Wronski TJ, Morey ER (1982) Skeletal abnormalities in rats induced by simulated weightlessness. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res 4:69–75
Yang JJ, Jeong DH, Lim YK (2018) Blood chemistry reference values for free-ranging Asiatic black bears (Ursus thibetanus) by season, age, and sex. J Wildl Dis 54:575–580
Zhang J, Li Y, Li G, Ma X, Wang H, Goswami N, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Chang H, Gao Y (2017) Identification of the optimal dose and calpain system regulation of tetramethylpyrazine on the prevention of skeletal muscle atrophy in hindlimb unloading rats. Biomed Pharmacother 96:513–523
Zhang L, Li G, Wang K, Wang Y, Dong J, Wang H, Xu L, Shi F, Cao X, Hu Z, Zhang S (2019) MiR-30 family members inhibit osteoblast differentiation by suppressing Runx2 under unloading conditions in MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 522(1):164–170
Zhang J, Chang H, Yin R, Xu S, Wang H, Gao Y (2020) A temporal study on musculoskeletal morphology and metabolism in hibernating Daurian ground squirrels (Spermophilus dauricus). Bone 144:115826
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funds from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (31640072), the Shaanxi Province Natural Science Basic Research Program (2020JM-428). Thank to Hannah V. Carey for her review and comments in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: HC and YG. Performed the experiments: XG, SQW, JZ, SYW, FB, JL, and JW. Analyzed the data: XG, SQW, and HW. Wrote the paper: SQW and HC. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Experimental Animal Protection Committee of the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China.
Additional information
Communicated by H.V. Carey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Wang, S., Zhang, J. et al. Differential bone remodeling mechanism in hindlimb unloaded rats and hibernating Daurian ground squirrels: a comparison between artificial and natural disuse. J Comp Physiol B 191, 793–814 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-021-01375-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-021-01375-9