Abstract
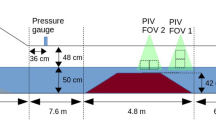
A submerged hydrofoil generated large steady breaking waves of 0.3 m and 0.4 m height in a circulating water channel. We measured water fraction in the breakers with conductivity probes. We observed the radar cross-section of the breakers at X-band with a pulsed step-frequency instrumentation radar with high spatial resolution in the downstream direction. The normalized radar cross-section increases with increasing elevation angle of observation for both vertical and horizontal polarization. This variation is consistent with a simple interpretation of the breaking wave as a diffuse (Lambertian) surface. However, the observed sizes and shapes of fluid elements in the breakers clearly show that construction of a theory for electromagnetic scattering from first principles will be challenging. We also obtained the velocity spectrum of the scattering features within the breakers. This spectrum indicates that slower moving small liquid elements rather than the faster moving large disturbances are responsible for most of the electromagnetic scattering.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 January 1999/Accepted: 7 August 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coakley, D., Haldeman, P., Morgan, D. et al. Electromagnetic scattering from large steady breaking waves. Experiments in Fluids 30, 479–487 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000220