Abstract
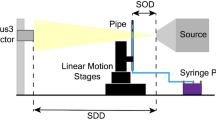
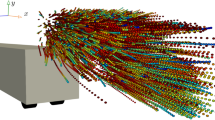
We demonstrate the measurement capabilities for a new horizontal shock tube facility designed to measure the displacements, velocities and accelerations of shock-accelerated particles just after shock passage. Eight-frame particle image accelerometry and particle tracking velocimetry accelerometry diagnostics are implemented, along with a shadowgraphy system for measuring the shock location during experiments. We demonstrate the driving conditions of the facility using a unique membraneless pneumatic driver and particle seeding system that can accommodate both solid and liquid particles in the carrier phase. Measurements of two types of solid particles show unsteady drag forces higher than those for steady drag.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ, Westerweel J (2011) Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press, New York
Boiko VM, Kiselev VP, Kiselev SP, Papyrin AN, Poplavsky SV, Fomin VM (1997) Shock wave interaction with a cloud of particles. Shock Waves 7:275–285
Britan A, Elperin T, Igra O, Jiang P (1995) Acceleration of a sphere behind planar shock waves. Exp Fluids 20:84–90
Butler PB, Schmitt RG (1990) Shock propagation through a perfect gas entrained with a normal distribution of the particles. Powder Technol 63:229–240
Chojnicki K, Clarke AB, Phillips JC (2006) A shock-tube investigation of the dynamics of gas–particle mixtures: implications for explosive volcanic eruptions. Geophys Res Lett 33:1–5. doi:10.1029/2006GL026414
Christensen KT, Adrian RJ (2002) Measurement of instantaneous eulerian acceleration fields by particle image accelerometry: method and accuracy. Exp Fluids 33:759–769
Clift R, Gauvin WH (1970) The motion of particles in turbulent gas streams. Pro Chem 1:14–28
Elsinga GE, Van Oudheusden BW, Scarano F (2005) Evaluation of aero-optical distortion effects in piv. Exp Fluids 39:246–256
Ferrari S, Rossi L (2008) Particle tracking velocimetry and accelerometry (ptva) measurements applied to quais-two dimensional multi-scale flows. Exp Fluids 44:873–886
Geng JH, Groenig H (2000) Dust suspensions accelerated by shock waves. Exp Fluids 28:360–367
Gore R, Crowe C (1989) Effect of particle on size on modulating turbulent intensity. Int J Multiph Flow 15:279
Hjelmfelt AT, Mockros FL (1966) Motion of discrete particles in a turbulent fluid. Appl Sci Res 16:149–161
Igra O, Takayama K (1993) Shock tube study of the drag coefficient of a sphere in a non-stationary flow. Proc R Soc A 442:231–247
Jourdan G, Houas L, Igra O, Estivalezes JL, Devals C, Meshkov EE (2007) Drag coefficient of a sphere in a non-stationary flow: new results. Proc R Soc 463:3323–3345
Kulick JD, Fessler JR, Eaton JK (1994) Particle response to turbulence modification in fully developed channel flow. J Fluid Mech 277:109
Ling Y, Wagner JL, Beresh SJ, Kearney SP, Balachandar S (2012) Interaction of a planar shock wave with a dense particle curtain: modeling and experiments. Phys Fluids 24:1–30
Longhorn AL (1952) The unsteady, subsonic motion of a sphere in a compressible inviscid fluid. Q J Mech Appl Math 5:64–81
Marble FE (1970) Dynamics of dusty gases. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 2:397–446
Maxey MR, Riley JJ (1983) Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a nonuniform flow. Phys Fluids 26:883–889
Miles JW (1951) On virtual mass and transient motion in subsonic compressible flow. Q J Mech Appl Math 4:388–400
Parmar M, Haselbacher A, Balachandar S (2008) On the unsteady inviscid force on cylinders and spheres in subcritical compressible flow. Philos Trans R Soc A 366:2161–2175
Parmar M, Haselbacher A, Balachandar S (2009) Modeling of the unsteady force for shock–particle interaction. Shock Waves 19:317–329
Parmar M, Haselbacher A, Balachandar S (2010) Improved drag correlation for spheres and application to shock-tube experiments. AIAA J 48:1273–1276
Rudinger G (1970) Effective drag coefficient for gas–particle flow in shock tubes. ASME J Basic Eng 92:165–172
Saito T, Saba M, Sun M, Takayama K (2007) The effect of an unsteady drag force on the structure of a non-equilibrium region behind a shock wave in a gas–particle mixture. Shock Waves 17:255–262. doi:10.1007/s00193-007-0109-7
Sommerfeld M (1985) The unsteadiness of shock waves propagating through gas–particle mixtures. Exp Fluids 3:197–206
Sun M, Saito T, Takayama K, Tanno H (2004) Unsteady drag on a sphere by shock wave loading. Shock Waves. doi:10.1007/s00193-004-0235-4
Sun M, Saito T, Takayama K, Tanno H (2005) Unsteady drag on a sphere by shock wave loading. Shock Waves 14:3–9
Tanaka T, Eaton JK (2010) Sub-kolmogorov resolution particle image velocimetry measurements of particle-laden forced turbulence. J Fluid Mech 643:177–206. doi:10.1017/S0022112009992023
Tanno H, Itoh K, Saito T, Abe A, Takayama K (2003) Interaction of a shock with a sphere suspended in a vertical shock tube. Shock Waves 13:191–200
Wagner J, Beresh S, Kearney S, Pruett B, Wright E (2012) Shock tube investigation of quasi-steady drag in shock–particle interactions. Phys Fluids 24:123301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Adam A. Martinez and Gregory C. Orlicz have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, A.A., Orlicz, G.C. & Prestridge, K.P. A new experiment to measure shocked particle drag using multi-pulse particle image velocimetry and particle tracking. Exp Fluids 56, 1854 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1854-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1854-x