Abstract
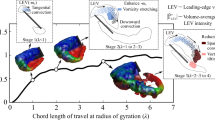
The dye visualization experiments show that a dual leading-edge vortex (LEV) structure exists on the suction side of a simplified butterfly model of Papilio ulysses at α = 8°−12°. Furthermore, the results of particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurement indicate that the axial velocity of the primary (outer) vortex core reaches the lower extreme value while a transition from a “wake-like” to a “jet-like” axial velocity profile occurs. The work reveals for the first time the existence of dual LEV structure on the butterfly-like forward-sweep wing configuration.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Maximum chord length
- d :
-
Distance from X′–Z′ coordinates plane to the left apex of the model
- L :
-
Maximum span length
- LEV:
-
Leading-edge vortex
- MAVs:
-
Micro air vehicles
- PIV:
-
Particle image velocimetry
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- S :
-
Span of the X′–Z′ coordinates plane over the left forewing of the model
- U :
-
Free-stream velocity
- U core :
-
Mean axial velocity
- WTV:
-
Wing-tip vortex
- X–Y:
-
Coordinates plane of the top view
- X′–Z′:
-
Coordinates plane of the section view
- α :
-
Angle of attack
- β :
-
Angle of sideslip
References
Backenbury JH (1991) Kinematics of take-off and climbing fight in butterflies. J Zool Lond 244:251–270
Betts CR, Wootton RJ (1988) Wing shape and fight behavior in butterflies (Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea and Hesperioidea): a preliminary analysis. J Exp Biol 138:271–288
Breitsamter C, Laschka B (2001) Vortical flowfield structure at forward swept-wing configurations. J Aircr 38(2):193–207
Chen L, Wang JJ, Zuo LX, Feng LH (2010) Vortex flows over 50° swept delta wing at low Reynolds number. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica 28:174–179 (in Chinese)
Dudley R (1990) Biomechanics of flight in Neotropical butterflies: morphometrics and kinematics. J Exp Biol 150:37–53
Gordnier R, Visbal M (2003) Higher–order compact difference scheme applied to the simulation of a low sweep delta wing flow. AIAA Paper: 2003–620
Hu Y, Wang JJ (2010) Experimental investigation on aerodynamic performance of gliding butterflies. AIAA J 48(10):2454–2457
Hu Y, Wang JJ, Zhang PF, Zhang C (2009) Experimental investigation on the flow structure over a simplified Papilio ulysses model. Chin Sci Bull 54:1026–1031
Hu Y, Wang JJ, Zhang C, Zhang PF (2010) Shape of a butterfly wing affects flow structures. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica 28:138–142 (in Chinese)
Lu Y, Shen GX, Lai GJ (2006) Dual leading-edge vortices on flapping wings. J Exp Biol 209:5005–5016
Okamoto M, Sunada S, Tokutake H (2009) Stability analysis of gliding flight of a swallowtail butterfly Papilio xuthus. J Exp Biol 257:191–202
OL M, Gharib M (2003) Leading–edge vortex structure of nonslender delta wings at low Reynolds number. AIAA J 41(1):16–26
Sane SP, Dickinson MH (2002) The aerodynamic effects of wing rotation and a revised quasi-steady model of flapping flight. J Exp Biol 205:1087–1096
Senda K, Sawamoto M, Shibahara T, Tanaka T (2004) Study on flapping of wings flight of butterfly with experimental measurement. AIAA Paper: 2004–5368
Srygley RB, Thomas ALR (2002) Unconventional lift–generating mechanisms in free–flying butterflies. Nature 420:660–664
Taylor GS, Schnorbus T, Gursul I (2003) An investigation of vortex flows over low sweep delta wings. AIAA Paper: 2003–4021
Traub LW, Lawrence J (2009) Aerodynamic characteristics of forward and aft swept arrow wings. J Aircr 46(4):1454–1457
Wang JJ, Tu JQ (2010) Effect of wing planform on leading-edge vortex structures. Chin Sci Bull 55:120–123
Wang JJ, Zhang W (2008) Experimental investigations on leading–edge vortex structures for flow over non–slender delta wings. Chinese Phys Lett 25:2550–2553
Wang JJ, Zhao X, Liu WC, Tu JQ (2007) Experimental investigation on flow structures over nonslender delta wings at low Reynolds numbers. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics 21:1–7 (in Chinese)
Zbikowski R (2002) On aerodynamic modeling of an insect–like flapping wing in hover for micro air vehicles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 360:273–290
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under grant No. 10425207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Wang, J.J. Dual leading-edge vortex structure for flow over a simplified butterfly model. Exp Fluids 50, 1285–1292 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-010-0990-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-010-0990-1