Abstract
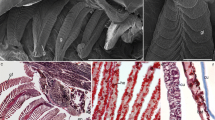
Hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha) is a clupeid that migrates from the off-shore area through the freshwater river for spawning. The purpose of this study was to investigate the involvement of branchial Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) and Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC) in maintaining ionic homeostasis in hilsa while moving across the salt barriers. Hilsa, migrating through marine and brackish waters, did not show any significant decline in NKA activity, plasma osmolality, and plasma ionic concentration. In contrast, all the parameters declined significantly, after the fish reached in freshwater zone of the river. Immunoblotting with NKA α antibody recognized two bands in gill homogenates. The intensity of the higher molecular NKA band decreased, while the other band subsequently increased accompanying the movement of hilsa from marine water (MW) to freshwater. Nevertheless, total NKA expression in marine water did not change prior to freshwater entry. NKCC expression was down-regulated in gill, parallel with NKA activity, as the fish approached to the freshwater stretch of river. The NKA α-1 and NKCC1 protein abundance decreased in freshwater individuals by 40% and 31%, respectively, compared to MW. NKA and NKCC1 were explicitly localized to branchial ionocytes and immunoreactive signal appeared throughout the cytoplasm except for the nucleus and the most apical region indicates a basolateral/tubular distribution. Immunoreactive ionocytes were distributed on the filaments and lamellae; lamellar ionocytes were more in number irrespective of habitat salinity. The decrease in salinity caused a slight reduction in ionocyte number, but not in size and the underlying distribution pattern did not alter. The overall results support previously proposed models that both the ion transporters are involved in maintaining ionic homeostasis and lamellar ionocytes may have the function in hypo-osmoregulation in migrating hilsa, unlike other anadromous teleosts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahasan DA, Naser MN, Bhaumik U, Hazra S, Bhattacharya SB (2014) Migration, spawning patterns and conservation of hilsa shad (Tenualosa ilisha) in Bangladesh and India. Academic Foundation, New Delhi, pp 1–95
Blanco G, Mercer RW (1998) Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 44:F633–F650
Chandrasekar S, Nich T, Tripathi G, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Dasgupta S (2014) Acclimation of brackish water pearl spot (Etroplus suratensis) to various salinities: relative changes in abundance of branchial Na+/K+-ATPase and Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter in relation to osmoregulation. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:983–996
Christensen AK, Hiroi J, Schultz ET, McCormick SD (2012) Branchial ionocyte organization and ion-transport protein expression in juvenile alewives acclimated to freshwater or seawater. J Exp Biol 215:642–652
Dymowska A, Goss G, Hwang PP (2012) Structure and function of mitochondria-rich cells in the freshwater fish gill. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:282–292
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Ferreira-Martins D, Coimbra J, Antunes C, Wilson JM (2016) Effects of salinity on upstream-migrating, spawning sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. Conserv Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/conphys/cov064
Flores AM, Shrimpton JM, Patterson DA, Hills JA, Cooke SJ, Yada T, Moriyama S, Hinch SG, Farrell AP (2012) Physiological and molecular endocrine changes in maturing wild sockeye salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka, during ocean and river migration. J Comp Physiol B 182:77–90
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutralcation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85:423–493
Hirai N, Tagawa M, Kaneko T, Seikai T, Tanaka M (1999) Distributional changes in branchial chloride cells during freshwater adaptation in Japanese sea bass Lateolabrax japonicus. Zool Sci 16:43–49
Hiroai J. McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2007) Variation in salinity tolerance, gill Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl– cotransporter and mitochondria-rich cell distribution in three salmonids Salvelinus namaycush, Salvelinus fontinalis and Salmo salar. J Exp Biol 210:1015–1024
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2008) Evidence for an apical Na–Cl cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211:2584–2599
Hirose S, Kaneko T, Naito N, Takei Y (2003) Molecular biology of major components of chloride cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 136B:593–620
Hwang PP, Lee TH, Lin LY (2011) Ion regulation in fish gills: recent progress in the cellular and molecular mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R28–R47
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2009) Morphological and functional classification of ion-absorbing mitochondria-rich cells in the gills of Mozambique tilapia. J Exp Biol 212:1003–1010
Kang CK, Liu FC, Chang WB, Lee TH (2012) Effects of low environmental salinity on the cellular profiles and expression of Na+, K+-ATPase and Na+/K+/2Cl–cotransporter 1 of branchial mitochondrion-rich cells in the juvenile marine fish Monodactylus argenteus. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:665–678
Katoh F, Cozzi RRF, Marshall WS, Goss GG (2008) Distinct Na+/K+/2Cl– cotransporter localization in kidneys and gills of two euryhaline species, rainbow trout and killifish. Cell Tissue Res 334:265–281
Lee TH, Hwang PP, Lin HC, Huang FL (1996c) Mitochondria-rich cells in the branchial epithelium of the teleost, Oreochromis mossambicus, acclimated to various hypotonic environments. Fish Physiol Biochem 15:513–523
Lin CH, Tsai RS, Lee TH (2004b) Expression and distribution of Na, K ATPase in gill and kidney of the spotted green pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis, in response to salinity challenge. Comp Biochem Physiol A 138:287–295
Lin YM, Chen CN, Yoshinaga T, Tsai SC, Shen ID, Lee TH (2006b) Short-term effects of hyposmotic shock on Na+/K+-ATPase expression in gills of the euryhaline milkfish, Chanos chanos. Comp Biochem Physiol A 143:406–415
Lorin-Nebel C, Boulo V, Bodinier C, Charmantier G (2006) The Na+/K+/2Cl– cotransporter in the sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax during ontogeny: involvement in osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 209:4908–4922
Lytle C, Xu JC, Biemesderfer D, Forbush B (1995) Distribution and diversity of Na–K–Cl cotransport proteins: a study with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Physiol 269:C1496–C1505
Marshall WS (2011) Mechanosensitivesignaling in fish gill and other ion-transporting epithelia. Acta Physiol 202:487–499
Marshall WS, Lynch EA, Cozzi RF (2002) Redistribution of immunofluorescence of CFTR anion channel and NKCC cotransporter in chloride cells during adaptation of the killifish Fundulus heteroclitus to sea water. J Exp Biol 205:1265–1273
McCormick SD (1993) Methods for nonlethal gill biopsy and measurements of Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:656–658
McCormick SD (1995) Hormonal control of gill Na+, K+-ATPase and chloride cell function. In: Wood CM, Shuttleworth TJ (eds) Cellular and molecular approach to fish ionic regulation. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 285–315
McCormick SD, Sundell K, Bjornsson BT, Brown CL, Hiroi J (2003) Influence of salinity on the localization of Na+/K+-ATPase. Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC) and CFTR anion channel in chloride cells of the Hawaiian goby (Stenogobius hawaiiensis). J Exp Biol 206:4575–4583
McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christensen AK (2009) Distinct freshwater and seawater isoforms of Na+/K+-ATPase in gill chloride cells of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 212:3994–4001
Miah S (2015) Climatic and anthropogenic factors changing spawning pattern and production zone of Hilsa fishery in the Bay of Bengal. Weather Clim Extrem 7:109–111
Muir WD, Zaugg WS, Giorgi AE, McCutcheon S (1994) Accelerating smolt development and downstream movement in yearling chinook salmon with advanced photoperiod and increased temperature. Aquaculture 123:387–399
Nebel LC, Boulo V, Bodinier C, Charmantier G (2006) The Na+/K+/2Cl– cotransporter in the sea bass Dicentrarchuslabrax during ontogeny: involvement in osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 209:4908–4922
Nordlie FG (2009) Environmental influences on regulation of blood plasma/serum components in teleost fishes: a review. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 19:481–564
Onuma TA, Ban M, Makino K, Katsumata H, Hu WW, Ando H, Fukuwaka M, Azumaya T, Urano A (2010) Changes in gene expression for GH/PRL/SL family hormones in the pituitaries of homing chum salmon during ocean migration through upstream migration. Gen Comp Endocrinol 166:537–548
Pelis RM, McCormick SD (2001) Effects of growth hormone and cortisol on Na+–K+–2Cl– cotransporter localization and abundance in the gills of Atlantic salmon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 124:134–143
Pelis RM, Zydlewski J, McCormick SD (2001) Gill Na+–K+–2Cl– cotransporter abundance and location in Atlantic salmon: effects of seawater and smolting. Am J Physiol 280:R1844–R1852
Richards JG, Semple JW, Bystriansky JS, Schulte PM (2003) Na+/K+-ATPase α-isoform switching in gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during salinity transfer. J Exp Biol 206:4475–4486
Sasai S, Kaneko T, Hasegawa S, Tsukamoto K (1998) Morphological alteration in two types of gill chloride cells in Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) during catadromous migration. Can J Zool 76:1480–1487
Scheiner-Bobis G (2002) The sodium pump. Its molecular properties and mechanics of ion transport. Eur J Biochem 269:2424–2433
Shrimpton JM, Björnsson BT, McCormick SD (2000) Can Atlantic salmon smolt twice? Endocrine and biochemical changes during smolting. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:1969–1976
Shrimpton JM, Patterson DA, Richards JG, Cooke SJ, Schulte PM, Hinch SG, Farrell AP (2005) Ionoregulatory changes in different populations of maturing sockeye salmon Oncorhynchus nerka during ocean and river migration. J Exp Biol 208:4069–4078
Stearly RL (1992) Historical ecology of Salmoninae, with special reference to Oncorhynchus. In: Mayden RL (ed) Systematics, historical ecology and North American freshwater Fishes. Stanford University Press, Stanford, pp 622–658
Takeyasu K, Tamkun MM, Renaud KJ, Fambrough DM (1988) Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the α-subunit of the avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem 263:4347–4354
Tipsmark CK, Madsen SS, Seidelin M, Christensen AS, Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Dynamics of Na+, K+, 2Cl–cotransporter and Na+, K+-ATPase expression in the branchial epithelium of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Exp Zool 293:106–118
Tipsmark CK, Breves JP, Seale AP, Lerner DT, Hirano T, Grau EG (2011) Switching of Na+, K+-ATPase isoforms by salinity and prolactin in the gill of a cichlid fish. J Endocrinol 209(2):237–244
Uchida K, Kaneko T, Yamauchi K, Hirano T (1996) Morphometrical analysis of chloride cell activity in the gill filaments and lamellae and changes in Na+, K+-ATPase activity during seawater adaptation in chum salmon fry. J Exp Zool 276:193–200
Varsamos S, Diaz JP, Charmantier G, Flik G, Blasco C, Connes R (2002) Branchial chloride cells in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) adapted to fresh water, seawater, and doubly concentrated seawater. J Exp Zool 293:12–26
Whitehead PJP (1986) Clupeoid fishes of the world (Suborder Clupeiodei). FAO Special Catalogue, Vol. 7. FAO Fish Synop 125:1–303
Wilson JM, Randall DJ, Donowitz M, Vogl AW, Ip AK (2000) Immunolocalization of ion-transport proteins to branchial epithelium mitochondria-rich cells in the mudskipper (Periophthalmodon schlosseri). J Exp Biol 203:2297–2310
Wu YC, Lin LY, Lee TH (2003) Na, K, 2Cl- cotransporter: a novel marker for identifying freshwater- and seawater-type mitochondria-rich cells in gills of euryhaline tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Zool Stud 42:186–192
Zaugg WS (1982) A simplified preparation for adenosine triphosphatase determination in gill tissue. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39:215–217
Zydlewski J, McCormick SD (2001) Developmental and environmental regulation of chloride cells in young American shad, Alosa sapidissima. J Exp Zool 290:73–87
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Gopal Krishna, Director, ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Education, Mumbai for providing necessary facilities for carrying out the research. This research was funded by National Agriculture Science Fund, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi under the project no. WQ-3021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, S., Ray, S.K., Pailan, G.H. et al. Alteration in branchial NKA and NKCC ion-transporter expression and ionocyte distribution in adult hilsa during up-river migration. J Comp Physiol B 189, 69–80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-018-1193-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-018-1193-y