Abstract
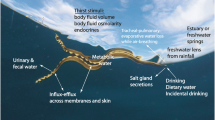
Dugongs (Dugong dugon) are fully marine mammals that live independently of fresh water so must balance water and electrolytes in a hyperosmotic environment. To investigate osmoregulation, matched plasma and urine from 51 live wild dugongs were analysed for osmolality, major electrolytes (Na+, Cl−, K+), urea, creatinine, and glucose. Maximum urine osmolality (1468 mOsm kg –1) and Na+, K+, and Cl– concentrations (757, 131.3, 677 mmol L–1, respectively) indicate that dugongs are capable of concentrating urine above seawater and could potentially realise a net gain of free water from drinking seawater. However, mean urine osmolality of 925.4 (± 46.6) mOsm kg–1 suggests that mariposia is unlikely to be an important osmoregulatory mechanism. Dugongs may obtain enough preformed water from their seagrass diet and metabolic oxidation to maintain homeostasis. Mean plasma osmolality of 339.6 (± 1.8) mOsm kg–1 is higher than in the related manatees but within the range for fully marine cetaceans. Relatively high mean plasma Na+ (175.5 ± 1.7 mmol L–1) and K+ (6.9 ± 0.1 mmol L–1), as well as mean urinary Na+ (469.6 ± 22.5 mmol L–1) and K+ levels (32.5 ± 4.5 mmol L–1) may reflect a salt-rich seagrass diet. Pregnant females had higher mean plasma osmolality (355.3 ± 4.9 mmol L–1) than non-pregnant females and males (337.9 ± 1.7 mOsm kg–1), suggesting that fluid retention was not a feature of pregnancy. Further research on water intake and endocrinology will enhance our understanding of osmoregulation in dugongs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Atherton JC, Dark JM, Garland HO, Morgan MR, Pidgeon J, Soni S (1982) Changes in water and electrolyte balance, plasma volume and composition during pregnancy in the rat. J Physiol 330(1):81–93
Bahamonde HA, Fernández V, Mattenet F, Peri PL (2016) Mineral elements in grasses growing in contrasting environmental conditions in southern Patagonia. N Z J Agric Res 59(3):235–249
Batrawi A (1957) The structure of the dugong kidney. Publications of the Marine Biology Station at Al Ghardaqa, Egypt 9:51–68
Best RC (1981) Foods and feeding habits of wild and captive Sirenia. Mammal Rev 11(1):3–29
Birch WR (1975) Some chemical and calorific properties of tropical marine angiosperms compared with those of other plants. J Appl Ecol 12(1):201–212
Burgess EA, Lanyon JM, Brown JL, Blyde D, Keeley T (2012a) Diagnosing pregnancy in free-ranging dugongs using fecal progesterone metabolite concentrations and body morphometrics: a population application. Gen Comp Endocrinol 177:82–92
Burgess EA, Lanyon JM, Keeley T (2012b) Testosterone and tusks: maturation and seasonal reproductive patterns of live, free-ranging male dugongs (Dugong dugon) in a subtropical population. Reproduction 143(5):683–697
Costa DP (1982) Energy, nitrogen and electrolyte flux and sea water drinking in the sea otter, Enhydra lutris. Physiol Zool 55:35–44
Costa DP (2017) Osmoregulation. In: Würsig B, Thewissen JGM, Kovacs K (eds) Encyclopedia of marine mammals, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 659–664
Costa DP, Maresh JL (2017) Energetics. In: Würsig B, Thewissen JGM, Kovacs K (eds) Encyclopedia of marine mammals, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 361–367
Costa DP, Trillmich F (1988) Mass changes and metabolism during the perinatal fast: a comparison between Antarctic (Arctocephalus gazella) and Galapagos fur seals (Arctocephalus galapagoensis). Physiol Zool 61:160–169
Durr J, Stamoutsos B, Lindheimer M (1981) Osmoregulation during pregnancy in the rat. Evidence for resetting of the threshold for vasopressin secretion during gestation. J Clin Investig 68(2): 337–46.
Fetcher ES Jr (1939) The water balance in marine mammals. Q Rev Biol 14:451–459
Fyfe SK (2004) Hyperspectral studies of New South Wales seagrasses with particular emphasis on the detection of light stress in eelgrass Zostera capricorni. Unpublished PhD dissertation, University of Wollongong.
Gentry RL (1981) Seawater drinking in eared seals. Comp Biochem Physiol A 68:81–86
Grings EE, Haferkamp MR, Heitschmidt RK, Karl MG (1996) Mineral dynamics in forages of the Northern Great Plains. J Range Manag 49:234–240
Guo AH, Hao YJ, Wang JZ, Zhao QZ, Wang D (2014) Concentrations of osmotically related constituents in plasma and urine of finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis): Implications for osmoregulatory strategies for marine mammals living in freshwater. Zool Stud 53:10
Harvey JW, Harr KE, Murphy D, Walsh MT, Chittick EJ, Bonde RK, Pate MG, Deutsch CJ, Edwards HH, Haubold EM (2007) Clinical biochemistry in healthy manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris). J Zoo and Wildl Med 38(2):269–279
Hill D, Reynolds J (1989) Gross and microscopic anatomy of the kidney of the West Indian manatee, Trichechus manatus (Mammalia: Sirenia). Acta Anat 135(1):53–56
Hinga KR (1979) The food requirement of whales in the Southern Hemisphere. Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Papers 26(5):569–577
Honeyfield DC, Froseth JA (1985) Effects of dietary sodium and chloride on growth, efficiency of feed utilization, plasma electrolytes and plasma basic amino acids in young pigs. J Nutr 10:1366–1371
Horgan P, Booth D, Nichols C, Lanyon JM (2014) Insulative capacity of the integument of the dugong (Dugong dugon): thermal conductivity, conductance and resistance measured by in vitro heat flux. Mar Biol 161(6):1395–1407
Hui CA (1981) Seawater consumption and water flux in the common dolphin Delphinus delphis. Physiol Zool 54(4):430–440
Husar S (1975) A review of the literature of the dugong (Dugong dugon). US Dep Internal Fish Wildl Res Rep 4:1–30
Irvine AB, Neal RC, Cardeilhac RT, Popp JA, Whiter FH, Jenkins RC (1980) Clinical observations on captive and free-ranging West Indian manatees, Trichechus manatus. Aquatic Mamm 8:2–10
Jeevitha M, Athiperumalsami T, Kumar V (2013) Dietary fibre, mineral, vitamin, amino acid and fatty acid content of seagrasses from Tuticorin Bay, southeast coast of India. Phytochemistry 90:135–146
Juknevičius S, Sabiene N (2007) The content of mineral elements in some grasses and legumes. Ekologija 53(1):44–52
Kjeld M (2001) Concentrations of electrolytes, hormones, and other constituents in fresh postmortem blood and urine of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus). Can J Zool 79:438–446
Kooyman GL, Drabek CL (1968) Observations on milk, blood, and urine constituents of the Weddell seal. Physiol Zool 41(2):187–194
Lanyon JM (1991) The nutritional ecology of the dugong (Dugong Dugon) in tropical North Queensland. Unpublished PhD Dissertation, Monash University.
Lanyon JM, Sanson GD (2006a) Degenerate dentition of the dugong (Dugong dugon) or why a grazer does not need teeth: morphology, occlusion and wear of mouthparts. J Zool Lond 268:133–152
Lanyon JM, Sanson GD (2006b) Mechanical disruption of seagrass in the digestive tract of the dugong. J Zool Lond 270:277–289
Lanyon JM, Newgrain K, Alli TSS (2006a) Estimation of water turnover rate in captive dugongs (Dugong dugon). Aquatic Mamm 32(1):103–108
Lanyon JM, Slade RW, Sneath HL, Broderick D, Kirkwood JM, Limpus D, Limpus CJ, Jessop T (2006b) A method for capturing dugongs (Dugong dugon) in open water. Aquatic Mamm 32(2):196–201
Lanyon JM, Sneath HL, Long T, Bonde RK (2010) Physiological response of wild dugongs (Dugong dugon) to out-of-water sampling for health assessment. Aquatic Mamm 36(1):46–58
Le Bas A (2003) Renal handling of water, urea and electrolytes in wild South America fur seal (Arctocephalus australis). Latin Am J Aquatic Mamm 2(1):13–20
Lester CW, Costa DP (2006) Water conservation in fasting northern elephant seals (Mirounga angusturostris). J Exp Biol 209:4283–4294
Maluf NSR (1989) Renal anatomy of the manatee, Trichechus manatus (Linnaeus). Am J Anat 184:269–286
Manire CA, Renner MS, and Reidarson TH (2004) Urinalysis and urine chemistries in the Florida manatee. International Association for Aquatic Animal Medicine Conference Proceedings. https://www.vin.com/apputil/content/defaultadv1.aspx?pId=11173&meta=generic&catId=29977&id=3981020. Accessed 14 Oct 2019
Marsh H, O'Shea TJ , Reynolds III JE (2011) Ecology and conservation of the Sirenia: dugongs and manatees (Vol. 18). Cambridge University Press, London
Michell AR, Moss P, Hill R, Vincent IC, Noakes DE (1988) The effect of pregnancy and sodium intake on water and electrolyte balance in sheep. Br Vet J 144(2):147–157
Ortiz RM (2001) Osmoregulation in marine mammals. J Exp Biol 204:1831–1844
Ortiz RM, Worthy GAJ, Mackenzie DS (1998) Osmoregulation in wild and captive West Indian manatees (Trichechus manatus). Physiol Zool 71:449–457
Ortiz RM, Worthy GAJ, Byers FM (1999) Estimation of water turnover rates of captive West Indian manatees (Trichechus manatus) held in fresh and salt water. J Exp Biol 201(1):33
Osman Hill WC (1945) Notes on the dissection of two dugongs. J Mamm 26(2):153–175
Preen A (1995) Diet of dugongs: are they omnivores? J Mamm 76(1):163
Ridgway SH (1972) Homeostasis in the aquatic environment. In: Ridgway SH (ed) Mammals of the sea: biology and medicine. Thomas, Springfield, pp 590–747
Schweigert FJ (1993) Effects of fasting and lactation on blood chemistry and urine composition in the grey seal (Halichoerus grypus). Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 105(2):353–357
Skalstad I, Nordøy ES (2000) Experimental evidence of seawater drinking in juvenile hooded (Cystophora cristata) and harp seals (Phoca groenlandica). J Comp Physiol B 170(5):395–401
St. Aubin D, Deguise S, Richard P, Smith T, Geraci J (2001) Hematology and plasma chemistry as indicators of health and ecological status in beluga whales Delphinapterus leucas. Arctic 54(3):317–331
Suzuki M, Ortiz RM (2016) Water balance. In: Castellini MA, Mellish J-A (eds) Marine mammal physiology: requisites for ocean living. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 139–168
Suzuki M, Endo N, Nakano Y, Kato H, Kishiro T, Asahina K (2008) Localization of aquaporin-2, renal morphology and urine composition in the bottlenose dolphin and the Baird’s beaked whale. J Comp Physiol B 178(2):149–156
Tarasoff F, Toews D (1972) The osmotic and ionic regulatory capacities of the kidney of the harbor seal, Phoca vitulina. J Comp Physiol 81:121–132
Telfer N, Cornell LH, Prescott JH (1970) Do dolphins drink water? J Am Vet Med Assoc 157:555–558
Touchette BW (2007) Seagrass-salinity interactions: physiological mechanisms used by submersed marine angiosperms for a life at sea. J Exp Mar Biol 350:194–215
Verlo A (2012) Seawater consumption in dehydrated hooded seals (Cystophora cristata). Unpublished Masters Thesis, University of Tromsø, Norway
Williams TM, Haun J, Davis RW, Fuiman LA, Kohin S (2001) A killer appetite: metabolic consequences of carnivory in marine mammals. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 129(4):785–796
Wong MSK (2016) Renin-angiotensin system. In: Takei Y, Ando H, Tsutsui K (eds) Handbook of hormones: comparative endocrinology for basic and clinical research. Oxford, Academic Press, Elsevier, pp 253–254
Woolford L, Wong A, Sneath H, Long T, Boyd S, Lanyon J (2015) Hematology of dugongs (Dugong dugon) in southern Queensland. Vet Clin Pathol 44(4):530–541
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Helen Peereboom for her assistance, as well as to The University of Queensland (UQ) Dugong Team and to Trevor Long (Sea World Australia). Dugong plasma and urine samples were obtained during annual health assessments conducted under UQ Animal Ethics permit no. ZOO/ENT/344/04/NSF/CRL, Moreton Bay Marine Parks permit no. QS2004/CVL228, and Scientific Purposes permit no. WISP01660304. Funding was provided by the Winifred Violet Scott Foundation, Sea World Research and Rescue Foundation Inc., (Australia) and Sea Life Conservation Fund. Thanks to David Appleton (UQ School of Agriculture and Food Sciences) for analysing salt content of seagrasses. Author order follows the convention of first, last, then other authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Communicated by Fritz Geiser.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smoll, L.I., Beard, L.A. & Lanyon, J.M. Osmoregulation and electrolyte balance in a fully marine mammal, the dugong (Dugong dugon). J Comp Physiol B 190, 139–148 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-019-01250-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-019-01250-8