Abstract
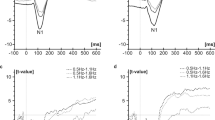
The evaluation of cortical evoked potentials after stimulation of the vesicourethral junction shows accurate and reproducible results and offers an elegant technique for evaluation of the viscerosensory pathways in patients with lower urinary tract dysfunction. The results must be considered in context with the results of simultaneously investigated pudendal somatosensory evoked potentials and the clinical symptomatology. They are of great help (1) in differentiating between intraspinal and extraspinal lesions of the afferent pathways of the detrusor if the etiology is unknown, (2) in differentiating between neurogenic and myogenic damage to the urinary bladder, and (3) in selecting patients not suitable for intravesical electrotherapy for bladder rehabilitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiss, G., Madersbacher, H. & Poewe, W. Cortical evoked potentials of the vesicourethral junction – a predictor for the outcome of intravesical electrostimulation in patients with sensory and motor detrusor dysfunction. World J Urol 16, 308–312 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450050073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450050073