Abstract
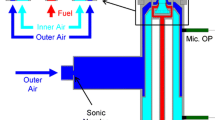
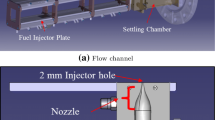
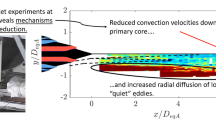
An experimental investigation explored the effects of varying reactant concentration and Reynolds number on the formation of product in a jet of air/N2/HCl flowing into a co-issuing stream of air/NH3. Turbulent mixing resulted in the production of NH4Cl particles by a chemical reaction with negligible heat release. Laser light was elastically scattered in the transition regime between Rayleigh and Mie scattering from the particles. Scattered light intensity served as an indicator of particle mass concentration. Radial profiles of mean and root mean square concentrations were obtained in the self-similar far field region of the jet. The stoichiometric mixture fraction was varied by varying the concentration of NH3 in the co-flowing stream. It was found that the “flame” length decreased with increasing stoichiometric mixture fraction, and was independent of Reynolds number. The overall amount of product decreased as the stoichiometric mixture fraction was increased from 0.06 to 0.27, while the amount of limiting reactant was the same in both cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 April 1998/Accepted: 16 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenkins, T., Kennedy, I. Measurements of aerosol product in an axisymmetric co-flow jet. Experiments in Fluids 29, 532–544 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000121
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000121