Abstract
Objective
To observe the efficacy and safety of Mirabegron in patients with distal, ureteral stones ≤ 10 mm.
Patients and methods
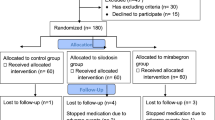
A total of 90 patients with distal ureteral stones ≤ 10 mm were prospectively randomized into two groups. Forty-five cases in the study group and 45 cases as control. The stone-free rates (SFRs) and renal colic episodes between two groups were compared at the 1st, 2nd and 4th week end by imaging examinations.
Result
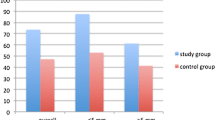
All of 90 patients were randomly assigned to two groups. In patients with ≤ 5 mm stones, the SFRs in the 1st week (63.6% vs. 33.3%, P = 0.040), the 2nd week (86.4% vs. 54.2%, P = 0.018), and the 4th week (90.9% vs. 66.7%, P = 0.046) after treatment were all significantly higher than that in the control group by the stratification analysis of stone size. Even though SFRs were all higher for patients with > 5 mm stones in study group, there was no statistically significant difference (All P > 0.05). In terms of renal colic episodes, the frequency of occurrence of the study group was significantly lower than that of the control group and need less antalgic.
Conclusions
The MET with Mirabegron has a significant role in improve SFR for the patients with distal ureteral stones ≤ 5 mm and no effect in > 5 mm stones. Furthermore, Mirabegron reduces the need for antalgic in ≤ 10 mm stones with low incidence of adverse effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romero V, Akpinar H, Assimos DG (2010) Kidney stones: a global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev Urol 12:e86–e96
Ketabchi AA, Aziziolahi GA (2008) Prevalence of symptomatic urinary calculi in Kerman. Iran Urol J 5:156–160
Papadoukakis S, Stolzenburg J, Truss MC (2006) Treatment strategies of ureteral stones. Eau-Ebu Update Ser 4:184–190
Pearle MS, Lotan Y (2012) Urinary lithiasis: etiology, epidemiology, and pathogenesis. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds) Campbell-Walsh urology, 10th edn. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1257–1286
Holdgate A, Pollock T (2004) Systematic review of the relative efficacy of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioids in the treatment of acute renal colic. BMJ 12(328):1401
Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G (2003) Efficacy of tamsulosin in the medical management of juxtavesical ureteral stones. J Urol 170:2202–2205
Teichman JM (2004) Clinical practice: acute renal colic from ureteral calculus. N Engl J Med 350:684–693
Rong-Zhen T, Zhi-Qiang Q, Fa-de L, Jian-Lin Lv (2019) Efficacy and safety of tamsulosin in the medical expulsion therapy for distal ureteral calculi: a systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Urol J 16(3):224–231. https://doi.org/10.22037/uj.v0i0.4758
Ye Z, Zeng G, Yang H et al (2017) Efficacy and safety of tamsulosin in medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral stones with renal colic: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Eur Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.10.033
Rong-Zhen T, Qing-Lai T, Shuang Z, Chun-Ping J, Jian-Lin Lv (2020) External physical vibration lithecbole facilitating the expulsion of upper ureteric stones 1.0–2.0 cm after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: a prospective randomized trial. Urolithiasis 48(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-018-1100-8
Shen H, Chen Z, Mokhtar AD, Bi X, Wu G, Gong S, Huang C, Li S, Du S (2017) Expression of β-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human normal and dilated ureter. Int Urol Nephrol 49(10):1771–1778
Mehmet S, Omer B, Ersan B (2019) Efficacy of mirabegron in medical expulsive therapy. Urolithiasis 47(3):303–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-018-1075-5
Ahmet U, Emre T, Ramazan T, Aytac S, Yuksel OH (2019) Mirabegron: a novel and promising medical expulsive treatment for ureteral stones? J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 29(1):73–74. https://doi.org/10.29271/jcpsp.2019.01.73
Igawa Y, Michel MC (2013) Pharmacological profile of b3-adrenoceptor agonists inclinical development for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386:177–183
Woo LH, Hee BC, Yeol LM et al (2011) Spontaneous contractions augmented by cholinergic and adrenergic systems in the human ureter. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 15:37–41
Sule Y, Mert E, Burak A et al (2013) Ureterovesical junction obstruction causes increment in smooth muscle contractility, and cholinergic and adrenergic activity in distal ureter of rabbits. J Pediatr Surg 48:1954–1961
Danuser H, Weiss R, Abel D et al (2001) Systemic and topical drug administration in the pig ureter: effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors alpha1, beta and beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists and antagonists on the frequency and amplitude of ureteral contractions. J Urol 166:714–720
Saki S, Daichi I, Mana K et al (2017) β- and β-adrenergic receptor stimulation differ in their effects on PGC-1α and atrogin-1/MAFbx gene expression in chick skeletal muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 211:1–6
Singh A, Alter HJ, Littlepage A (2007) A systematic review of medical therapy to facilitate passage of ureteral calculi. Ann Emerg Med 50:552–563
Beach MA, Mauro LS (2006) Pharmacologic expulsive treatment of ureteral calculi. Ann Pharmacother 40:1361–1368
Nitti V, Herschorn S, Auerbach S et al (2011) The efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with overactive bladder syndrome-results from a North-American phase III trial. Eur Urol Suppl 10:278
Chapple C, Wyndaele JJ, van Kerrebroeck P et al (2010) Doseranging study of once-daily mirabegron (YM178), a novel selective b3-adrenoceptor agonist, in patients with overactive bladder (OAB). Eur Urol Suppl 9:249
Funding
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q-LT: project development; SZ: data collection; RZT and D-JW: data analysis and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Affiliated Jiangning Hospital with Nanjing Medical University and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Ql., Wang, Dj., Zhou, S. et al. Mirabegron in medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral stones: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. World J Urol 39, 4465–4470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03772-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03772-9