Abstract
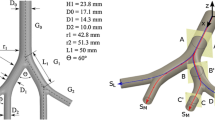
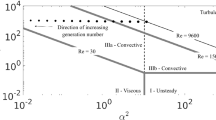
This work investigates the fundamental flow in a converging bifurcation. Particle image velocimetry (PIV) and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) experiments were conducted in a transparent model composed of three machined tubes mated together in a Y-shape. Measurements were taken in a plane containing the axes of the tubes and in the cross-sectional plane of the parent tube to elucidate flow patterns in the bifurcating passages of the human respiratory system. The primary objective was to determine the amount of secondary flow in a bifurcation during expiration. PIV measurements in the transverse plane show detailed characteristics of the secondary flow. Results at higher Re illustrate unsteadiness associated with a hairpin vortex and symmetry-breaking. This study addresses the transport of particles of small Stokes number that survive inertial impaction during inhalation and remain in suspension over multiple breathing cycles. Knowledge of the underlying airflow is required to develop an accurate dosimetry model to transport prescription drugs with precision into the bloodstream. Similarly, the harmful impact of pollutants on the respiratory system can only be assessed by first understanding the carrier airflow.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comer CK, Kleinstreuer C, Zhang Z (2001) Flow structures and particle deposition patterns in a double-bifurcation airway models. 1. Air flow fields. J Fluid Mech 435:25–54
Drazin PG, Reid WH (1981) Hydrodynamic stability. Cambridge University Press, New York
Horsfield K, Dart G, Olson DE, Filley GF, Cumming G (1971) Models of the human bronchial tree. J Appl Physiol 31:207–217
Kim CS, Garcia L (1991) Particle deposition in cyclic converging tube flow. Aerosol Sci Technol 14:322–330
Kim CS, Fisher DM, Lutz DJ, Gerrity TR (1994) Particle deposition in bifurcating airway models with varying airway geometry. J Aerosol Sci 25:567–581
Olson DE (1971) Fluid mechanics relevant to respiration: flow within curved or elliptical tubes and bifurcating systems. PhD Thesis, Imperial College, London
Pedley TJ (1977) Pulmonary fluid dynamics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 9:229–274
Sarangapani R, Wexler AS (1999) Modeling aerosol bolus dispersion in human airways. J Aerosol Sci 30:1345–1362
Schroter RC, Sudlow MF (1969) Flow patterns in models of the human bronchial airways. Respir Physiol 7:341-355
Weibel ER (1963) Morphometry of the lung. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Zhao Y, Lieber BB (1994) Steady expiratory flow in a model symmetric bifurcation. J Biomech Eng 116:318–323
Zhang Z, Kleinstreuer C (2002) Transient airflow structures and particle transport in a sequentially branching airway model. Phys Fluids 14:862–880
Zhang Z, Kleinstreuer C, Kim CS (2001) Flow structure and particle transport in a triple bifurcation airway model. J Fluids Eng 123:320–330
Acknowledgements
Research described in this article was supported by Philip Morris Incorporated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fresconi, F.E., Wexler, A.S. & Prasad, A.K. Expiration flow in a symmetric bifurcation. Exp Fluids 35, 493–501 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-003-0713-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-003-0713-y