Abstract
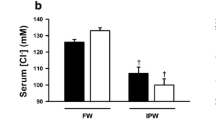
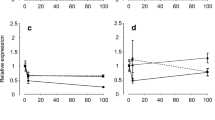
With an emphasis on the tight junction protein occludin, the response of goldfish following abrupt exposure (0–120 h) as well as long-term acclimation (14 and 28 days) to ion-poor water (IPW) was examined. Both abrupt and long-term exposure to IPW lowered serum osmolality, [Na+] and [Cl−], and elevated serum glucose. After abrupt exposure to IPW, gill tissue exhibited a prompt and sustained decrease in Na+–K+–ATPase activity, and a transient increase in occludin expression that returned to control levels by 6 h. Following 14 and 28 days in IPW, gill occludin expression was markedly elevated, while Na+–K+–ATPase activity was only significantly different (elevated) at day 14. Kidney tissue exhibited an elevation in both Na+–K+–ATPase activity and occludin expression after 28 days; however, in the intestine, occludin expression declined at day 14 but did not differ from FW fish at day 28. These studies demonstrate that goldfish can tolerate abrupt as well as sustained exposure to ion-poor surroundings. Data also suggests that occludin may play an adaptive role in fishes acclimated to ion-poor conditions by contributing to the modulation of epithelial barrier properties in ionoregulatory tissues.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagherie-Lachidan M, Wright SI, Kelly SP (2008) Claudin-3 tight junction proteins in Tetraodon nigroviridis: cloning, tissue specific expression and a role in hydromineral balance. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R1638–R1647
Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, González S, Cereijido M, Matter K (1996) Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol 134:1031–1049
Chasiotis H, Kelly SP (2008) Occludin immunolocalization and protein expression in goldfish. J Exp Biol 50:656–658
Cuthbert AW, Maetz J (1972) The effects of calcium and magnesium on sodium fluxes through gills of Carassius auratus, L. J Physiol 221:633–643
Dantzler WH (2003) Regulation of renal proximal and distal tubule transport: sodium, chloride and organic anions. Comp Biochem Physiol A 136:453–478
Feldman GJ, Mullin JM, Ryan MP (2005) Occludin: structure, function and regulation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:883–917
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
González-Marsical L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE (2003) Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:1–44
Jacob WF, Taylor MH (1983) The time course of seawater acclimation in Fundulus heteroclitus L. J Exp Zool 228:33–39
Kelly SP, Peter RE (2006) Prolactin-releasing peptide, food intake and hydromineral balance in goldfish. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:R1474–R1481
Kelly SP, Woo NYS (1999) The response of seabream following abrupt hyposmotic exposure. J Fish Biol 55:732–750
Kelly SP, Wood CM (2001) Effect of cortisol on the physiology of cultured pavement cell epithelia from freshwater trout gills. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281:R811–R820
Kelly SP, Wood CM (2002a) Cultured gill epithelia from freshwater tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): effect of cortisol and homologous serum supplements from stressed and unstressed fish. J Membr Biol 190:29–42
Kelly SP, Wood CM (2002b) Prolactin effects on cultured pavement cell epithelia and pavement cell plus mitochondria-rich cell epithelia from freshwater rainbow trout gills. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:44–56
Kelly SP, Wood CM (2008) Cortisol stimulates calcium transport across cultured gill epithelia from freshwater rainbow trout. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 44:96–104
Leray C, Colin DA, Florentz A (1981) Time course of osmotic adaptation and gill energetics of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.) following abrupt changes in external salinity. J Comp Physiol 144:175–181
Mancera JM, Perez-Figares JM, Fernandez-Llebrez P (1993) Osmoregulatory responses to abrupt salinity changes in the euryhaline gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 106A:245–250
Marshall WS, Grosell M (2005) Ion transport, osmoregulation, and acid–base balance. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 177–210
McCarthy KM, Skare IB, Stankewich MC, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Rogers RA, Lynch RD, Schneeberger EE (1996) Occludin is a functional component of the tight junction. J Cell Sci 109:2287–2298
McCormick SD (1993) Methods for nonlethal gill biopsy and measurement of Na+, K+-ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:656–658
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Nishimura H, Fan Z (2003) Regulation of water movement across vertebrate renal tubules. Comp Biochem Physiol 136A:479–498
Perry SF, Laurent P (1989) Adaptational responses of rainbow trout to lowered external NaCl concentration—contribution of the branchial chloride cell. J Exp Biol 147:147–168
Scott GR, Schulte PM, Wood CM (2006) Plasticity of osmoregulatory function in the killifish intestine: drinking rates, salt and water transport, and gene expression after freshwater transfer. J Exp Biol 209:4040–4050
Tipsmark CK, Baltzegar DA, Ozden O, Grubb BJ, Borski RJ (2008) Salinity regulates claudin mRNA and protein expression in the teleost gill. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R1004–R1014
Usher ML, Talbot C, Eddy FB (1991) Effects of transfer to seawater on growth and feeding in Atlantic salmon smolts (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 94:309–326
Wong V, Gumbiner BM (1997) A synthetic peptide corresponding to the extracellular domain of occludin perturbs the tight junction permeability barrier. J Cell Biol 136:399–409
Wood CM, Laurent P (2003) Na+ versus Cl− transport in the intact killifish after rapid salinity transfer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1618:106–119
Zall DM, Fisher D, Garner MD (1956) Photometric determination of chlorides in water. Anal Chem 28:1665–1678
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSERC Discovery Grants and CFI New Opportunities Funds to SPK. All procedures conformed to the guidelines of the Canadian Council for Animal Care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. V. Carey.
Helen Chasiotis and Jennifer C. Effendi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chasiotis, H., Effendi, J.C. & Kelly, S.P. Occludin expression in goldfish held in ion-poor water. J Comp Physiol B 179, 145–154 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-008-0297-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-008-0297-1