Abstract
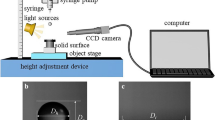
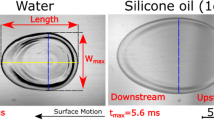
The spreading behavior of droplets on solid surfaces in air has been widely investigated; however, relatively few studies are conducted on the spreading of oil droplets over solid surfaces in aqueous environments, and furthermore, the differences in the oil droplet spreading behavior in the two media environments have not been specifically reported. In this work, the spreading dynamics behavior of a millimeter-sized oleic acid droplet (referred to as oil droplet) on a highly hydrophilic substrate (glass slide) in air and deionized water environments was studied in terms of dynamic contact angle by using a high-speed imaging technology, and their spreading behavior differences were revealed. Results showed that the spreading of an oil droplet on the glass slide in air could be divided into three stages: the early linear rapid spreading stage dominated by inertial force, the intermediate exponential slow spreading stage dominated by viscous forces and the long-term spreading stage tending to the quasi-equilibrium state. In contrast, the spreading process of oil droplets on glass slides in deionized water consisted of two sub-processes: the initial linear slow spreading process and the long-term spreading process tending to the equilibrium state. It is clear that the spreading behavior of oil droplets on glass slides in air and deionized water was different, and their differences were mainly due to the presence of the hydration layer on the glass slide surface and the action of the fluid around the oil droplet in deionized water. These findings can provide guidance for the recovery of crude oil in geological reservoirs and help to understand the spreading mechanism of oil droplets on solid surfaces.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjmandi-Tash O, Kovalchuk NM, Trybala A, Kuchin IV, Starov V (2017) Kinetics of wetting and spreading of droplets over various substrates. Langmuir 33:4367–4385. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04094
Atilhan M, Aparicio S (2021) Review on chemical enhanced oil recovery: utilization of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. J Petrol Sci Eng 205:108746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108746
Atta DY, Negash BM, Yekeen N, Habte AD (2021) A state-of-the-art review on the application of natural surfactants in enhanced oil recovery. J Mol Liq 321:114888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114888
Biance A, Clanet C, Quéré D (2004) First steps in the spreading of a liquid droplet. Phys Rev E 69:016301. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.69.016301
Blake TD, Haynes JM (1969) Kinetics of liquid/liquid displacement. J Colloid Interf Sci 30:421–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(69)90411-1
Bonn D, Eggers J, Indekeu J, Meunier J, Rolley E (2009) Wetting and spreading. Rev Mod Phys 81:739–805. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.739
Chen L, Bonaccurso E (2014) Effects of surface wettability and liquid viscosity on the dynamic wetting of individual drops. Phys Rev E 90:22401. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.90.022401
Cox RG (1986) The dynamics of the spreading of liquids on a solid surface. Part 1. Viscous Flow J Fluid Mech 168:195–220. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112086000344
de Ruijter MJ, De Coninck J, Oshanin G (1999) Droplet spreading: partial wetting regime revisited. Langmuir 15:2209–2216. https://doi.org/10.1021/la971301y
Ding F, Gao M (2021) Pore wettability for enhanced oil recovery, contaminant adsorption and oil/water separation: a review. Adv Colloid Interfac 289:102377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102377
Fu J, Chen K, Wang H, Guo C, Liang W (2012) Recovering molybdenite from ultrafine waste tailings by oil agglomerate flotation. Miner Eng 39:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.07.006
Gao Y, Pan L (2021) Understanding the mechanism of froth flotation of molybdenite using oily collectors from a perspective of thinning and rupture of thin liquid film. Miner Eng 163:106805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106805
Gmür TA, Mandal J, Cayer-Barrioz J, Spencer ND (2021) Towards a Polymer-Brush-Based friction modifier for oil. Tribol Lett 69:124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01496-w
Han Y, Yang Z, He L, Luo X, Zhou R, Shi K, Su J (2018) The influences of special wetting surfaces on the dynamic behaviors of underwater oil droplet. Colloid Surf A 543:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.01.049
Izbassarov D, Muradoglu M (2016) Effects of viscoelasticity on drop impact and spreading on a solid surface. Phys Rev Fluids 1:023302. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.1.023302
Jian G, Fernandez CA, Puerto M, Sarathi R, Bonneville A, Biswal SL (2021) Advances and challenges in CO2 foam technologies for enhanced oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs. J Petrol Sci Eng 202:108447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108447
Khojasteh D, Kazerooni M, Salarian S, Kamali R (2016) Droplet impact on superhydrophobic surfaces: A review of recent developments. J Ind Eng Chem 42:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.07.027
Kosior D, Zawala J, Malysa K (2014) Influence of n-octanol on the bubble impact velocity, bouncing and the three phase contact formation at hydrophobic solid surfaces. Colloid Surf A 441:788–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.10.025
Kovalchuk N, Trybala A, Mahdi F, Starov V (2016) Kinetics of spreading of synergetic surfactant mixtures in the case of partial wetting. Colloid Surf A 505:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.11.026
Kovalchuk NM, Barton A, Trybala A, Starov V (2015) Mixtures of catanionic surfactants can be superspreaders: Comparison with trisiloxane superspreader. J Colloid Interf Sci 459:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.08.024
Li Z, Liao K, Liao F, Xiao Q, Jiang F, Zhang X, Liu B, Sun C, Chen G (2016) Wetting and spreading behaviors of nanodroplets: the interplay among substrate hydrophobicity, roughness, and surfactants. J Phys Chem C 120:15209–15215. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b04299
Li C, Xu G, Wang L, Li J, Lu H (2021) Tribological properties of graphene oxide and polyethylene glycol composites under dry friction and oil lubrication conditions. J Appl Polym Sci e51935. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51935
Liao Y, Yang Z, An M, Cao Y, Hao X, Song X, Ren H, Yang A, Chen L (2022) Spreading behavior of dodecane-oleic acid collector mixture in low-rank coal flotation. Fuel 308:122071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122071
Lin Q, Gu G, Wang H, Liu Y, Fu J, Wang C (2018) Flotation mechanisms of molybdenite fines by neutral oils. Int J Min Met Mater 25:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1540-8
Lü Y, Wang Y, Wang S, He L, Ye T (2021) Experimental and theoretical investigation of the spreading behaviors of oil droplets on the surfaces with different wettabilities. Colloid Surf A 620:126467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126467
Lu G, Wang X, Duan Y (2016) A critical review of dynamic wetting by complex fluids: from Newtonian fluids to non-Newtonian fluids and nanofluids. Adv Colloid Interface 236:43–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2016.07.004
Massinon M, Lebeau F (2012) Experimental method for the assessment of agricultural spray retention based on high-speed imaging of drop impact on a synthetic superhydrophobic surface. Biosyst Eng 112:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2012.02.005
Pierre-Louis O (2016) Solid-state wetting at the nanoscale. Prog Cryst Growth Ch 62:177–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2016.04.009
Raiyan A, Mclaughlin TS, Annavarapu RK, Sojoudi H (2018) Effect of superamphiphobic macrotextures on dynamics of viscous liquid droplets. Sci Rep-UK 8:15344. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33656-9
Ramiasa M, Ralston J, Fetzer R, Sedev R (2014) The influence of topography on dynamic wetting. Adv Colloid Interfac 206:275–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.04.005
Ranabothu SR, Karnezis C, Dai LL (2005) Dynamic wetting: hydrodynamic or molecular-kinetic? J Colloid Interf Sci 288:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.02.074
Rasouli S, Rezaei N, Hamedi H, Zendehboudi S, Duan X (2021) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: a comprehensive review. Mater Design 204:109599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109599
Samsonov VM (2011) On computer simulation of droplet spreading. Curr Opin Colloid in 16:303–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2011.03.004
Sedev R (2015) The molecular-kinetic approach to wetting dynamics: achievements and limitations. Adv Colloid Interfac 222:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.09.008
Semenov S, Trybala A, Rubio RG, Kovalchuk N, Starov V, Velarde MG (2014) Simultaneous spreading and evaporation: recent developments. Adv Colloid Interface 206:382–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.08.006
Shi L, Liu Y, Lu H, Meng Y, Hu G, Tian Y (2017) Viscous force retards initial droplet spreading. J Phys Chem C 121:22054–22059. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b06124
Starov VM, Kosvintsev SR, Velarde MG (2000) Spreading of surfactant solutions over hydrophobic substrates. J Colloid Interface Sci 227:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.6851
Su C, Chen W (2021) Thermal behavior on motorized spindle considering bearing thermal deformation under oil-air lubrication. J Manuf Process 72:483–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.10.041
Tanner LH (1979) The spreading of silicone oil drops on horizontal surfaces. J Phys D Appl Phys 12:1473–1484. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/12/9/009
Voinov OV (1976) Hydrodynamics of wetting. Fluid Dynam+ 11:714–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01012963
Wan Ikhsan SN, Yusof N, Aziz F, Ismail AF, Jaafar J, Wan Salleh WN, Misdan N (2021) Superwetting materials for hydrophilic-oleophobic membrane in oily wastewater treatment. J Environ Manage 290:112565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112565
Wang XD, Zhang Y, Lee DJ, Peng XF (2007) Spreading of completely wetting or partially wetting power-law fluid on solid surface. Langmuir 23:9258–9262. https://doi.org/10.1021/la700232y
Wang J, Wu Y, Cao Y, Li G, Liao Y (2020b) Influence of surface roughness on contact angle hysteresis and spreading work. Colloid Polym Sci 298:1107–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04680-x
Wang J, Cao Y, Xing Y, Gui X, Li G (2022) Study on the wetting behavior between oil droplets and kaolinite substrate based on interaction force measurement and high-speed dynamic visualization. Colloid Interface Sci 46:100585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2022.100585
Wang J, Cao Y, Xing Y, Li G, Liao Y, Li S, An M (2020b) Spreading behavior of oil droplets over polytetrafluoroethylene plates in deionized water. J Disper Sci Technol 41:1984–1990. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1645025
Xia Y, Zhang R, Xing Y, Gui X (2019) Improving the adsorption of oily collector on the surface of low-rank coal during flotation using a cationic surfactant: an experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Fuel 235:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.059
Zhao Y (2014) Moving contact line problem: advances and perspectives. Theor Appl Mech Lett 4:34002. https://doi.org/10.1063/2.1403402
Zhu C, Xing Y, Xia Y, Wang Y, Li G, Gui X (2020) Flotation intensification of low-rank coal using a new compound collector. Powder Technol 370:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.05.027
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (U1704252) and Key R & D and popularized project in Henan Province (212102310009) for which the authors express their appreciation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Cao, Y. & Li, G. Experimental study on the spreading dynamics behavior of oil droplets over hydrophilic surfaces in air and water phases. Exp Fluids 63, 50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03400-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03400-1