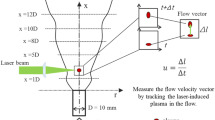
Abstract
High-velocity and rarefied plasma flow has found great application in aerospace science and technology. However, it is difficult to characterize such a flow using traditional methods based on the continuous medium flow hypothesis. With principles similar to those of particle imaging velocimetry, a specific signal imaging velocimetry method is proposed to measure the fluid velocity. Instead of using tracing particles, a specific signal was used as a fingerprint, which facilitated better fluid followability and measurement accuracy. As a verification example, the axial velocity distribution of a plasma plume along the flow direction was experimentally measured. The results agreed well with intrusive electrostatic probe measured values, which shows that SSIV has a great potential for fast and two-dimensional velocity measurements in similar flows. Considering the abilities and requirements of the experimental equipment and the signal processing techniques, the applicability of the proposed specific signal imaging velocimetry method was discussed.
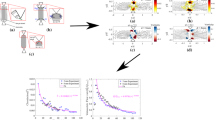
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Amplitude
- D :
-
Diameter
- f :
-
Frequency
- I :
-
Intensity
- L :
-
Characteristic length
- m :
-
Integer number
- n :
-
Integer number
- N :
-
Integer number
- px :
-
Pixel
- r :
-
Radial position
- t :
-
Time
- U :
-
Velocity of fluid flow
- v :
-
Environmental velocity
- w :
-
Width
- x :
-
Axial position
- ε :
-
Dissipation rate per unit mass
- μ :
-
Viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
- τ :
-
Characteristic time
- υ :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- φ :
-
Phase of a signal
- CCD:
-
Charge-coupled device
- DC:
-
Direct current
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transformation
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- MTV:
-
Molecular tagging velocimetry
- OSR:
-
Object space resolution
- PIV:
-
Particle imaging velocimetry
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- SSIV:
-
Specific signal imaging velocimetry
- WD:
-
Working distance
- 0 :
-
Initial value
- ∞ :
-
Infinite value
- a :
-
Camera
- i :
-
Index number in axial direction
- j :
-
Index number in radial direction
- max:
-
Maximum value
- min:
-
Minimum value
- p :
-
Particle
- px :
-
Pixel
- s :
-
Specific signal
References
Acrivlellis M (1980) Measurements by means of triple-sensor probes (turbulent flows). J Phys E Sci Instrum 13:986
Ahedo E (2011) Plasmas for space propulsion. Plasma Phys Contr Fusion 53:124037. https://doi.org/10.1088/0741-3335/53/12/124037
Auweter-Kurtz M, Glocker B, Golz T, Kurtz HL, Messerschmid EW, Riehle M, Zube DM (1996) Arcjet thruster development. J Propul Power 12:1077–1083. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.24146
Boulos MI, Fauchais P, Wender E (1997) Thermal plasmas: Fundamentals and applications volume 1 vol 14. vol 2. Plenum Press, New York
Brossa M, Pfender E (1988) Probe measurements in thermal plasma jets. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 8:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01016932
Bufton SA, Burton RL (1997) Velocity and temperature measurements in a low-power hydrazine arcjet. J Propuls Power 13:768–774. https://doi.org/10.2514/2.5231
Chapman S, Cowling TG (1958) The mathematical theory of non-uniform gases.
Chazot O, Panerai F (2015) High-enthalpy facilities and plasma wind tunnels for aerothermodynamics ground testing.
Coudert JF, Planch MP, Fauchais P (1995) Velocity measurement of dc plasma jets based on arc root fluctuations. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 15:47–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01596681
Dubreus T, Sheeley J, Stewart J Development of a mid-pressure arc-heated facility for hypersonic vehicle testing. In: Us Air Force T&e Days, 2013.
Farmer WM, Brayton DB (1971) Analysis of atmospheric laser Doppler velocimeters. Appl Opt 10:2319–2324. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.10.002319
Fauchais P (2004) Understanding plasma spraying. J Phys D Appl Phys 37:R86–R108. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/37/9/r02
Fauchais P, Vardelle A (1997) Thermal plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 25:1258–1280. https://doi.org/10.1109/27.650901
Fauchais P, Coudert JF, Vardelle M (1989) 7 - Diagnostics in thermal plasma processing. In: Auciello O, Flamm DL (eds) Plasma Diagnostics. Academic Press, pp 349–446. doi:https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-067635-4.50012-0
Fauchais PL, Heberlein JVR, Boulos MI (2014) Overview of thermal spray. In: Thermal Spray Fundamentals: From Powder to Part. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp 17–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68991-3_2
Gendrich CP, Koochesfahani MM (1996) A spatial correlation technique for estimating velocity fields using molecular tagging velocimetry (MTV). Exp Fluids 22:67–77
Gendrich CP, Koochesfahani MM, Nocera DG (1997) Molecular tagging velocimetry and other novel applications of a new phosphorescent supramolecule. Exp Fluids 23:361–372
Huang H, Eguchi K, Yoshida T (2003) Novel structured yttria-stabilized zirconia coatings fabricated by hybrid thermal plasma spraying. Sci Technol Adv Mater 4:617–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stam.2004.01.004
Huang H, Pan WX, Guo ZY, Wu CK (2010) Instabilities in a non-transferred direct current plasma torch operated at reduced pressure. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:085202. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/43/8/085202
Huang H, Pan W, Wu C (2012) Energy fluctuations in a direct current plasma torch with inter-electrode inserts operated at reduced pressure. Plasma Chemistry Plasma Process 32:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-011-9331-2
Johnson LK, Bromaghim DR, Dulligan MW, Hoskins WA, Spanjers GG (2015) On-orbit optical observations of electric propulsion space experiment 26 kilowatt Arcjet. J Propuls Power 18:763–767
Johnson BH, Murphree DL (1969) Plasma velocity determination by electrostatic probes. AIAA J 7:2028–2030. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.5504
Kado S, Shikama T, Kajita S, Oishi T, Tanaka S (2004) Plasma flow measurements in linear divertor simulator MAP-II using Mach probe and directional Langmuir probe. Contribu Plasma Phys 44:656–661
Kambara M et al (2014) Nano-composite Si particle formation by plasma spraying for negative electrode of Li ion batteries. J Appl Phys 115:143302. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4870600
Kawall JG, Shokr M, Keffer JF (2006) A digital technique for the simultaneous measurement of streamwise and lateral velocities in turbulent flows. J Fluid Mech 133:83–112
Keane RD, Adrian RJ (1990) Optimization of particle image velocimeters: II. Multiple pulsed systems. Meas Sci Technol 1:1202–1215
Kohli R (2012) Chapter 5 - Developments in imaging and analysis techniques for micro- and nanosize particles and surface features. In: Kohli R, Mittal KL (eds) Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning. William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, pp 215–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-7883-0.00005-5
Lekakis IC, Adrian RJ, Jones BG (1989) Measurement of velocity vectors with orthogonal and non-orthogonal triple-sensor probes. Exp Fluids 7:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198002
Lempert WR, Jiang N, Sethuram S, Mo S (2002) Molecular tagging velocimetry measurements in supersonic microjets. AIAA J 40:1065–1070
Lyn DA, Einav S, Rodi W, Park JH (1995) A laser-Doppler velocimetry study of ensemble-averaged characteristics of the turbulent near wake of a square cylinder. J Fluid Mech 304:285–319. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112095004435
Maclatchy CS, Boucher C, Poirier DA, Gunn J (1992) Gundestrup: a Langmuir/Mach probe array for measuring flows in the scrape-off layer of TdeV. Rev Sci Instrum 63:3923
Mazouffre S (2016) Electric propulsion for satellites and spacecraft: established technologies and novel approaches. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 25:033002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/25/3/033002
Metcalfe J, Quigley M (1975) Heat transfer in plasma-arc welding. Weld J 54:99–103
Optical Flow and Trajectory Estimation Methods (2016). SpringerBriefs in Computer Science.
Pan W, Meng X, Huang H, Wu C (2016) Producing ultra-high-speed nitrogen jets by arc heating in a low-pressure chamber. Theor Appl Mech Lett 6:60–63
Peterson BJ, Talmadge JN, Anderson DT, Anderson FSB, Shohet JL (1994) Measurement of ion flows using an ‘“unmagnetized”’ Mach probe in the interchangeable module stellarator. Rev Sci Instrum 65:2599–2606
Pfender E (1999) Thermal plasma technology: where do we stand and where are we going? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 19:1–31
Planche MP, Coudert JF, Fauchais P (1998) Velocity measurements for arc jets produced by a DC plasma spray torch. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 18:263–283. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021606701022
Raffel M, Willert CE, Scarano F, Kähler CJ, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2017) Particle image velocimetry—a practical guide, 3rd edn. Springer, Switzerland
Ramakrishnan S, Gershenzon M, Polivka F, Kearney TN, Rogozinski MW (1997) Plasma generation for the plasma cutting process. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 25:937–946. https://doi.org/10.1109/27.649600
Segall J, Brown MS, Skaggs PA, Debarber PA, Pitz RW, Nandula SP, Brown TM (1996) Unseeded velocity measurement by ozone tagging velocimetry. Opt Lett 21:755–757
Shen Q (2005) Rarefied gas dynamics—fundamentals, simulations and micro flows, vol 3. Springer, Germany
Taylor GI (1938) The spectrum of turbulence. Proc R Soc Lon Ser-A 164:0476–0490
Tennekes H, Lumley JL (1972) A first course in turbulence. The MIT Press, Cambridge
Underwood TC, Loebner KTK, Miller VA, Cappelli MA (2020) Schlieren diagnostic for cinematic visualization of dense plasma jets at Alfvenic timescales. Exp Fluids 61:17
V Le, M B, D G (2003) Thermal spray 2003: advancing the science and applying the technology. In: Paper presented at the ASM International Materials Park. Vol. 2, Ohio, USA
Wang Q, Wu Y, Cheng HT, Mei XH, Zhao CY (2019) A schlieren motion estimation method for seedless velocimetry measurement. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 109:109880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2019.109880
Wehrmeyer JA, Ribarov LA, Oguss DA, Pitz RW (1999) Flame flow tagging velocimetry with 193-nm H2O photodissociation. Appl Opt 38:6912
Westerweel J, Elsinga GE, Adrian RJ (2013) Particle image velocimetry for complex and turbulent flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45:409
Wilson F (2006) Recent advances in satellite propulsion and associated mission benefits. In: Aiaa International Communications Satellite Systems Conference, 2006
Zhang S, Yu X, Yan H, Huang H, Liu H (2017) Molecular tagging velocimetry of NH fluorescence in a high-enthalpy rarefied gas flow. Appl Phys B 123:122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6703-1
Zhukov MF, Zasypkin IM (2007) Thermal plasma torches: design, characteristics, application. Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA17030100) and the National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant 11735004 and Grant 11575273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (AVI 7516 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Huang, H., Pan, W. et al. Specific signal imaging velocimetry for rarefied plasma flows. Exp Fluids 61, 247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-03080-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-03080-9