Abstract
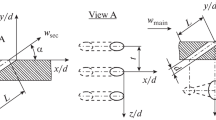
A test rig incorporating the injection from a single cylindrical hole with an inclination of 30° to a thermally uniform mainstream flow was used for determining variations in flow structures due to injectant pulsation. The average blowing ratios (\( \overline{M} \)) were 0.65, 1, and 1.25. The periodic variations in injectant flow were rendered by a loudspeaker-based pulsation system to nondimensionalized excitation frequency (\( St \)) of 0, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5. Pulsation resulting in a close-wall orientation of injectant fluid compared with steady blowing bearing outward orientation was only observed in few cases. At \( \overline{M} \) = 0.65, jet fluid remains aligned and covers a significant part of the wall under steady blowing. At higher blowing ratios, pulsation induces large spatial variations in the jet trajectory, collapsing of the jet body, and the shedding of wake structures due to the periodic variation of injection flow rate. It was found that the pulsation improves wall coverage of the injectant fluid under low frequency excitation as the separation of the jet from the wall becomes evident (\( \overline{M} \) = 1 and 1.25).















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \( \overline{M} \) :
-
Blowing ratio (=\( {{\rho_{i} u_{i} } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\rho_{i} u_{i} } {\rho_{\infty } u_{\infty } }}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\rho_{\infty } u_{\infty } }} \))
- \( \rho \) :
-
Fluid density (kg/m3)
- \( D \) :
-
Hole diameter (mm)
- \( St \) :
-
Strouhal number (=\( {{f \cdot D} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{f \cdot D} {\overline{{U_{i} }} }}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\overline{{U_{i} }} }} \))
- \( U \) :
-
Streamwise velocity (m/s)
- \( V \) :
-
Normal velocity (m/s)
- \( u \) :
-
Streamwise velocity fluctuation (m/s)
- \( v \) :
-
Normal velocity fluctuation (m/s)
- \( u_{\tau } \) :
-
Friction velocity (m/s)
- \( U^{ + } \) :
-
U normalized by friction velocity (=\( {U \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {U u}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} u}_{\tau }^{{}} \))
- \( IT_{{}} \) :
-
Turbulent intensity (%)
- \( \delta \) :
-
Boundary layer thickness (mm)
- \( \delta^{*} \) :
-
Displacement thickness (mm)
- \( \sqrt {\overline{{u^{2} }} } \) :
-
X-component of RMS velocity (m/s)
- \( \sqrt {\overline{{v^{2} }} } \) :
-
Y-component of RMS velocity (m/s)
- \( \overline{uv} \) :
-
Reynolds shear stress (m/s)²
- \( t \) :
-
Time (s)
- \( T \) :
-
Period of pulsation (s)
- \( f \) :
-
Frequency (Cycles/s)
- \( \theta \) :
-
Phase (radian).
- \( \phi \) :
-
Phase shift (radian)
- \( \omega \) :
-
Angular frequency (radians/s)
- \( x,y \) :
-
Streamwise and normal coordinates (mm)
- \( y^{ + } \) :
-
Normal coordinate in wall units (=\( {{y \cdot u_{\tau } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{y \cdot u_{\tau } } \nu }} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \nu } \))
- i :
-
Injectant
- ∞:
-
Free-stream
- rms :
-
Root mean square
- — :
-
Time-averaged
- ~:
-
Periodic component
- a:
-
Amplitude
- h:
-
Nominal hole
- j :
-
Index number
- acq :
-
Acquisition
- s :
-
Excitation
References
Andreopoulos J (1983) Heat transfer measurement in a heated jet-pipe flow issuing into a cold cross steam. Phys Fluids 26:3201–3210
Andreopoulos J (1985) On the structure of jets in a crossflow. J Fluid Mech 157:163–197
Benedict LH, Gould RD (1996) Towards better uncertainty estimates for turbulence statistics. Exp Fluids 22:129–136
Bons JP, Rivir JB, Mac Arthur CD, Pestian DJ (1996) The effect of unsteadiness on film cooling effectiveness. Wright Laboratory, WL-TR-96–2096
Brundage AL, Plesniak MW, Ramadhyani S (1999) Influence of coolant feed direction and hole length on film cooling jet velocity profiles. International gas turbine and aeroengine congress and exhibition, June 1999, Indianapolis, Indiana
Burd SW, Kaszeta RW, Simon TW (1996) Measurement in film cooling flows: hole L/D and turbulence intensity effects. Gas turbine heat transfer session, 1996 IMECE conference, Atlanta, GA
Dorignac E, Vullierme JJ, Deniboire P, Foucault E, Bousgarbies JL (1992) Thermographie Infrarouge et tomographie laser appliqués à l’étude des films de refroidissement. 5ème colloque national de visualisation et de traitement d’images en mécanique des fluides, pp 2–5 Juin 1992, Poitiers
Dorignac E, Vullierme JJ, Delouche E, Garem JH, Leblanc R (1993) Blowing rate effects on the heat transfer coefficient on a film heated surface at transonic speed. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on experimental and computational aerodynamics of internal flow, July 12–15 1993, Prague
Eckert ERG (1970) Gas‐to‐gas film cooling. Published in Inzhenerno-Rizicheskii Zhurnal, SpringerLink, 19:426–440
Eriksen VL, Goldstein RJ (1974) Heat transfer and film cooling following injection through inclined circular tubes. ASME J Heat Transf 96:239–245
Foucault E, Deniboire P, Bousgarbies JL, Vullierme JJ, Dorignac E, (1992) Etude expérimentale du transfert de chaleur près d’une paroi plane chauffée en présence d’injection multiples (Ecoulement subsonique). Heat transfer and cooling in gas turbine, AGARD-CP-527, p 4
Goldstein RJ, Eckert ERG (1974) Effects of hole geometry and density on three-dimensional film cooling. Int J Heat Mass Transf 17:595–607
Kartuzova O, Danila D, Ibrahim MB (2009) Computational simulation of cylindrical film hole with jet pulsation on flat plates. AIAA J Propul 6(25):1249–1258
Kelso RM, Lim TT, Perry AE (1996) An experimental study of round jets in cross-flow. J Fluid Mech 306:111–144
Kim J, Moin P, Moser R (1987) Turbulence statistics in fully developed channel flow at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 177:133–166
Lee SW, Lee JS, Ro ST (1994) Experimental study on the flow characteristics of streamwise inclined jets in crossflow on flat plate. ASME J Turbomach 116:97–105
Ligrani PM, Ciriello S, Bishop DT (1992) Heat transfer, adiabatic effectiveness, and injectant distribution downstream of a single row and two staggered rows of compound angle film cooling holes. ASME J Turbomach 114:687–700
Ligrani PM, Gong R, Cuthrell JM (1996a) Bulk flow pulsations and film cooling-I: injectant behavior. Int J Heat Mass Transf 39:2271–2282
Ligrani PM, Gong R, Cuthrell JM (1996b) Bulk flow pulsations and film cooling-II: flow structure and film effectiveness. Int J Heat Mass Transf 39:2283–2292
Ligrani PM, Gong R, Cuthrell JM, Lee JS (1997) Effects of bulk flow pulsations on film-cooled boundary layer structure. ASME J Fluids Eng 119:56–66
Marek CJ, Tacina RR (1975) Effect of free-stream turbulence on film cooling. NASA technical note, NASA TN D-7958
Moussa ZM, Trischka JW, Eskinazi S (1977) The near field in the mixing of a round jet with a cross-stream. J Fluid Mech 80:49–80
Muldoon F, Acharya S (2009) DNS study of pulsed film cooling for enhanced cooling effectiveness. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:3118–3127
Pietrzyk JR, Bogard DG, Crawford ME (1989) Hydrodynamic measurement of jets in crossflow for gas turbine film cooling application. ASME J Turbomach 111:139–145
Rutledge JL, King PI, Rivir R (2009) CFD prediction of the frequency dependence of pulsed film cooling heat flux on a turbine blade leading edge. In: Proceedings of the 47th AIAA aerospace sciences meeting, Jan 2009, Orlando. AIAA paper 2009–0680
Sargison JE, Guo SM, Oldfield MLG, Lock GD, Rawlinson AJ (2002) A converging slot-hole film-cooling geometry. Part 1: low-speed flat plate heat transfer and loss. ASME J Turbomach 124:453–460
Seo HJ, Lee JS, Ligrani PM (1998) The effect of injection hole length on film cooling with bulk flow pulsation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 41:3515–3528
Sinha AK, Bogard DG, Crawford ME (1991) Gas turbine film cooling: Flowfield due to a second row of holes. ASME J Turbomach 113:450–456
Walters DK, Leylek JH (2000) A detailed analysis of film cooling physics. Part 1: streamwise injection with cylindrical holes. ASME J Turbomach 122:102–111
Yuen CHN, Martinez-Botas RF (2003) Film cooling characteristics of a single round hole at various streamwise angles in a crossflow. Part I: effectiveness. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:221–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sultan, Q., Lalizel, G., Fénot, M. et al. Experimental time-resolved study of the interaction between a pulsating injectant and a steady cross-flow: aerodynamics of film cooling. Exp Fluids 51, 1245–1259 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1144-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1144-9