Abstract
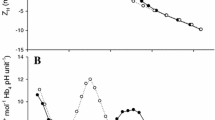
Haemoglobin function and respiratory status of sub-adult sharks, Heterodontus portusjacksoni was investigated for up to 1 week following transfer from 100% to either 75% or 50% seawater. Metabolic rates were unusually low and arterial–venous differences in blood O2 small. Haemodilution from osmotic inflow lowered haematocrit and reduced blood O2 content by up to 50%. There was no change in O2 consumption rate, blood O2 partial pressure, cardiac output, or the arterial-venous O2 content difference, and thus O2 delivery was maintained. Ventilation was acutely elevated but returned to normal within 24 h. The O2 delivery to the tissues was facilitated by decreased blood O2-affinity that could not be simply ascribed to changes in the osmolyte concentration. The Hb was unaffected by changes in intra-erythrocyte fluid urea or trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) but was sensitive to changes in NaCl. The Bohr shifts in whole blood were low and there was little role for pH in modulating O2 transport. Venous Hb saturation remained close to 65%, at the steepest part of the in vivo O2 equilibrium curve, such that O2 unloading could be facilitated by small reductions in pressure without increasing cardiac or ventilatory work. H. portusjacksoni tolerated 50% seawater for at least 1 month, but there was little evidence of respiratory responses being adaptive which instead appeared to be consequential on changes in osmotic and ionic status.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a–v :
-
arterial–venous
- CO 2 :
-
CO2 content
- C a O 2 :
-
content of O2 in arterial blood
- C v O 2 :
-
content of O2 in venous blood
- %E :
-
branchial O2 extraction efficiency
- f v :
-
ventilatory frequency
- GTP :
-
guanosine triphosphate
- Hct :
-
haematocrit
- [Hb] :
-
haemoglobin concentration
- ITP :
-
inosine triphosphate
- met[Hb] :
-
methaemoglobin
- \( \dot{M}O_{2} \) :
-
oxygen consumption
- NTP :
-
nucleoside triphosphate
- OEC :
-
oxygen equilibrium curve
- P a O 2 :
-
partial pressure of O2 in arterial blood
- P e O 2 :
-
partial pressure of expired O2
- P i O 2 :
-
partial pressure of inspired O2
- P in O 2 :
-
inflow partial pressure of O2
- PO 2 :
-
partial pressure of O2
- P out O 2 :
-
outflow partial pressure of O2
- pH a :
-
arterial blood pH
- pH pl :
-
whole blood pH
- PV :
-
plasma volume
- P v CO 2 :
-
partial pressure of CO2in venous blood
- P v O 2 :
-
partial pressure of O2in venous blood
- \( \dot{Q} \) :
-
cardiac output
- SW :
-
seawater
- TMAO :
-
trimethylamine-N-oxide
- \( \dot{V} \) :
-
ventilation volume
References
Baldwin J, Wells RMG (1990) Oxygen transport potential in tropical elasmobranchs from the Great Barrier Reef: relationship between haematology and blood viscosity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 144:145–155
Birchard GF (1997) Optimal hematocrit: theory, regulation and implications. Am Zool 37:65–72
Bonaventura J, Bonaventura C, Sullivan B (1974a) Hemoglobin of the electric Atlantic torpedo, Torpedo nobiliana: a cooperative hemoglobin without Bohr effects. Biochim Biophys Acta 371:147–154
Bonaventura J, Bonaventura C, Sullivan B (1974b) Urea tolerance as a molecular adaptation of elasmobranch hemoglobins. Science 186:57–59
Boyd TA, Cha CJ, Forster RP, Goldstein L (1977) Free amino acids in tissues of the skate Dasyatis sabina: effects of environmental dilution. J Exp Zool 199:435–442
Bridges CR, Pelster B, Scheid P (1985) Oxygen binding in blood of Xenopus laevis (Amphibia) and evidence against Root effect. Resp Physiol 61:125–136
Brunori M, Falcioni G, Fortuna G, Giardnia B (1975) Effect of anions on the oxygen binding properties of the hemoglobin components from trout (Salmo irideus). Arch Biochem Biophys 168:512–519
Burke JD (1974) Hemoglobin stability in bull sharks. Am J Anat 139:425–429
Bushnell PG, Lutz PL, Steffensen JF, Oikari A, Gruber SH (1982) Increases in arterial blood oxygen during exercise in the lemon shark (Negaprion brevirostris). J Comp Physiol 147:41–47
Cameron JN (1986) Principles of physiological measurement. Academic Press, San Diego
Cameron JN, Davis JC (1970) Gas exchange in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) with varying blood oxygen capacity. J Fish Res Bd Can 27:1069–1085
Carlson JK, Parsons GR (1999) Seasonal differences in routine oxygen consumption rates of the bonnethead shark. J Fish Biol 55:876–879
Carlson JK, Parsons GR (2001) The effects of hypoxia on three sympatric shark species: physiological and behavioral responses. Environ Biol Fishes 61:427–433
Chan DKO, Wong TM (1977a) Physiological adjustments to dilution of the external medium in the lip-shark, Hemiscyllium plagiosum (Bennett) I. Size of body compartments and osmolyte composition. J Exp Zool 200:71–84
Chan DKO, Wong TM (1977b) Physiological adjustments to dilution of the external medium in the lip-shark, Hemiscyllium plagiosum (Bennett). III. Oxygen consumption and metabolic rate. J Exp Zool 200:97–102
Claireaux G, Lagardére JP (1999) Influence of temperature, oxygen and salinity on the metabolism of the European sea bass. J Sea Res 42:157–168
Claireaux G, Webber DM, Kerr SR, Boutilier RG (1995) Physiology and behaviour of free-swimming Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) facing fluctuating salinity and oxygen conditions. J Exp Biol 198:61–69
Coates M, Paton BC, Thompson J (1978) High levels of inosine monophosphate in the erythrocytes of elasmobranchs. J Exp Zool 203:331–337
Cooper AR, Morris S (1998a) Osmotic, ionic and haematological response of the Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni, and the common stingaree, Trygonoptera testacea, upon exposure to diluted seawater. Mar Biol 132:29–42
Cooper AR, Morris S (1998b) The blood respiratory, haematological, acid-base and ionic status of the Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni, during recovery from anaesthesia and surgery: a comparison with sampling by direct caudal puncture. Comp Biochem Physiol 119:895–903
Cooper AR, Morris S (2003) Fluid and osmolyte regulation, and acid-base balance of the Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni, upon transfer to diluted seawater. J Comp Physiol B (In press)
Evans DH (1993) Osmotic and ionic regulation. In: Evans DH (ed) The physiology of fishes. CRC, Florida, pp 315–341
Farrell AP (1993) Cardiovascular system. In: Evans DH (ed) The physiology of fishes. CRC, Florida, pp 251–278
Forster RP, Goldstein L (1976) Intracellular osmoregulatory role of amino acids and urea in marine elasmobranchs. Am J Physiol 230:925–931
Fyhn VEH, Sullivan B (1975) Elasmobranch hemoglobins: dimerization and polymerization in various species. Comp Biochem Physiol B 50:119–129
Gallaugher P, Farrell AP (1998) Hematocrit and blood oxygen-carrying capacity. In: Perry SF, Tufts B (eds) Fish respiration. Academic Press, London, pp 185–227
Gallaugher P, Thorarensen H, Farrell AP (1995) Hematocrit in oxygen transport and swimming in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Respir Physiol102:279–292
Goldstein L, Forster RP (1971) Osmoregulation and urea metabolism in the little skate Raja erinacea. Am J Physiol 220:742–746
Gonzalez RJ, McDonald DG (1992) The relationship between oxygen consumption and ion loss in freshwater fish. J Exp Biol 163:317–332
Gonzalez RJ, McDonald DG (1994) The relationship between oxygen uptake and ion loss in from diverse habitats. J Exp Biol 190:95–108
Grigg GC (1970) Use of the first gill slits for water intake in a shark. J Exp Biol 52:569–574
Grigg GC (1974) Respiratory function of blood in fishes. In: Florkin M, Scherr BT (eds) Chemical zoology, Vol VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 331–368
Grigg GC, Read J (1971) Gill function in an elasmobranch. Z Vergl Physiol 73:439–451
Head BP, Graham JB, Shabetai R, Lai NC (2001) Regulation of cardiac function in the horn shark by changes in pericardial fluid volume mediated through the pericardioperitoneal canal Fish Physiol Biochem 24:141–148
Holeton GF, Heisler N (1983) Contribution of net ion transfer mechanisms to the acid-base regulation after exhausting activity in the larger spotted dogfish (Scyliorhinus stellaris). J Exp Biol 103:31–46
Holmes WN, Donaldson EM (1969) Body compartments and distribution of electrolytes. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol I. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–89
Hopkins TE, Cech JJ (2003) The influence of environmental variables on the distribution and abundance of three elasmobranchs in Tomales Bay, California. Environ Biol Fishes 66:279–291
Hughes GM, Wood SC (1974) Respiratory properties of the blood of the thornback ray. Experientia 30:167–168
Jensen FB (1989) Hydrogen-ion equilibria in fish hemoglobins. J Exp Biol 143:225–234
Jensen FB (1991) Multiple strategies in oxygen and carbon dioxide transport by hemoglobin. In: Woakes AJ, Grieshaber MK, Bridges CR (eds) Physiological strategies for gas exchange and metabolism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 55–78
Kaufmann R, Forstner H, Wieser W (1989) Respirometry—methods and approaches. In: Bridges CR, Butler PJ (eds) Techniques in comparative respiratory physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 51–76
Lai NC, Graham JB, Lowell WR (1989) Elevated pericardial pressure and cardiac output in the leopard shark Triakis semifasciata during exercise: the role of the pericardioperitoneal canal. J Exp Biol 147:263–277
Lai NC, Graham JB, Burnett L (1990) Blood respiratory properties and the effect of swimming on blood gas transport in the leopard shark Triakis semifasciata. J Exp Biol 151:161–173
Lai NC, Korsmeyer KE, Katz S, Holts DB, Laughlin LM, Graham JB (1997) Hemodynamics and blood properties of the shortfin Mako shark (Isurus oxyrinchus). Copeia 1997:424–428
Last PR, Stevens JD (1994) Sharks and rays of Australia. CSIRO, Australia, pp 513
Lenfant C, Johansen K (1966) Respiratory function in the elasmobranch Squalus suckleyi G. Respir Physiol 1:13–29
Lowe TE, Wells RMG, Baldwin J (1995). Absences of regulated blood-oxygen transport in response to strenuous exercise by the shovelnosed ray, Rhinobatos typus. Mar Freshw Res 46:441–446
Martin JP, Bonaventura J, Fyhn HJ, Fyhn UNH, Garlick RL, Powers DA (1979) Structural and functional studies of hemoglobins isolated from Amazon stingrays of the genus Potamotrygon. Comp Biochem Physiol 62:131–138
Maxime V, Peyraud-Waitzenegger M, Claireaux G, Peyraud C (1990) Effects of rapid transfer from sea water to fresh water on respiratory variables, blood acid-base status and O2 affinity of hemoglobin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Comp Physiol 160:31–39
McLaughlin RH, O’Gower AK (1971) Life history and underwater studies of a heterodont shark. Ecol Monogr 41:271–289
McMahon BR, Wilkens JL (1983) Ventilation, perfusion and oxygen uptake. In: Mantel L (ed) Biology of the Crustacea vol 5. Internal anatomy and physiological regulation. Academic Press, New York, pp 289–372
Meloni CJ, Cech JJ, Katzman SM (2002) Effect of brackish salinities on oxygen consumption of bat rays (Myliobatis californica) Copeia 2002:462–465
Miklos P, Katzmana SM, Cech JJ (2003) Effect of temperature on oxygen consumption of the leopard shark, Triakis semifasciata. Environ Biol Fishes 66:15–18
Mumm DP, Atha DH, Riggs A (1978) The hemoglobin of the common sting-ray, Dasyatis sabina: structural and functional properties. Comp Biochem Physiol 60:189–193
Nash AR, Fisher WK, Thompson EOP (1976) Haemoglobins of the shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni II. Amino acid sequence of the α-chain. Aust J Biol Sci 29:73–97
Nikinmaa M (1997) Oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in vertebrate erythrocytes: an evolutionary change in the role of membrane transport. J Exp Biol 200:369–380
Nikinmaa M, Salama A (1998) Oxygen transport in fish. In: Perry SF, Tufts B (eds) Fish respiration. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 141–184
Nilsson S (1986) Control of gill blood flow. In: Nilsson S, Holmgren S (eds) Fish physiolgy: recent advances, Croom Helm, London, pp 87–101
O’Gower AK (1995). Speculations on a spatial memory for the Port Jackson shark (Heterodontus portusjacksoni) (Meyer) (Heterodontidae). Mar Fresh Res 46:861–871
Pang PKT, Griffith RW, Atz JW (1977) Osmoregulation in elasmobranchs. Am Zool 17:365–377
Parsons GR, Carlson JK (1998) Physiological and behavioral responses to hypoxia in the bonnethead shark, Sphyrna tiburo: routine swimming and respiratory regulation. Fish Physiol Biochem 19:189–196
Pennelly RR, Noble RW, Riggs A (1975) Equilibria and ligand binding kinetics of hemoglobins from the sharks, Prionace glauca and Carcharhinus milberti. Comp Biochem Physiol 52:83–87
Perry SF, Gilmour KM (1996) Consequences of catecholamine release on ventilation and blood oxygen transport during hypoxia and hypercapnia in an elasmobranch (Squalus acanthias) and a teleost (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 199:2105–2118
Perry SF, Gilmour KM (2002) Sensing and transfer of respiratory gases at the fish gill. J Exp Zool 293:249–263
Perry SF, McDonald DG (1993) Gas exchange. In: Evans DHG (ed) The physiology of fishes. CRC, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 251–278
Piiper J, Schumann D (1967) Efficiency of O2 exchange in the gills of the dogfish, Scyliorhinus stellaris. Respir Physiol 2:135–148
Piiper J, Meyer M, Drees F (1972) Hydrogen ion balance in the elasmobranch Scyliorhinus stellaris after exhausting activity. Respir Physiol 16:290–303
Piiper J, Meyer M, Worth H, Willmer H (1977) Respiration and circulation during swimming activity in the dogfish Scyliorhinus stellaris. Respir Physiol 30:221–239
Powers DA, Fyhn HJ, Fyhn UEH, Martin JP, Garlick RL, Wood SC (1979) A comparative study of the oxygen equilibria of blood from 40 genera of Amazonian fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol 62:67–85
Randall DJ, Baumgarten D, Malyusz M (1972) The relationship between gas and ion transfer across the gills of fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol 41:629–637
Rao GMM (1968) Oxygen consumption of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to activity and salinity. Can J Zool 46:781–786
Robin H, Harley JD (1964) Practical applications of the simultaneous determination of oxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin concentration. Aust Ann Med 13:313–319
Routley MH, Nilsson GE, Renshaw GMC (2002) Exposure to hypoxia primes the respiratory and metabolic responses of the epaulette shark to progressive hypoxia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 131:313–321
Satchell GH (1991) Physiology and form of fish circulation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Scholnick DA, Mangum CP (1991) Sensitivity of hemoglobins to intracellular effectors: primitive and derived features. J Exp Zool 259:32–42
Shuttleworth TJ (1988) Salt and water balance—extrarenal mechanisms. In: Shuttleworth TJ (ed) Physiology of elasmobranch fishes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–199
Sick H, Gersonde K (1969) Method of continuous registration of O2-binding curves of hemoproteins by means of a diffusion chamber. Anat Biochem 32:362–376
Sulikowski JA, Maginniss LA (2001) Effects of environmental dilution on body fluid regulation in the yellow stingray, Urolophus jamaicensis. Comp Biochem Physiol 128:223–232
Tetens V, Wells RMG (1984) Oxygen binding properties of blood and hemoglobin solutions in the carpet shark (Cephaloscyllium isabella): roles of ATP and urea. Comp Biochem Physiol 79:165–168
Toulmond A, Dejours P, Truchot JP (1982) Cutaneous O2 and CO2 exchanges in the dogfish, Scyliorhinus canicula. Respir Physiol 48:169–181
Tufts BL, Perry SF (1998) Carbon dioxide transport and excretion. In: Perry SF, Tufts B (eds) Fish respiration. Academic Press, London, pp 229–282
Weber RE (1983) TMAO-independence of oxygen affinity and its urea and ATP sensitivities in an elasmobranch haemoglobin. J Exp Zool 228:551–554
Weber RE, Wells RMG, Rossetti JE (1983a) Allosteric interactions governing oxygen equilibria in the haemoglobin system of the spiny dogfish, Squalus acanthias. J Exp Biol 103:109–120
Weber RE, Wells RMG, Tougaard S (1983b) Antagonistic effect of urea on oxygenation-linked binding of ATP in an elasmobranch hemoglobin. Life Sci 32:2157–2161
Wells RMG (1999) Haemoglobin function in aquatic animals: molecular adaptations to environmental challenge. Mar Freshwater Res 50:933–939
Wells RMG, Weber RE (1983) Oxygenational properties and phosphorylated metabolic intermediates in blood erythrocytes of the dogfish, Squalus acanthias. J Exp Biol 103:95–108
Wells RMG, Weber RE (1989) The measurement of oxygen affinity in blood and haemoglobin solutions. In: Bridges CR, Butler PJ (eds) Techniques in comparative respiratory physiology: an experimental approach. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 279–303
Wells RMG, Baldwin J, Ryder JM (1992) Respiratory-function and nucleotide composition of erythrocytes from tropical elasmobranchs. Comp Biochem Physiol A 103:157–162
Withers PC, Morrison G, Guppy M (1994a) Buoyancy role of urea and TMAO in an elasmobranch fish, the Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni. Physiol Zoo l 67:693–705
Withers PC, Morrison G, Hefter GT, Pang TS (1994b) Role of urea and methylamines in buoyancy of elasmobranchs. J Exp Biol 188:175–189
Wood CM, McMahon BR, McDonald DG (1979) Respiratory, ventilatory, and cardiovascular responses to experimental anaemia in the starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus. J Exp Biol 82:139–162
Wyman J (1964) Linked functions and reciprocal effects in hemoglobin: a second look. Adv Protein Chem 19:223–286
Yancey PH, Somero GN (1978) Urea-requiring lactate dehydrogenases of marine elasmobranch fishes. J Comp Physiol 125:135–141
Yancey PH, Somero GN (1979) Counteraction of urea destabilization of protein structure by methylamine osmoregulatory compounds of elasmobranch fishes. Biochem J 183:317–323
Yancey PH, Somero GN (1980) Methylamine osmoregulatory solutes of elasmobranch fishes counteract urea inhibition of enzymes. J Exp Zool 212:205–213
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to A. Broadhurst for the collection of the sharks and to the Darling Harbour aquarium for facilities. This work was carried while A.R.C. was in receipt of an Australian Research Council Post-Graduate Award. The work was carried out under animal ethics approval LO4/9-94/3/1079 and supported by funds from Morlab and Natural Events (http://www.natural-events.com).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, A.R., Morris, S. Haemoglobin function and respiratory status of the Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni, in response to lowered salinity. J Comp Physiol B 174, 223–236 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-003-0405-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-003-0405-1