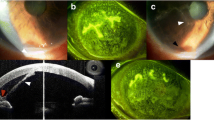
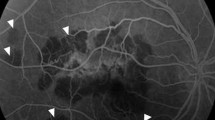
Background: Hypopyon-uveitis has been identified as a dosage-dependent side effect in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome who are treated for Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection with systemic rifabutin.
Patients and methods: We report a 38-year-old female AIDS patient with bilateral hypopyon uveitis under therapy with rifabutin in combination with clarithromycin and indinavir.
Results: At the time of presentation of the bilateral hypopyon uveitis the patient was treated with rifabutin (300 mg/day), clarithromycin (1000 mg/day) and ethambutol (1000 mg/day) for an M. avium complex infection. Also, the patient received the protease inhibitor indinavir. The rifabutin dose was reduced to 150 mg/day. Hypopyon and inflammation resolved under therapy with steroids.
Conclusions: The concomitant use of rifabutin, clarithromycin, and protease inhibitors may lead to hypopyon uveitis. Reduction of dosage of rifabutin (150 mg/day) and treatment with topical steroids are required.
Hintergrund: Die Hypopyon-Uveitis wurde als dosisabhängiger Nebeneffekt bei AIDS-Patienten beschrieben, die auf Grund einer Mycobacterium avium complex-Infektion systemisch mit Rifabutin behandelt wurden.
Patienten und Methode: Wir berichten von einer 38-jährigen AIDS-Patientin mit bilateraler Hypopyon-Uveitis unter Therapie mit Rifabutin in Kombination mit Clarithromycin und Indinavir.
Ergebnisse: Die Patientin wurde zum Zeitpunkt der bilateralen Hypopyon-Uveitis auf Grund einer atypischen Mykobakteriose mit Rifabutin (300 mg/d), Clarithromycin (1000 mg/d) und Ethambutol (1000 mg/d) behandelt. Weiter bekam die Patientin im Rahmen der antiretroviralen Therapie den Proteaseinhibitor Indinavir. Unter Dosisreduktion von Rifabutin (150 mg/d) und Steroidtherapie bildeten sich Entzündung und Hypopyon zurück.
Schlußfolgerung: Die gleichzeitige Therapie mit Rifabutin, Clarithromycin und Proteaseinhibitoren kann zu einer Hypopyon-Uveitis führen. Eine Dosisreduktion von Rifabutin (150 mg/d) und Behandlung mit lokalen Steroiden ist erforderlich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaller, U., Michl, G., Goebel, FD. et al. Acute hypopyon uveitis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome treated for systemic Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection with rifabutin. Ophthalmologe 96, 267–269 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050404
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050404