Abstract
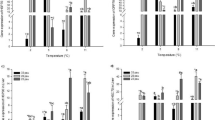
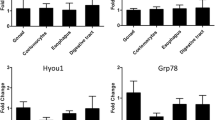
Members of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family of transcription factors have regulatory control over numerous processes related to cell fate determination, including differentiation, proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In mammals, abnormalities in the expression of some isoforms of C/EBPs are pathogenic and are implicated as being involved in myeloid leukemia and breast cancers. Next to nothing is known about their regulation, function or stress-responsiveness in poikilotherms. Here, both acute heat stress and thermal acclimation were demonstrated to induce the expression of one isoform, C/EBP-δ, in the liver, white muscle and gill of the eurythermal estuarine goby, Gillichthys mirabilis. The established role of C/EBP-δ in causing cell cycle arrest and/or promoting apoptosis in other vertebrates suggests that the heat-inducibility of this protein in poikilotherms may be part of the conserved cellular stress response with the hypothesized role of causing temporary cessation of cell growth and/or programmed cell death during bouts of environmental stress. The observed regulation of c/ebp-δ during hyperthermia represents a novel, heat-inducible signaling pathway in fishes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley BA, Hofmann GE (2002) Thermal acclimation changes DNA-binding activity of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) in the goby Gillichthys mirabilis: implications for plasticity in the heat-shock response in natural populations. J Exp Biol 205:3231–3240
Buckley BA, Somero GN (2009) cDNA microarray analysis reveals the capacity of the cold-adapted Antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii to alter gene expression in response to heat stress. Polar Biol 32:403–415
Buckley BA, Gracey AY, Somero GN (2006) The cellular response to heat stress in the goby Gillichthys mirabilis: a cDNA microarray and protein-level analysis. J Exp Biol 209:2660–2677
Cantwell CA, Sterneck E, Johnson PF (1998) Interleukin-6-specific activation of the C/EBP-δ gene in hepatocytes is mediated by Stat3 and Sp1. Mol Cell Biol 18:2108–2117
Castilho P, Buckley BA, Somero GN, Block BA (2009) Heterologous hybridization to a cDNA microarray reveals the effect of thermal acclimation in the endothermic bluefin tuna, (Thunnus orientalis). Mol Ecol 18:2092–2102
Clarkson RWE, Boland MP, Kritikou EA, Lee JM, Freeman TC, Tiffen PG, Watson CJ (2006) The genes induced by signal transducer and activators of transcription (STAT)3 and STAT5 in mammary epithelial cells define the roles of these STATs in mammary development. Mol Endocrinol 20(3):675–685
Dearth LR, DeWille J (2003) Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of C/EBPδ in G0 growth-arrested mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278(13):11246–11255
Desalvo MK, Voolstra CR, Sunagawa S, Schwarz JA, Stillman JH, Coffroth MA, Szmant AM, Medina M (2008) Differential gene expression during thermal stress and bleaching in the Caribbean coral Montastrea faveolata. Mol Ecol 17:3952–3971
Evans T, Somero GN (2008) A microarray-based transcriptomic time-course of hyper- and hypoosmotic signaling events in the euryhaline fish Gillichthys mirabilis: osmosenors to effectors. J Exp Biol 211:3636–3649
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 61:243–282
Gery S, Koeffler HP (2009) Per2 is a C/EBP target gene implicated in myeloid leukemia. Integr Cancer Ther. doi:10.1177/1534735409352084
Gery S, Gombart AF, Yi WS, Koeffler C, Hofmann W-K, Koeffler HP (2005) Transcriptional profiling of C/EBP targets identifies Per2 as a gene implicated in myeloid leukemia. Neoplasia 106:2827–2836
Gracey AY (2008) The Gillichthys mirabilis Cooper array: a platform to investigate the molecular basis of phenotypic plasticity. J Fish Biol 72:2118–2132
Gracey AY, Troll JV, Somero GN (2001) Hypoxia-induced gene expression profiling in the euryoxic fish Gillichthys mirabilis. Proc Nat Acad Sci 98:1993–1998
Hightower LE (1980) Cultured animal cells exposed to amino acid analogues or puromycin rapidly synthesize several polypeptides. J Cell Physiol 102(3):407–427
Hungness ES, Robb BW, Luo G-j, Hershko DD, Hasselgren P-O (2002) Hyperthermia-induced heat shock activates the transcription factor C/EBP-β and augments IL-6 production in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Am Coll Surg 195(5):619–626
Johnson PF (1993) Identification of C/EBP basic region residues involved in DNA sequence recognition and half-site space preference. Mol Cell Biol 13(11):6919–6930
Johnson PF (2005) Molecular stop signs: regulation of cell-cycle arrest by C/EBP transcription factors. J Cell Sci 118:2545–2555
Kassahn KS, Caley MJ, Ward AC, Connolly AR, Stone G, Crozier RH (2007) Heterologous hybridization to study the early gene response to heat stress in a coral reef fish. Mol Ecol 16:1749–1763
Katschinski DM, Le L, Heinrich D, Wagner KF, Hofer T, Schindler SG, Wenger RH (2002) Heat induction of the unphosphorylated form of hypoxia inducible factor-1α is dependent on heat shock protein-90 activity. J Biol Chem 277(11):9262–9267
Kim D, Kim S-H, Li GC (1999) Proteasome inhibitors MG132 and lactacystin hyperphosphorylate HSF1 and induce hsp70 and hsp27 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 254:264–268
Kimura H, Weisz A, Ogura T, Hitomi Y, Kurashima Y, Hashimoto K, D’Acquisto F, Makuuchi M, Esumi H (2001) Identification of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 ancillary sequence and its function in vascular endothelial growth factor gene induction by hypoxia and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 276(3):2292–2298
Kültz D (2005) Molecular and evolutionary basis of the cellular stress response. Ann Rev Physiol 67:225–257
Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, McKnight SL (1988) The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 240:1759–1764
Lekstrom-Himes J, Xanthopolous KG (1998) Biological role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family of transcription factors. J Biol Chem 273:28545–28548
Lyons SE, Shue BC, Lei L, Oates AC, Zon LI, Liu PP (2001) Molecular cloning, genetic mapping, and expression analysis of four zebrafish c/ebp genes. Gene 281:43–51
Ma Y, Freitag P, Zhou J, Brune B, Frede S, Fandrey J (2004) Thyroid hormone induces erythropoietin gene expression through augmented accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Am J Phys 287:R600–R607
Milde-Langosch K, Löning T, Bamberger A-M (2003) Expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins C/EBPα, C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ in breast cancer: correlations with clinicopathologic parameters and cell-cycle regulatory proteins. Breast Cancer Res Treat 79:175–185
Miller M, Shuman JD, Sebastian T, Dauter Z, Johnson PF (2003) Structural basis for DNA recognition by the basic region leucine zipper transcription factor CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein alpha. J Biol Chem 278(17):15178–25284
Nerlov C (2007) The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol 17(7):318–324
O’Rourke JP, Newbound GC, Hutt JA, DeWille J (1999) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ regulates mammary epithelial cell Go growth arrest and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 23:16582–16589
Osada S, Yamamoto H, Nishihara T, Imagawa M (1996) DNA binding specificity of the CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein transcription factor family. J Biol Chem 271(7):3891–3896
Page EL, Robitaille GA, Pouysseger J, Richard DE (2002) Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha by transcriptional and translational mechanisms. J Biol Chem 277:48403–48409
Porter DA, Krop IE, Nasser S, Sgroi D, Kaelin CM, Marks JR, Riggins G, Polyak K (2001) A SAGE (serial analysis of gene expression) view of breast tumor progression. Cancer Res 61:5697–5702
Porter DA, Lahit-Domenici J, Keshaviah A, Bae YK, Argani P, Marks J, Richardson A, Cooper A, Strausberg R, Riggins GJ, Schnitt S, Gabrielson E, Gelman R, Polyak K (2003) Molecular markers in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Mol Cancer Res 1:362–375
Ramji DP, Foka P (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365:561–575
Reinhold AC, Ekström J (2004) Expressions of C/EBP-enhancer-binding proteins and c-Myc in the parotid gland of the rat: in vivo effects of isoprenaline, bethanechol, vasoactive intestinal peptide and food intake. Arch Oral Biol 49(5):345–354
Richard DE, Berra E, Pouyssegur J (2000) Nonhypoxic pathway mediates the induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 275:26765–26771
Richier S, Rodriguez-Lanetty, Schnitzler CE, Weis VM (2008) Response of the symbiotic cnidarian Anthopleura elegantissima transcriptome to temperature and UV increase. Comp Biochem Physiol D 3:283–289
Rissanen E, Tranberg HK, Sollid J, Nilsson GE, Nikinmaa M (2006) Temperature regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) in a poikilothermic vertebrate, crucian carp (Carassius carassius). J Exp Biol 209:994–1003
Rosenbauer F, Tenen DG (2007) Transcription factors in myeloid development: balancing differentiation with transformation. Nature Rev Immunol 7(2):105–117
Sivko GS, DeWille JW (2004) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ (C/EBP- δ) regulation and expression in human mammary epithelial cells: I. “Loss of function” alterations in the C/EBP- δ growth inhibitory pathway in breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem 93:830–843
Sivko GS, Sanford DC, Dearth LD, Tang D, DeWille JW (2004) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ (C/EBP- δ) regulation and expression in human mammary epithelial cells: II. Analysis of activating signal transduction pathways, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational control. J Cell Biochem 93:844–856
Tang D, Sivko GS, DeWille J (2006) Promoter methylation reduces C/EBPδ (CEBPD) gene expression in the SUM-52PE human breast cancer cell line and in primary breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 95:161–170
Thangaraju M, Rudelius M, Bierie B, Raffeld M, Sharan S, Hennighhausen L, Huang A-M, Sterneck E (2005) C/EBP-δ is a crucial regulator of pro-apoptotic gene expression during mammary gland involution. Development 132(21):4675–4683
Vinson CR, Sigler PB, McKnight SL (1989) Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science 246:911–916
Wedel A, Zeigler-Heitbrock HW (1995) The C/EBP family of transcription factors. Immunobiology 193:171–185
Wenger RH (2002) Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J 16:1151–1162
Wood SC (1991) Interactions between hypoxia and hypothermia. Ann Rev Physiol 53:71–85
Yiangou M, Paraskeva E, Hsieh C-C, Markou E, Victoratos P, Scouras Z, Papaconstantinou J (1998) Induction of a subgroup of acute phase protein genes in mouse liver by hyperthermia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1396:191–206
Zhang Y, Sif S, DeWille J (2007) The mouse C/EBPdelta gene promoter is regulated by STAT3 and Sp1 transcriptional activators, chromatin remodeling and c-Myc repression. J Cell Biochem 102(5):1256–1270
Zhang Y, Liu T, Yan P, Huang T, DeWille J (2008) Identification and characterization of CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein delta (C/EBPdelta) target genes in G0 growth arrested mammary epithelial cells. BMC Mol Biol 9:83
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Oregon Health Sciences University Medical Research Foundation grant #0801 to BAB. The author thanks Dr. George Somero for use of laboratory space at Stanford University’s Hopkins Marine Station for the heat exposures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.V. Carey.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
360_2011_572_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1. Western blots demonstrating specificity of custom anti-C/EBP-δ antibody (Affinity Bioreagents). Fifteen μg of total protein were separated via SDS-PAGE, electrotransferred to nitrocellulose blots and probed via immunohistochemistry using the custom anti-C/EBP-δ antibody. Lane 1: pre-immune serum (negative control). Lanes 2, 3, 4: gill, white muscle and liver tissue from heat-shocked Gillichthys mirabilis, respectively. B) Lanes 1, 2, 3: gill, white muscle and liver tissue fromheat-shocked Gillichthys mirabilis separated via SDS-PAGE, electrotransferred to nitrocellulose blots and probed via immunohistochemistry using custom anti-C/EBP-δ antibody that was pre-incubated with a 200 molar excess of the antigenic C/EBP-δ peptide. (PDF 19 kb)
360_2011_572_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Fig. S2 Levels of C/EBP-δ mRNA, histone H2B mRNA and histone H4 mRNA in the gill tissues of Gillichthys mirabilis exposed to heat shock at 32°C for a range of durations. Each datapoint represents a pooled sample from n = 4 individuals. Data are adapted from gene expression profile patterns reported in Buckley et al., 2006. (PDF 38 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buckley, B.A. Acute heat stress and thermal acclimation induce CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta in the goby Gillichthys mirabilis . J Comp Physiol B 181, 773–780 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-011-0572-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-011-0572-4