Abstract.
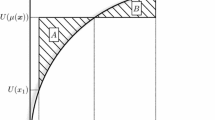
We introduce a new centrist or intermediate inequality concept, between the usual relative and absolute notions, which is shown to be a variant of the α-ray invariant inequality measures in Pfingsten and Seidl (1997). We say that distributions x and y have the same (x, π)-inequality if the total income difference between them is allocated among the individuals as follows: 100π% preserving income shares in x, and 100(1−π)% in equal absolute amounts. This notion can be made as operational as current standard methods in Shorrocks (1983).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 May 1998/Accepted: 25 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
del Río, C., Ruiz-Castillo, J. Intermediate inequality and welfare. Soc Choice Welfare 17, 223–239 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003550050017
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003550050017