Abstract
Purpose
To investigate and assess outcomes, complications, and functional results amongst different modifications of endoscopic enucleation of the prostate (EEP).
Methods
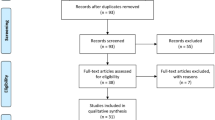
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis according to the PRISMA checklist. We searched the Medline, Cochrane, and Embase databases. We included only randomised-controlled trials (RCT) comparing modifications of EEPs and assessed the risk of bias (RoB).
Results
Seven RCTs were included in the study. Overall, 1266 patients were treated with Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and 80 patients with thulium laser vapo-enucleation of the prostate (ThuVEP). The operative time during pulse shape-modified HoLEP was shorter when compared to standard pulse HoLEP (MD 18.08 min, 95% CI 8.11–28.05 min, p = 0.0004). The decrease in haemoglobin was significantly lower for two-lobe HoLEP when compared to three-lobe HoLEP (MD 0.16 g/dl, 95% CI 0.22–0.1 g/dl, p < 0.00001). Virtual Basket (VB) HoLEP showed a smaller haemoglobin decrease when compared to standard pulse HoLEP (1.12 ± 1.78 vs. 2.54 ± 1.23 g/dl, p = 0.03). When directly comparing one- vs. two- vs. three-lobe HoLEP, surgical time (p < 0.001) and enucleation efficiency (p = 0.006) were significantly different and favouring one- and two-lobe HoLEP in the study with the largest patient population included. No significant differences for complications were observed; however, Clavien–Dindo IVa events were reported for two patients.
Conclusion
All variations of EEP improve symptoms and functional parameters with a low incidence of high-grade complications. One- and two-lobe approaches and pulse shape-modified HoLEP seem to be beneficial in terms of operative time and blood loss.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable due to review format.
References
Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs FD, Fourcade R et al (2003) The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms in men and women in four centres. The UrEpik study. BJU Int 92(4):409–414. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04369.x
Gravas SCJ, Gacci M, Gratze C, Hermann TR, Mamoulakis C et al (2022) EAU Guidelines on Management of Non-Neurogenic Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS), including Benign Prostatic Obstruction (BPO). EAU Guidel
Lin Y, Wu X, Xu A, Ren R, Zhou X, Wen Y et al (2016) Transurethral enucleation of the prostate versus transvesical open prostatectomy for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Urol 34(9):1207–1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1735-9
Gopee EL, Hong MK, Pham T (2016) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate in a 400 cc prostate: case report. J Endourol Case Rep 2(1):21–23. https://doi.org/10.1089/cren.2015.0017
Reddy SK, Utley V, Gilling PJ (2020) The evolution of endoscopic prostate enucleation: a historical perspective. Andrologia 52(8):e13673. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13673
Scoffone CM, Cracco CM (2019) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Curr Opin Urol 29(3):304–305. https://doi.org/10.1097/mou.0000000000000609
Oh SJ (2019) Current surgical techniques of enucleation in holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Investig Clin Urol 60(5):333–342. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.5.333
Fraundorfer MR, Gilling PJ (1998) Holmium:YAG laser enucleation of the prostate combined with mechanical morcellation: preliminary results. Eur Urol 33(1):69–72. https://doi.org/10.1159/000019535
Scoffone CM, Cracco CM (2016) The en-bloc no-touch holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) technique. World J Urol 34(8):1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1741-y
Saitta G, Becerra JEA, Del Álamo JF, González LL, Elbers JR, Suardi N et al (2019) “En Bloc” HoLEP with early apical release in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol 37(11):2451–2458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02671-4
Elshal AM, El-Nahas AR, Ghazy M, Nabeeh H, Laymon M, Soltan M et al (2018) Low-power vs high-power holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: critical assessment through randomized trial. Urology 121:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.07.010
Shah HN, Etafy MH, Katz JE, Garcia Lopez EA, Shah RH (2021) A randomized controlled trial comparing high and medium power settings for holmium laser enucleation of prostate. World J Urol 39(8):3005–3011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03535-y
Bozzini G, Maltagliati M, Besana U, Berti L, Calori A, Sighinolfi MC et al (2021) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate with Virtual Basket mode: faster and better control on bleeding. BMC Urol 21(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-021-00797-5
Kavoussi NL, Nimmagadda N, Robles J, Forbes C, Wang A, Stone B et al (2021) MOSESTM technology for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a prospective double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Urol 206(1):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000001693
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Mamoulakis C, Efthimiou I, Kazoulis S, Christoulakis I, Sofras F (2011) The modified Clavien classification system: a standardized platform for reporting complications in transurethral resection of the prostate. World J Urol 29(2):205–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-010-0566-y
Rucker F, Lehrich K, Bohme A, Zacharias M, Ahyai SA, Hansen J (2021) A call for HoLEP: en-bloc vs. two-lobe vs. three-lobe. World J Urol 39(7):2337–2345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03598-5
Tiburtius C, Gross AJ, Netsch C (2015) A prospective, randomized comparison of a 1940 nm and a 2013 nm thulium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser device for Thulium VapoEnucleation of the prostate (ThuVEP): first results. Indian J Urol 31(1):47–51. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-1591.148308
Xu C, Xu Z, Lin C, Feng S, Sun M, Chen J et al (2019) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: modified two-lobe technique versus traditional three-lobe technique—a randomized study. Biomed Res Int 2019:3875418. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3875418
Fried NM, Irby PB (2018) Advances in laser technology and fibre-optic delivery systems in lithotripsy. Nat Rev Urol 15(9):563–573. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-018-0035-8
Ventimiglia E, Traxer O (2019) What is Moses effect: a historical perspective. J Endourol 33(5):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2019.0012
Nevo A, Faraj KS, Cheney SM, Moore JP, Stern KL, Borofsky M et al (2021) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate using Moses 2.0 vs non-Moses: a randomised controlled trial. BJU Int 127(5):553–559. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15265
Ito T, Tamura K, Otsuka A, Shinbo H, Takada S, Kurita Y et al (2019) Development of a complete en-bloc technique with direct bladder neck incision: a newly modified approach for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Endourol 33(10):835–840. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2018.0773
Kim YJ, Lee YH, Kwon JB, Cho SR, Kim JS (2015) A novel one lobe technique of thulium laser enucleation of the prostate: “All-in-One” technique. Korean J Urol 56(11):769–774. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.11.769
Houssin V, Olivier J, Brenier M, Pierache A, Laniado M, Mouton M et al (2021) Predictive factors of urinary incontinence after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a multicentric evaluation. World J Urol 39(1):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03169-0
Shigemura K, Tanaka K, Yamamichi F, Chiba K, Fujisawa M (2016) Comparison of predictive factors for postoperative incontinence of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate by the surgeons’ experience during learning curve. Int Neurourol J 20(1):59–68. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.1630396.198
Hartung FO, Kowalewski KF, von Hardenberg J, Worst TS, Kriegmair MC, Nuhn P et al (2021) Holmium versus thulium laser enucleation of the prostate: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Urol Focus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.024
Zhang Y, Yuan P, Ma D, Gao X, Wei C, Liu Z et al (2019) Efficacy and safety of enucleation vs. resection of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 22(4):493–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-019-0135-4
Enikeev D, Glybochko P, Rapoport L, Gahan J, Gazimiev M, Spivak L et al (2018) A Randomized trial comparing the learning curve of 3 endoscopic enucleation techniques (HoLEP, ThuFLEP, and MEP) for BPH using mentoring approach-initial results. Urology 121:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.06.045
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GO and KHP had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. TT and CSB were involved in study concept and design, and supervision. GO, KHP, and CYY acquired the data. GO and KHP carried out analysis and interpretation, drafted the manuscript, and conducted the statistical analysis. GO, KHP, CYY, TRWH, CSB, and TT critically revised the manuscript and provided administrative, technical or material support. No funding was obtained.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Gernot Ortner certifies that all conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript (e.g. employment/affiliation, grants or funding, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, or patents filed, received, or pending), are the following: None.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This review does not involve human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
Not applicable due to review format.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ortner, G., Pang, K.H., Yuan, Y. et al. Peri- and post-operative outcomes, complications, and functional results amongst different modifications of endoscopic enucleation of the prostate (EEP): a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Urol 41, 969–980 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04308-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04308-z