Abstract
Introduction
The BPH surgical armamentarium is composed of a rapidly expanding number of technologies and techniques. These include greenlight photovaporization of the prostate (PVP), greenlight enucleation of the prostate (GreenLEP), holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP), thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP) and, more recently, the aquablation procedure. To the best of our knowledge, no direct comparison in operative time has been performed.
Methods
Data for this study were pooled from five sources. For aquablation, patient-level data from four studies of the aquablation procedure were provided by the device manufacturer as well as from a high-volume commercial user. PVP, GreenLEP, HoLEP, and ThuLEP were performed by high-volume, experienced experts. Endpoints included total operative time, resection time, and proportion of total operative time for resection. General linear models were used to evaluate the relationship between prostate volume (or other continuous predictors) and procedure time.
Results
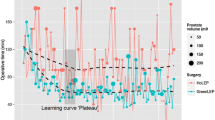
Total procedure time was related to prostate size. Except for the small prostate size range (size < 40 cc), at any given prostate volume, procedure time was highest for PVP, intermediate for LEPs, and lowest for Aquablation. The relationship between procedure time and prostate size (i.e., slope of the fitted lines) was 0.16 min/g for aquablation, 0.32 min/g, 0.28 min/g and 0.32 min/g for GreenLEP, HoLEP and ThuLEP, respectively, and 0.63 min/g for PVP.
Conclusion
In our analysis of pooled data of multi-surgical techniques and technologies, aquablation provided the lowest operative time across all prostate volumes. PVP had the longest procedure time for prostates > 40 cc.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lue TF, McAninch JW (eds) (2013) Smith & Tanagho's general urology. McGraw-Hill Medical
Vuichoud C, Loughlin KR (2015) Benign prostatic hyperplasia: epidemiology, economics and evaluation. Can J Urol 22(Suppl 1):1–6
Foster HE, Barry MJ, Dahm P, Gandhi MC, Kaplan SA, Kohler TS, Lerner LB, Lightner DJ, Parsons JK, Roehrborn CG, Welliver C, Wilt TJ, McVary KT (2018) Surgical management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia: AUA guideline. J Urol 200(3):612–619
Nickel JC, Aaron L, Barkin J, Elterman D, Nachabé M, Zorn KC (2018) Canadian Urological Association guideline on male lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia (MLUTS/BPH): 2018 update. Can Urol Assoc J 12(10):303–312. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.5616
Gratzke C, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A et al (2015) EAU guidelines on the assessment of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 67(6):1099–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.038
Kuntz RM (2006) Current role of lasers in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Eur Urol 49(6):961–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURURO.2006.03.028
Le Duc A, Gilling PJ (1999) Holmium laser resection of the prostate. Eur Urol 35(2):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1159/000019836
Wilson LC, Gilling PJ, Williams A et al (2006) A randomised trial comparing holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection in the treatment of prostates larger than 40 grams: results at 2 years. Eur Urol 50(3):569–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURURO.2006.04.002
Krambeck AE, Handa SE, Lingeman JE (2010) Experience with more than 1000 holmium laser prostate enucleations for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 183(3):1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.11.034
Ahyai SA, Gilling P, Kaplan SA et al (2010) Meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement. Eur Urol 58(3):384–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURURO.2010.06.005
Herrmann TRW, Bach T, Imkamp F et al (2010) Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP): transurethral anatomical prostatectomy with laser support. Introduction of a novel technique for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction. World J Urol. 28(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-009-0503-0
Bach T, Netsch C, Haecker A, Michel M-S, Herrmann TRW, Gross AJ (2010) Thulium:YAG laser enucleation (VapoEnucleation) of the prostate: safety and durability during intermediate-term follow-up. World J Urol 28(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-009-0461-6
Sachs B, Misrai V, Tabatabaei S, Woo HH (2019) Multicenter experience with photoselective vaporization of the prostate on men taking novel oral anticoagulants. Asian J Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJUR.2019.07.005
Hueber PA, Liberman D, Ben-Zvi T, Woo H, Hai MA, Te AE, Chughtai B, Lee R, Rutman M, Gonzalez RR, Barber N, Al-Hathal N, Al-Qaoud T, Trinh QD, Zorn KC (2013) 180 W vs 120 W lithium triborate photoselective vaporization of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a global, multicenter comparative analysis of perioperative treatment parameters. Urology 82(5):1108–1113
Thomas JA, Tubaro A, Barber N et al (2016) A multicenter randomized noninferiority trial comparing greenlight-XPS laser vaporization of the prostate and transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction: two-yr outcomes of the GOLIATH study. Eur Urol 69(1):94–102
Ajib K, Mansour M, Zanaty M et al (2018) Photoselective vaporization of the prostate with the 180-W XPS-Greenlight laser: five-year experience of safety, efficiency, and functional outcomes. Can Urol Assoc J 12(7):E318–E324. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.4895
Huet R, Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Vincendeau S (2015) Énucléation prostatique au laser Greenlight (GreenLEP) versus Photovaporisation prostatique (PVP) GreenlightXPS 180 W pour les volumes de %3e 80 mL : étude monocentrique comparative et prospective des résultats péri-opératoires et fonctionnels à moyen terme. Progrès en Urol 25(13):732. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PUROL.2015.08.034
Elshal AM, Elkoushy MA, El-Nahas AR et al (2015) GreenLightTM Laser (XPS) photoselective vapo-enucleation versus holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized controlled study. J Urol 193(3):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JURO.2014.09.097
Gilling PJ, Barber N, Bidair M et al (2019) Randomized controlled trial of aquablation versus transurethral resection of the prostate in benign prostatic hyperplasia: one-year outcomes. Urology 125:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.UROLOGY.2018.12.002
Gilling P, Barber N, Bidair M et al (2018) WATER: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of aquablation vs transurethral resection of the prostate in benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 199(5):1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.12.065
Desai M, Bidair M, Bhojani N et al (2018) WATER II (80–150 mL) procedural outcomes. BJU Int. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14360
Misrai V, Rijo E, Zorn KC, Barry-Delongchamps N, Descazeaud A (2019) Waterjet ablation therapy for treating benign prostatic obstruction in patients with small- to medium-size glands: 12-month results of the first french aquablation clinical registry. Eur Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURURO.2019.06.024
Bach T, Giannakis I, Bachmann A et al (2018) Aquablation of the prostate: single-center results of a non-selected, consecutive patient cohort. World J Urol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2509-y
Azizi M, Tholomier C, Meskawi M et al (2017) Safety, perioperative, and early functional outcomes of vapor incision technique using the greenlight XPS 180 W system: direct comparison with photoselective vaporization of the prostate. J Endourol 31(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2016.0474
Gomez Sancha F, Rivera VC, Georgiev G, Botsevski A, Kotsev J, Herrmann T (2015) Common trend: move to enucleation—is there a case for GreenLight enucleation? Development and description of the technique. World J Urol 33(4):539–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1339-9
Bhojani N, Nguyen D-DD, Kaufman RP, Elterman D, Zorn KC (2019) Comparison of %3c 100 cc prostates and %3e 100 cc prostates undergoing aquablation for benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol 37(7):1361–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2535-9
Funding
WATER, WATER II, OPEN WATER, and FRANCAIS WATER clinical studies were funded by PROCEPT BioRobotics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D-DN: protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing. VM: data collection, manuscript editing. TB: data collection, manuscript editing. NB: manuscript editing. JEL: data collection, manuscript editing. DSE: manuscript editing. KCZ: protocol/project development, data collection, data management, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Consultants and proctors for Boston Scientific for greenlight: KZ, DE, VM. Investigators and consultants for PROCEPT BioRobotics: VM, TB, NB, KZ. DDN were supported by a summer scholarship from the Endourological Society.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This research involves humans.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, DD., Misraï, V., Bach, T. et al. Operative time comparison of aquablation, greenlight PVP, ThuLEP, GreenLEP, and HoLEP. World J Urol 38, 3227–3233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03137-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03137-8