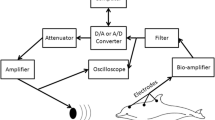
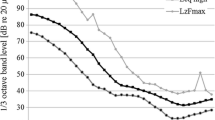
Abstract
During echolocation, toothed whales produce ultrasonic clicks at extremely rapid rates and listen for the returning echoes. The auditory brainstem response (ABR) duration was evaluated in terms of latency between single peaks: 5.5 ms (from peak I to VII), 3.4 ms (I–VI), and 1.4 ms (II–IV). In comparison to the killer whale and the bottlenose dolphin, the ABR of the harbour porpoise has shorter intervals between the peaks and consequently a shorter ABR duration. This indicates that the ABR duration and peak latencies are possibly related to the relative size of the auditory structures of the central nervous system and thus to the animal’s size. The ABR to a sinusoidal amplitude modulated stimulus at 125 kHz (sensitivity threshold 63 dB re 1 μPa rms) was evaluated to determine the modulation rate transfer function of a harbour porpoise. The ABR showed distinct envelope following responses up to a modulation rate of 1,900 Hz. The corresponding calculated equivalent rectangular duration of 263 μs indicates a good temporal resolution in the harbour porpoise auditory system similar to the one for the bottlenose dolphin. The results explain how the harbour porpoise can follow clicks and echoes during echolocation with very short inter click intervals.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- EFR:
-
Envelope following response
- ERB:
-
Equivalent rectangular bandwidth
- ERD:
-
Equivalent rectangular duration
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- ICI:
-
Inter click interval
- MRTF:
-
Modulation rate transfer function
- rms:
-
Root-mean-square
- SAM:
-
Sinusoidal amplitude modulated
References
Andersen S (1970) Auditory sensitivity of the harbour porpoise Phocoena phocoena. In: Pilleri G (ed) Investigations of Cetacea, vol 2. University of Bern, Switzerland, pp 255–260
Au WWL (1988) Sonar target detection and recognition by odontocetes. In: Nachtigall PE, Moore P (eds) Animal sonar: Processes and Performance. Plenum Press, USA, pp 451–465
Au WWL (1993) The sonar of dolphins. Springer, New York
Bullock T, Grinnell A, Ikezono E, Kameda K, Katsuki Y, Nomoto M, Sato O, Suga N, Yanagisawa K (1968) Electrophysiological studies of central auditory mechanisms in cetaceans. J Comp Physiol A 59(2):117–156
Cook MLH, Varela RA, Goldstein JD, McCulloch SD, Bossart GD, Finneran JJ, Houser D, Mann DA (2006) Beaked whale auditory evoked potential hearing measurements. J Comp Physiol A 192(5):489–495. doi:10.1007/s00359-005-0086-1
Dolphin WF (2000) Electrophysiological measures of auditory processing in odontocetes. In: Au WWL, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Hearing by whales and dolphins, vol 12. Springer handbook of auditory research. Springer, New York, pp 294–329
Dolphin W, Mountain D (1992) The envelope following response: scalp potentials elicited in the Mongolian gerbil using sinusoidally AM acoustic signals. Hear Res 58(1):70–78
Dolphin WF, Au WWL, Nachtigall PE, Pawloski J (1995) Modulation rate transfer-functions to low-frequency carriers in 3 species of Cetaceans. J Comp Physiol A 177(2):235–245
Finneran JJ, London HR, Houser DS (2007) Modulation rate transfer functions in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) with normal hearing and high-frequency hearing loss. J Comp Physiol A 193(8):835–843
Houser DS, Finneran JJ (2006) A comparison of underwater hearing sensitivity in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) determined by electrophysiological and behavioral methods. J Acoust Soc Am 120(3):1713–1722. doi:10.1121/1.2229286
Houser DS, Gomez-Rubio A, Finneran JJ (2008) Evoked potential audiometry of 13 Pacific bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus gilli). Marine Mamm Sci 24(1):28–41
Kastelein RA, Brunskoek P, Hagedoom M, Au WWL, de Haan D (2002) Audiogram of a harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) measured with narrow-band frequency-modulated signals. J Acoust Soc Am 112(1):334–344
Ketten D (2000) Cetacean ears. In: Au WWL, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Hearing by whales and dolphins, vol 12. Springer handbook of auditory research. Springer, New York, pp 43–108
Kloepper LN, Nachtigall PE, Gisiner R, Breese M (2010) Decreased echolocation performance following high-frequency hearing loss in the false killer whale (Pseudorca crassidens). J Exp Biol 213:3717–3722
Kuwada S, Batra R, Maher VL (1986) Scalp potentials of normal and hearing-impaired subjects in response to sinusoidally amplitude-modulated tones. Hear Res 21(2):179–192
Møhl B, Andersen S (1973) Echolocation: high-frequency component in the click of the harbour porpoise (Phocoena ph. L.). J Acoust Soc Am 54:1368–1372
Mooney TA, Nachtigall PE, Yuen MML (2006) Temporal resolution of the Risso’s dolphin, Grampus griseus, auditory system. J Comp Physiol A 192:373–380
Mooney TA, Nachtigall PE, Taylor KA, Rasmussen MH, Miller LA (2009) Auditory temporal resolution of a wild white-beaked dolphin (Lagenorhynchus albirostris). J Comp Physiol A 195(4):375–384. doi:10.1007/s00359-009-0415-x
Mooney TA, Li S, Ketten DR, Wang K, Wang D (2011) Auditory temporal resolution and evoked responses to pulsed sounds for the Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis). J Comp Physiol A 197:1149–1158
Moore PW, Hall RW, Friedl WA, Nachtigall PE (1984) The critical interval in dolphin echolocation: what is it? J Acoust Soc Am 76(1):314–317
Moore BCJ, Glasberg BR, Plack CJ, Biswas AK (1988) The shape of the ears temporal window. J Acoust Soc Am 83(3):1102–1116
Mulsow J, Reichmuth C (2007) Electrophysiological assessment of temporal resolution in pinnipeds. Aqua Mam 33(1):122–131
Nachtigall P, Mooney T, Taylor K, Miller L, Rasmussen M, Akamatsu T, Teilmann J, Linnenschmidt M, Vikingsson G (2008) Shipboard measurements of the hearing of the white-beaked dolphin Lagenorhynchus albirostris. J Exp Biol 211(4):642–647
Pacini AF, Nachtigall PE, Kloepper LN, Linnenschmidt M, Sogorb A, Matias S (2010) Audiogram of a formerly stranded long-finned pilot whale (Globicephala melas) measured using auditory evoked potentials. J Exp Biol 213(18):3138–3143. doi:10.1242/jeb.044636
Pacini AF, Nachtigall PE, Quintos CT, Schofield TD, Look DA, Levine GA, Turner JP (2011) Audiogram of a stranded Blainville’s beaked whale (Mesoplodon densirostris) measured using auditory evoked potentials. J Exp Biol 214(14):2409–2415
Popov VV, Supin AY (1990) Auditory brain stem responses in characterization of dolphin hearing. J Comp Physiol A 166(3):385–393
Popov VV, Supin AY (1998) Auditory evoked responses to rhythmic sound pulses in dolphins. J Comp Pysiol A 183:519–524
Popov VV, Supin AY, Wang D, Wang K, Xiao J, Li S (2005) Evoked-potential audiogram of the Yangtze finless porpoise Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis (L). J Acoust Soc Am 117:2728–2731
Ridgway SH, Bullock TH, Carder DA, Seeley RL, Woods D, Galambos R (1981) Auditory brainstem response in dolphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 78:1943–1947
Simmons JA, Fenton MB, Ofarrell MJ (1979) Echolocation and pursuit of prey by bats. Science 203(4375):16–21. doi:10.1126/science.758674
Supin AY, Popov VV (1995a) Temporal resolution in the dolphin’s auditory system revealed by double- click evoked potential study. J Acoust Soc Am 97(4):2586–2593
Supin AY, Popov VV (1995b) Envelope-following response and modulation transfer function in the dolphin’s auditory system. Hear Res 92(1–2):38–46
Supin AY, Popov VV, Mass AM (2001) The sensory physiology of aquatic mammals. Springer, London
Surlykke A, Bojesen O (1996) Integration time for short broad band clicks in echolocating FM-bats (Eptesicus fuscus). J Comp Physiol A 178(2):235–241
Szymanski MD, Supin AY, Bain DE, Henry KR (1998) Killer whale (Orcinus orca) auditory evoked potentials to rhythmic clicks. Marine Mamm Sci 14(4):676–691
Szymanski MD, Bain DE, Kiehl K, Pennington S, Wong S, Henry KR (1999) Killer whale (Orcinus orca) hearing: auditory brainstem response and behavioral audiograms. J Acoust Soc Am 106(2):1134–1141
Urick RJ (1983) Principles of underwater sound. Peninsula Publishing, Los Altos
Vel’min V, Dubrovskiy N (1976) The critical interval of active hearing in dolphins. Sov Phys Acoust 2:351–352
Viemeister NF (1979) Temporal modulation transfer functions based upon modulation thresholds. J Acoust Soc Am 66(5):1364–1380
Villadsgaard A, Wahlberg M, Tougaard J (2007) Echolocation signals of wild harbour porpoises, Phocoena phocoena. J Exp Biol 210(1):56–64. doi:10.1242/jeb.02618
Wiegrebe L, Schmidt S (1996) Temporal integration in the echolocating bat, Megaderma lyra. Hear Res 102(1–2):35–42
Yuen MML, Nachtigall PE, Breese M, Supin AY (2005) Behavioral and auditory evoked potential audiograms of a false killer whale (Pseudorca crassidens). J Acoust Soc Am 118(4):2688–2695. doi:10.1121/1.2010350
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research, the Faculty of Science at the University of Southern Denmark, the Graduate School on Sense Organs, Nerve Systems, Behaviour, and Communication, and Fjord&Bælt. The animals at Fjord&Bælt are kept under the permission from the Danish Forest and Nature Agency (J. nr. SN 343/FY-0014 and 1996-3446-0021). The experiments were conducted in agreement with all current Danish laws and animal care was provided according to permit nr. DK-7-0001008. We thank Jakob Tougaard and Paul Nachtigall for detailed comments that improved earlier versions of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linnenschmidt, M., Wahlberg, M. & Damsgaard Hansen, J. The modulation rate transfer function of a harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J Comp Physiol A 199, 115–126 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-012-0772-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-012-0772-8