Abstract
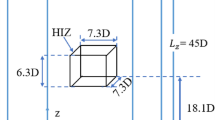
The upward penetration of the mid-latitude baroclinic waves has been well known to influence the air motion in the stratosphere. To study this in the laboratory, we present a new type of rotating fluid annulus experiment where a radial temperature difference is imposed on water near the flat bottom to produce a baroclinic wave in a lower layer and the water surface is heated to create a stratified upper layer. To test this model, we carried out experiments to study baroclinic waves penetrating into the stratified layer by a quasi-geostrophic potential vorticity equation in the atmospheric dynamics. The baroclinic waves produced in the lower fluid layer were observed to penetrate into the stratified upper layer. As expected from the equation, the vorticities of the flows for wavenumbers 3, 4 and 5 decayed exponentially with height and showed a weaker decay for lower wavenumbers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastin ME, Read PL (1997) A laboratory study of baroclinic waves and turbulence in an internally heated rotating fluid annulus with sloping endwalls. J Fluid Mech 339:173–198
Fincham AM, Spedding GR (1997) Low cost, high resolution DPIV for measurement of turbulent fluid flow. Exp Fluids 23:449–462
Holton JR (1972) An introduction to dynamic meteorology, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York
Luff JD, Drouillard T, Rompage AM, Linne MA, Hertzberg JR (1999) Experimental uncertainties associated with particle image velocimetry (PIV) based vorticity algorithms. Exp Fluids 26:36–54
Marcus PS (1988) Numerical simulation of Jupiter's Great Red Spot. Nature 331:693–696
Read PL, Hide R (1984) An isolated baroclinic eddy as a laboratory analogue of the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. Nature 308:45–48
Sommeria J, Meyers SD, Swinney HL (1988) Laboratory simulation of Jupiter's Great Red Spot. Nature 331:689–693
Tajima T, Kawahira K (1993) Liquid crystal techniques of visualization in rotating annulus experiments. Exp Fluids 14:65–69
Tajima T, Nakamura T (2000) Meridional flow field of axisymmetric flows in a rotating annulus. J Atmos Sci 57:3109–3121
Utami T, Blackwelder RF, Ueno T (1991) A cross-correlation technique for velocity field extraction from particulate visualization. Exp Fluids 10:213–223
Van Heijist GJF, Kloosterziel RC (1989) Tripolar vortices in a rotating fluid. Nature 338:569–571
Weeks ER, Tian Y, Urbach JS, Ide K, Swinney HL, Ghil M (1997) Transitions between blocked and zonal flows in a rotating annulus with topography. Science 278:1598–1601
Acknowledgements
T.T. thanks B.B. Plapp, C.N. Baroud, and H.L. Swinney for encouragement and advising him on PIV techniques. We also benefited from discussions with R. Kimura, H. Niino, and K. Kawahira.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tajima, T., Nakamura, T. Experiments to study baroclinic waves penetrating into a stratified layer by a quasi-geostrophic potential vorticity equation. Exp Fluids 34, 744–747 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-003-0619-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-003-0619-8