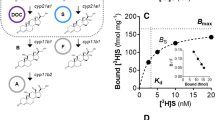
Abstract
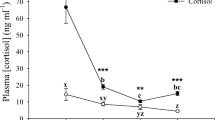
The objectives of this study were to characterize the pattern of pulsatile urea excretion in the gulf toadfish in the wake of exogenous cortisol loading and to determine the receptors involved in the regulation of this mechanism. Toadfish were fitted with indwelling arterial catheters and were infused with isosmotic NaCl for 48 h after which fish were treated with cortisol alone, cortisol+peanut oil, cortisol+RU486 (a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist) or cortisol+spironolactone (a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist). Upon cortisol loading, fish treated with cortisol alone, cortisol+oil or cortisol+spironolactone experienced a two- to threefold reduction in pulsatile urea excretion. This reduction was due to a decrease in urea pulse size with no effect on pulse frequency compared to values measured during the control NaCl infusion period. In addition, these fish showed an increase in plasma urea concentrations upon treatment. These apparent effects of cortisol treatment were abolished in fish treated with cortisol+RU486. In contrast, these fish showed an increase in pulsatile urea excretion mediated by a twofold increase in pulse size with no change in frequency. Likewise, fish treated with cortisol+RU486 showed a significant decrease in plasma urea concentrations over the course of the experiment. The findings of this study indicate that high levels of cortisol reduce pulsatile urea excretion by decreasing pulse size. In addition, it appears that glucocorticoid receptors and not mineralocorticoid receptors are involved in the regulation of the toadfish pulsatile urea excretion mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertagna X, Bertagna C, Luton J, Husson J, Girad F (1984) The new steroid analog RU486 inhibits glucocorticoid action in man. J Clin EndocrinoI Metab 59:25–28
Borski RJ, Helms LM, Richman NH III, Grau EG (1991) Cortisol rapidly reduces prolactin release and cAMP and 45Ca2+ accumulation in the cichlid fish pituitary in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:2758–2762
Borski RJ, Hyde GN, Fruchtman S, Wellington ST (2001) Cortisol suppresses prolactin release through a non-genomic mechanism involving interactions with the plasma membrane. Comp Biochem Physiol 129B:533–541
Borski RJ, Hyde GN, Fruchtman S (2002) Signal transduction mechanisms mediating rapid, nongenomic effects of cortisol an prolactin release. Steroids 67:539–548
Brown SB, Eales JG, Hara TJ (1986) A protocol for estimation of cortisol plasma clearance in acid-exposed rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Gen Comp Endocrinol 62:493–502
Brown SB, MacLatchy DL, Hara TJ, Eales JG (1989) Effects of low ambient pH and aluminum an plasma kinetics of cortisol, T3 and T4 in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Can J Zool 68:1537–1543
Butler DG (1973) Effect of hypophysectomy an renal function in the freshwater North American eel (Anguilla rostrata LeSueur). Gen Comp Endocrinol 20:125–136
Chandrashekar V, Steger RW, Batike A, Fadden CT, Kienast SG (1991) Influence of diabetes on the gonadotropin response to the negative feedback effect of testosterone and hypothalamic neurotransmitter tumover in adult make rats. Neuroendocrinology 54:30–35
Chaouloff F (1993) Physiopharmacological interactions between stress hormones and central serotonergic systems. Brain Res Rev 18:1–32
Christensen LJ, Korsgård B, Bjerregård P (1999) The effect of 4-nonylphenol on the synthesis of vitellogenin in the flounder Platichthys flesus. Aquat Toxicol 46:211–219
Christowitz D, Matteyse FJ, Balinsky JB (1981) Dietary and hormonal regulation of urea cycle enzymes in rat liver. Enzyme 26:113–121
Colombe L, Fostier A, Bury N, Pakdel F, Guiguen Y (2000) A mineralocorticoid-like receptor in the rainbow trout, Oncarhynchus mykiss: cloning and characterization of its steroid binding domain. Steroids 65:319–328
Delyani JA (2000) Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: the evolution of utility and pharmacology. Kidney Int 57:1408–1411
Gaillard RC, Paffet D, Riondel AM, Saurat J (1985) RU486 inhibits peripheral effects of glucocorticoids in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:863–865
Grantham JJ, Burg MB (1966) Effect of cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol 211:255–259
Grote H, loannou I, Voigt J, Sekeris CE (1993) Localization of the glucocorticoid receptor in rat liver cells-evidence for plasma membrane bound receptor. Int J Biochem 25:1593–1599
Healy DL, Chrousos GP, Schulte HM, Williams RF, Gold PW, Baulieu EE, Hodgen GD (1983) Pituitary and adrenal responses to the anti-progesterone and anti-glucocorticoid steroid RU486 in primates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:863–865
Hopkins TE, Wood CM, Walsh PJ (1995) Interactions of cortisol and nitrogen metabolism in the ureogenic gulf toadfish Opsanus beta. J Exp Biol 198:2229–2235
Höglund E, Balm PHM, Winberg S (2002) Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of 5-HTIA receptors an adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol secretion in an teleost fish, the Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Neurosci Lett 324:193–196
Inoue T, Terris 7, Ecelbarger C, Chou CL, Nielsen S, Knepper MA (1999) Vasopressin regulates apical targeting of aquaporin-2 but not of UT1 urea transporter in renal collecting duct. Am J Physiol 276:F559–F566
Ivancic I, Degobbis D (1984) An optimal manual procedure for ammonia analysis in natural waters by the indophenol blue method. Water Res IB:1143–1147
Knepper MA, Danielson RA, Saidel GM, Johnston KH (1975) Effects of dietary protein restriction and glucocorticoid administration an urea excretion in rats. Kidney Int 8:303–315
McDonald MD, Walsh PJ (2004) 5-HT2-like receptors are involved in triggering pulsatile urea excretion in the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. J Exp Biol 207:2003–2010
McDonald MD, Wood CM (2004) The effect of chronic cortisol elevation an urea metabolism and excretion in the rainbow traut (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Comp Physiol 174B:71–81
McDonald MD, Wood CM, Wang Y, Walsh PJ (2000) Differential branchial and renal handling of urea, acetamide and thiourea in the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta: evidence for two transporters. J Exp Biol 203:1027–1037
McDonald MD, Grosell M, Wood CM, Walsh PJ (2003) Branchial and renal handling of urea in the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta: the effect of exogenous urea loading. Comp Biochem Physiol 134A:763–776
Mommsen TP, Danulat E, Walsh PJ (1992) Metabolic actions of glucagon and dexamethasone in liver of the ureogenic teleost Opsanus beta. Gen Comp Endocrinol 85:316–326
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Naruse M, Klein JD, Ashkar ZM, Jacobs JD, Sands JM (1997) Glucocorticoids downregulate the vasopressin-regulated urea transporter in rat terminal inner medullary collecting ducts. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:5I7–523
Nemenyi P, Dixon SK, White NB, Hedstrom ML (1977) Statistics from scratch. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Oppenheimer JH, Gurpide, E (1979) Quantitation of the production, distrubution and interconversion of homornes. In: DeGroot LJ (ed) Endocrinology, vol 3. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 2029–2036
Øverli O, Harris CA, Winberg S (1999) Short-term effects of fights for social dominance and the establishment of dominant-subordinate relationships an brain monoamines and cortisol in rainbow trout. Brain Behav Evol 54:263–275
Part P, Wood CM, Gilmour KM, Perry SF, Laurent P, Zadunaisky J, Walsh PJ (1999) Urea and water permeability in the ureotelic gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta). J Exp Zool 283:1–12
Peng T, Sands JM, Bagnasco SM (2002) GIucocorticoids inhibit transcription and expression of the UT-A urea transporter gene. Am J Physiol 282:F853–F858
Perry SF, Gilmour KM, Wood CM, Part P, Laurent P, Walsh PJ (1998) The effects of arginine vasotocin and catecholamines an nitrogen excretion and the cardio-respiratory physiology of the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. J Comp Physiol 168B:461–472
Rahmatullah M, Boyde TR (1980) Improvements in the determination of urea using diacetyl monoxime; methods with and without deproteination. Clin Chim Acta 107:3–9
Sands JM (1999) Regulation of renal urea transporters. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:635–646
Shih YL, Chou S, Chi CW, Tchen TT, Lo SJ (1990) Tropic effect of dexamethasone an goldfish melanocytoma cells: induction of calcium-dependent but protein synthesis dependent changes. Life Sci 47:313–318
Sloman KA, Desforges PR, Gilmour KM (2001) Evidence for a mineralocorticoid-like receptor linked to branchial chloride cell proliferation in freshwater rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 204:3953–3961
Smith CP, Heitz MJ, Wood CM, Walsh PJ (1998) Molecular identification of a gulftoadfish (Opsanus beta) urea transporter. J Physiol (Lond) 511:33P
Smith CP, Rousselet G (2001) Facilitative urea transporters. J Membr Biol 183:1–14
Star RA, Nonoguchi H, Balaban R, Knepper MA (1988) Calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate as second messengers for vasopressin in the rat inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest 81:1879–1888
Stoskopf MK (1993) Fish medicine. Saunders, Phliladelphia
Sunny F, Lakshmy PS, Oommen 0V (2002) Rapid action of cortisol and testosterone on lipogenic enzymes in a freshwater fish Oreochromis mossambicus: short-term in vivo and in vitro study. Comp Biochem Physiol 131B:297–304
Sunny F, Oommen OV (2001) Rapid action of glucocorticoids on branchial ATPase activity in Oreochromis mossambicus: an in vivo and in vitro study. Comp Biochem Physiol 130B:323–330
Vijayan MM, Leatherland JF (1989) Cortisol-induced changes in plasma glucose, protein, and thyroid hormone levels, and Iiver glycogen content of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch Walbaum). Can J Zool 67:2746–2750
Vijayan MM, Mommsen TP, Glemet HC, Moon TW (1996) Metabolic effects of cortisol treatment in a marine teleost, the sea raven. J Exp Biol 199:1509–1514
Walsh PJ (1987) Lactate uptake by toadfish hepatocytes: passive diffusion is sufficient. J Exp Biol 130:295–304
Walsh P, Milligan C (1995) Effects of feeding and confinement on nitrogen metabolism and excretion in the gulf toadfish Opsanus beta. J Exp Biol 198:1559–1566
Walsh PJ, Danulat EM, Mommsen TP (1990) Variation in urea excretion in the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. Mar Biol 106:323–328
Walsh P, Tucker B, Hopkins T (1994) Effects of confinement/crowding on ureogenesis in the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. J Exp Biol 191:195–206
Walsh PJ, Heitz MJ, Campbell CE, Cooper GJ, Medina M, Wang YS, Goss GG, Vincek V, Wood CM, Smith CP (2000) Molecular characterization of a urea transporter in the gill of the gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta). J Exp Biol 203:2357–2364
Winberg S, Nilsson A, Hylland P, Soderstom V, Nilsson GE (1997) Serotonin as a regulator of hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal activity in teleost fish. Neurosci Lett 230:113–116
Wood C, Hopkins T, Hogstrand C, Walsh P (1995) Pulsatile urea excretion in the ureagenic toadfish Opsanus beta: an analysis of rates and routes. J Exp Biol 198:1729–1741
Wood C, Hopkins T, Walsh P (1997) Pulsatile urea excretion in the toadfish (Opsanus beta) is due to a pulsatile excretion mechanism, not a pulsatile production mechanism. J Exp Biol 200:1039–1046
Wood CM, Gilmour KM, Perry SF, Part P, Walsh PJ (1998) Pulsatile urea excretion in gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta): evidence for activation of a specific facilitated diffusion transport system. J Exp Biol 201:805–817
Wood CM, Warne M, Wang Y, McDonald MD, Balment RJ, Laurent P, Walsh PJ (2001) Do circulating plasma AVT and/or cortisol levels control pulsatile urea excretion in the gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta)? Comp Biochem Physiol 129A:859–872
Wood CM, McDonald MD, Sundin L, Laurent P, Walsh PJ (2003) Pulsatile urea excretion in the gulf toadfish: mechanisms and controls. Comp Biochem Physiol 136B:667–684
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an OGS (CANADA) scholarship awarded to M.D.M., an NSERC (CANADA) basic discovery grant awarded to C.M.W., an NSF (USA) research grant (IBN-0090355) to P.J.W. and an NIEH Marine and Freshwater Biomedical Sciences Center Grant (ES 05705) to the University of Miami. Sincere thanks to Jimbo Luznar and his boat captains for their supply of toadfish. C.M.W. is supported by the Canada Research Chair program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, M.D., Wood, C.M., Grosell, M. et al. Glucocorticoid receptors are involved in the regulation of pulsatile urea excretion in toadfish. J Comp Physiol B 174, 649–658 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-004-0456-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-004-0456-y