Abstract.
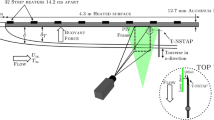
A probe consisting of four X-wires (a total of eight hot wires operated in constant temperature mode) and two pairs of parallel cold wires (operated in constant current mode) is in principle capable of providing simultaneous data for the instantaneous energy and temperature dissipation rates. To evaluate the performance of this probe, measurements have been made in decaying turbulence downstream of a grid/screen combination. The directly measured mean values of the energy and temperature dissipation rates are compared with those obtained from the streamwise decay rates of the mean turbulent energy and temperature variance. The probe also yields all three fluctuating vorticity components; after applying spatial resolution corrections, their spectra are in close agreement with isotropic calculations over nearly all wavenumbers. Both the vorticity variance and the mean energy dissipation rate exhibit the same power-law decay rate. Transport equations for the mean energy and temperature dissipation rates are satisfied to within ±10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, .T., Antonia, .R. & Chua, .L. Performance of a probe for measuring turbulent energy and temperature dissipation rates. Exp Fluids 33, 334–345 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-002-0443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-002-0443-6