Abstract
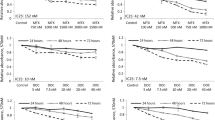
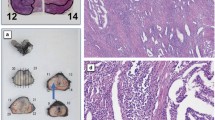
Surgery, radiation, or hormone deprivation alone does not adequately affect local control of clinical or pathologic stage T3 prostate cancer. Lack of local cancer control ultimately leads to a higher incidence of morbidity, distant metastasis, and decreased survival, with patients having disease-specific mortality exceeding 75%. Other novel therapies against this devastating and common disease are needed for the achievement of long-term local cancer control. For this purpose, therapeutic interventions should target prostate-cancer cells at the molecular and cellular level in ways not possible by current modalities of cancer treatment. Any strategy that can modify the biologic behavior of these cells may potentially have the most significant clinical impact. As prostate cancer represents an accumulation of genetic mutations that causes a prostate cell to lose the ability to control its growth, one new approach against prostate cancer may be gene therapy. Identification of key missing or mutated tumor-suppressor genes that, when replaced, may inhibit or destroy prostate-cancer cells may have the best chance of clinical success. One such gene appears to be tumor-suppressor gene p16 (also known as MTS1, INK4A, and CDKN2). Tumor-suppressor gene p16 is an important negative cell-cycle regulator whose functional loss may significantly contribute to malignant transformation and progression. Alterations in the p16 gene and its protein expression often occur in prostate cancer. An adenoviral vector containing wild-type p16 (Adp16) had a high transduction efficiency in prostate-cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, prostate tumors injected with Adp16 expressed p16 and the adenoviral vector expressed the transgene for up to 14 days. Wild-type p16 inhibited prostate-cancer proliferation in vitro and markedly suppressed tumors in vivo. Pathologic evaluation of the Adp16-treated tumors showed dose-dependent necrosis and fibrosis. Although the mechanism of p16 inhibition in cancer remains to be elucidated, senescence and apoptosis may both be important; however, the data suggest that p16-induced growth inhibition can function independently of the retinoblastoma gene product.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allay, J., Steiner, M., Zhang, Y. et al. Adenovirus p16 gene therapy for prostate cancer. World J Urol 18, 111–120 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450050182
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450050182