Abstract
Background
Claudin-1 is a membrane-tight junction protein and important for the sealing of the paracellular cleft in epithelial and endothelial cells. Differential expression of Claudin-1 is linked to disease outcome in various cancers.
Material and methods
To evaluate the potential relevance of Claudin-1 expression in prostate cancer, a tissue microarray containing samples of 17,747 tumors with annotated clinico-pathological and molecular data was immunohistochemically analyzed for Claudin-1 expression.
Results
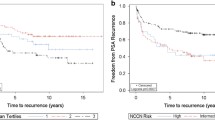
In normal prostate, glandular cells were always Claudin-1-negative while there was a strong staining of gland-surrounding basal cells. In contrast to normal prostatic glands, a positive Claudin-1 immunostaining, was found, however, in 38.7% of 12,441 interpretable cancers and was considered weak in 12.7%, moderate in 13.2%, and strong in 12.8% of cases. Positive Claudin-1 immunostaining was associated with favorable tumor features like low pT (p = 0.0032), low Gleason grade (p< 0.0001), and a reduced risk of PSA recurrence (p = 0.0005). A positive Claudin-1 staining was markedly more frequent in ERG-positive (63%) than in ERG-negative cancers (23%; p < 0.0001). Subset analyses revealed that all associations of Claudin-1 expression and favorable phenotype and prognosis were driven by ERG-positive cancers. Multivariate analyses revealed, however, that even in ERG-positive cancers, the prognostic impact of high Claudin-1 expression was not independent of established clinico-pathological parameters. Comparison with 12 previously analyzed chromosomal deletions identified conspicuous associations with PTEN and 12p13 deletions potentially indicating functional interactions.
Conclusion
These data identify a peculiar role for Claudin-1 in prostate cancer. The protein is overexpressed in a fraction of prostate cancers and increased Claudin-1 expression levels predict a favorable prognosis in ERG-positive cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Bill-Axelson A, Holmberg L, Ruutu M, Garmo H, Stark JR, Busch C, Nordling S, Haggman M, Andersson SO, Bratell S, Spangberg A, Palmgren J, Steineck G, Adami HO, Johansson JE, Investigators S (2011) Radical prostatectomy versus watchful waiting in early prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 364(18):1708–1717. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1011967
Wilt TJ, Jones KM, Barry MJ, Andriole GL, Culkin D, Wheeler T, Aronson WJ, Brawer MK (2017) Follow-up of prostatectomy versus observation for early prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 377(2):132–142. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1615869
Klotz L, Vesprini D, Sethukavalan P, Jethava V, Zhang L, Jain S, Yamamoto T, Mamedov A, Loblaw A (2015) Long-term follow-up of a large active surveillance cohort of patients with prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 33(3):272–277. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.55.1192
Fenton JJ, Weyrich MS, Durbin S, Liu Y, Bang H, Melnikow J (2018). In: prostate-specific antigen-based screening for prostate cancer: A systematic evidence review for the U.S. preventive services task force. U.S. preventive services task force evidence syntheses, formerly systematic evidence reviews. rockville (MD)
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE (2003) Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81(1):1–44
France MM, Turner JR (2017) The mucosal barrier at a glance. J Cell Sci 130(2):307–314. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.193482
Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, Noda T, Kubo A, Tsukita S (2002) Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 156(6):1099–1111. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200110122
Jiang WG, Puntis MC, Hallett MB (1994) Molecular and cellular basis of cancer invasion and metastasis: implications for treatment. Br J Surg 81(11):1576–1590
Leotlela PD, Wade MS, Duray PH, Rhode MJ, Brown HF, Rosenthal DT, Dissanayake SK, Earley R, Indig FE, Nickoloff BJ, Taub DD, Kallioniemi OP, Meltzer P, Morin PJ, Weeraratna AT (2007) Claudin-1 overexpression in melanoma is regulated by PKC and contributes to melanoma cell motility. Oncogene 26(26):3846–3856. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210155
Sobel G, Paska C, Szabo I, Kiss A, Kadar A, Schaff Z (2005) Increased expression of claudins in cervical squamous intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma. Hum Pathol 36(2):162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2004.12.001
Hoellen F, Waldmann A, Banz-Jansen C, Holtrich U, Karn T, Oberlander M, Habermann JK, Hormann M, Koster F, Ribbat-Idel J, Thill M, Rody A, El-Balat A, Hanker L (2017) Claudin-1 expression in cervical cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 7(5):880–884. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2017.1391
Lee JW, Lee SJ, Seo J, Song SY, Ahn G, Park CS, Lee JH, Kim BG, Bae DS (2005) Increased expressions of claudin-1 and claudin-7 during the progression of cervical neoplasia. Gynecol Oncol 97(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.11.058
Chao YC, Pan SH, Yang SC, Yu SL, Che TF, Lin CW, Tsai MS, Chang GC, Wu CH, Wu YY, Lee YC, Hong TM, Yang PC (2009) Claudin-1 is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(2):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200803-456OC
de Oliveira SS, de Oliveira IM, De Souza W, Morgado-Diaz JA (2005) Claudins upregulation in human colorectal cancer. FEBS Lett 579(27):6179–6185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.091
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou SR, Schmidt C, Neff J, Washington MK, Beauchamp RD (2005) Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J Clin Invest 115(7):1765–1776. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI24543
Resnick MB, Konkin T, Routhier J, Sabo E, Pricolo VE (2005) Claudin-1 is a strong prognostic indicator in stage II colonic cancer: a tissue microarray study. Modern Pathol 18(4):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800301
Huo Q, Kinugasa T, Wang L, Huang J, Zhao J, Shibaguchi H, Kuroki M, Tanaka T, Yamashita Y, Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Kuroki M (2009) Claudin-1 protein is a major factor involved in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 29(3):851–857
Kinugasa T, Huo Q, Higashi D, Shibaguchi H, Kuroki M, Tanaka T, Futami K, Yamashita Y, Hachimine K, Maekawa S, Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Kuroki M (2007) Selective up-regulation of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 27(6A):3729–3734
Higashi Y, Suzuki S, Sakaguchi T, Nakamura T, Baba S, Reinecker HC, Nakamura S, Konno H (2007) Loss of claudin-1 expression correlates with malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res 139(1):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2006.08.038
Tokes AM, Kulka J, Paku S, Szik A, Paska C, Novak PK, Szilak L, Kiss A, Bogi K, Schaff Z (2005) Claudin-1, -3 and -4 proteins and mRNA expression in benign and malignant breast lesions: a research study. Breast Cancer Res 7(2):R296–305. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr983
Lu S, Singh K, Mangray S, Tavares R, Noble L, Resnick MB, Yakirevich E (2013) Claudin expression in high-grade invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: correlation with the molecular subtype. Mod Pathol 26(4):485–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2012.187
Resnick MB, Gavilanez M, Newton E, Konkin T, Bhattacharya B, Britt DE, Sabo E, Moss SF (2005) Claudin expression in gastric adenocarcinomas: a tissue microarray study with prognostic correlation. Hum Pathol 36(8):886–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2005.05.019
Wang H, Yang X (2015) The expression patterns of tight junction protein claudin-1, -3, and -4 in human gastric neoplasms and adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(1):881–887
Huang J, Li J, Qu Y, Zhang J, Zhang L, Chen X, Liu B, Zhu Z (2014) The expression of claudin 1 correlates with beta-catenin and is a prognostic factor of poor outcome in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 44(4):1293–1301. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2298
Weischenfeldt J, Simon R, Feuerbach L, Schlangen K, Weichenhan D, Minner S, Wuttig D, Warnatz HJ, Stehr H, Rausch T, Jager N, Gu L, Bogatyrova O, Stutz AM, Claus R, Eils J, Eils R, Gerhauser C, Huang PH, Hutter B, Kabbe R, Lawerenz C, Radomski S, Bartholomae CC, Falth M, Gade S, Schmidt M, Amschler N, Hass T, Galal R, Gjoni J, Kuner R, Baer C, Masser S, von Kalle C, Zichner T, Benes V, Raeder B, Mader M, Amstislavskiy V, Avci M, Lehrach H, Parkhomchuk D, Sultan M, Burkhardt L, Graefen M, Huland H, Kluth M, Krohn A, Sirma H, Stumm L, Steurer S, Grupp K, Sultmann H, Sauter G, Plass C, Brors B, Yaspo ML, Korbel JO, Schlomm T (2013) Integrative genomic analyses reveal an androgen-driven somatic alteration landscape in early-onset prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 23(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.01.002
Pyo JS, Kim NY, Cho WJ (2019) Prognostic role of claudin-1 immunohistochemistry in malignant solid tumors: a meta-analysis. J Pathol Transl Med 53(3):173–179. https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.03
Vare P, Loikkanen I, Hirvikoski P, Vaarala MH, Soini Y (2008) Low claudin expression is associated with high Gleason grade in prostate adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 19(1):25–31
Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Ross JS (2007) Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol 38(4):564–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2006.11.007
Seo KW, Kwon YK, Kim BH, Kim CI, Chang HS, Choe MS, Park CH (2010) Correlation between claudins expression and prognostic factors in prostate cancer. Korean J Urol 51(4):239–244. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2010.51.4.239
Krajewska M, Olson AH, Mercola D, Reed JC, Krajewski S (2007) Claudin-1 immunohistochemistry for distinguishing malignant from benign epithelial lesions of prostate. Prostate 67(9):907–910. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20578
Sauter G, Steurer S, Clauditz TS, Krech T, Wittmer C, Lutz F, Lennartz M, Janssen T, Hakimi N, Simon R, von Petersdorff-Campen M, Jacobsen F, von Loga K, Wilczak W, Minner S, Tsourlakis MC, Chirico V, Haese A, Heinzer H, Beyer B, Graefen M, Michl U, Salomon G, Steuber T, Budaus LH, Hekeler E, Malsy-Mink J, Kutzera S, Fraune C, Gobel C, Huland H, Schlomm T (2016) Clinical utility of quantitative gleason grading in prostate biopsies and prostatectomy specimens. Eur Urol 69(4):592–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.10.029
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4(7):844–847
Tennstedt P, Koster P, Bruchmann A, Mirlacher M, Haese A, Steuber T, Sauter G, Huland H, Graefen M, Schlomm T, Minner S, Simon R (2012) The impact of the number of cores on tissue microarray studies investigating prostate cancer biomarkers. Int J Oncol 40(1):261–268. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2011.1216
Minner S, Enodien M, Sirma H, Luebke AM, Krohn A, Mayer PS, Simon R, Tennstedt P, Muller J, Scholz L, Brase JC, Liu AY, Schluter H, Pantel K, Schumacher U, Bokemeyer C, Steuber T, Graefen M, Sauter G, Schlomm T (2011) ERG status is unrelated to PSA recurrence in radically operated prostate cancer in the absence of antihormonal therapy. Clin Cancer Res 17(18):5878–5888. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-11-1251
Minner S, Wittmer C, Graefen M, Salomon G, Steuber T, Haese A, Huland H, Bokemeyer C, Yekebas E, Dierlamm J, Balabanov S, Kilic E, Wilczak W, Simon R, Sauter G, Schlomm T (2011) High level PSMA expression is associated with early PSA recurrence in surgically treated prostate cancer. Prostate 71(3):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.21241
Krohn A, Seidel A, Burkhardt L, Bachmann F, Mader M, Grupp K, Eichenauer T, Becker A, Adam M, Graefen M, Huland H, Kurtz S, Steurer S, Tsourlakis MC, Minner S, Michl U, Schlomm T, Sauter G, Simon R, Sirma H (2013) Recurrent deletion of 3p13 targets multiple tumour suppressor genes and defines a distinct subgroup of aggressive ERG fusion-positive prostate cancers. J Pathol 231(1):130–141. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4223
Burkhardt L, Fuchs S, Krohn A, Masser S, Mader M, Kluth M, Bachmann F, Huland H, Steuber T, Graefen M, Schlomm T, Minner S, Sauter G, Sirma H, Simon R (2013) CHD1 is a 5q21 tumor suppressor required for ERG rearrangement in prostate cancer. Can Res 73(9):2795–2805. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-1342
Kluth M, Hesse J, Heinl A, Krohn A, Steurer S, Sirma H, Simon R, Mayer PS, Schumacher U, Grupp K, Izbicki JR, Pantel K, Dikomey E, Korbel JO, Plass C, Sauter G, Schlomm T, Minner S (2013) Genomic deletion of MAP3K7 at 6q12-22 is associated with early PSA recurrence in prostate cancer and absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions. Modern Pathol 26(7):975–983. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2012.236
Kluth M, Amschler NN, Galal R, Moller-Koop C, Barrow P, Tsourlakis MC, Jacobsen F, Hinsch A, Wittmer C, Steurer S, Krech T, Buscheck F, Clauditz TS, Beyer B, Wilczak W, Graefen M, Huland H, Minner S, Schlomm T, Sauter G, Simon R (2017) Deletion of 8p is an independent prognostic parameter in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8(1):379–392. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13425
Krohn A, Diedler T, Burkhardt L, Mayer PS, De Silva C, Meyer-Kornblum M, Kotschau D, Tennstedt P, Huang J, Gerhauser C, Mader M, Kurtz S, Sirma H, Saad F, Steuber T, Graefen M, Plass C, Sauter G, Simon R, Minner S, Schlomm T (2012) Genomic deletion of PTEN is associated with tumor progression and early PSA recurrence in ERG fusion-positive and fusion-negative prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 181(2):401–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.04.026
Kluth M, Ahrary R, Hube-Magg C, Ahmed M, Volta H, Schwemin C, Steurer S, Wittmer C, Wilczak W, Burandt E, Krech T, Adam M, Michl U, Heinzer H, Salomon G, Graefen M, Koop C, Minner S, Simon R, Sauter G, Schlomm T (2015) Genomic deletion of chromosome 12p is an independent prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 6(29):27966–27979. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4626
Kluth M, Scherzai S, Buschek F, Fraune C, Moller K, Hoflmayer D, Minner S, Gobel C, Moller-Koop C, Hinsch A, Neubauer E, Tsourlakis MC, Sauter G, Heinzer H, Graefen M, Wilczak W, Luebke AM, Burandt E, Steurer S, Schlomm T, Simon R (2018) 13q deletion is linked to an adverse phenotype and poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer 57(10):504–512. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22645
Kluth M, Jung S, Habib O, Eshagzaiy M, Heinl A, Amschler N, Masser S, Mader M, Runte F, Barow P, Frogh S, Omari J, Moller-Koop C, Hube-Magg C, Weischenfeldt J, Korbel J, Steurer S, Krech T, Huland H, Graefen M, Minner S, Sauter G, Schlomm T, Simon R (2017) Deletion lengthening at chromosomes 6q and 16q targets multiple tumor suppressor genes and is associated with an increasingly poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8(65):108923–108935. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22408
Kluth M, Harasimowicz S, Burkhardt L, Grupp K, Krohn A, Prien K, Gjoni J, Hass T, Galal R, Graefen M, Haese A, Simon R, Huhne-Simon J, Koop C, Korbel J, Weischenfeld J, Huland H, Sauter G, Quaas A, Wilczak W, Tsourlakis MC, Minner S, Schlomm T (2014) Clinical significance of different types of p53 gene alteration in surgically treated prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 135(6):1369–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28784
Kluth M, Graunke M, Moller-Koop C, Hube-Magg C, Minner S, Michl U, Graefen M, Huland H, Pompe R, Jacobsen F, Hinsch A, Wittmer C, Lebok P, Steurer S, Buscheck F, Clauditz T, Wilczak W, Sauter G, Schlomm T, Simon R (2016) Deletion of 18q is a strong and independent prognostic feature in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 7(52):86339–86349. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13404
Heinrich MC, Gobel C, Kluth M, Bernreuther C, Sauer C, Schroeder C, Moller-Koop C, Hube-Magg C, Lebok P, Burandt E, Sauter G, Simon R, Huland H, Graefen M, Heinzer H, Schlomm T, Heumann A (2018) PSCA expression is associated with favorable tumor features and reduced PSA recurrence in operated prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 18(1):612. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4547-7
Tsourlakis MC, Eleftheriadou A, Stender A, Weigand P, Grupp K, Hube-Magg C, Kluth M, Schroeder C, Steurer S, Hinsch A, Luebke A, Angerer A, Wittmer C, Friedrich E, Gobel C, Buscheck F, Heinzer H, Graefen M, Simon R, Sauter G, Wilczak W, Minner S, Schlomm T, Jacobsen F (2017) FOXA1 expression is a strong independent predictor of early PSA recurrence in ERG negative prostate cancers treated by radical prostatectomy. Carcinogenesis 38(12):1180–1187. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgx105
Epstein JI, Feng Z, Trock BJ, Pierorazio PM (2012) Upgrading and downgrading of prostate cancer from biopsy to radical prostatectomy: incidence and predictive factors using the modified Gleason grading system and factoring in tertiary grades. Eur Urol 61(5):1019–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.01.050
Shah RB, Zhou M, LeBlanc M, Snyder M, Rubin MA (2002) Comparison of the basal cell-specific markers, 34betaE12 and p63, in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Am J Surg Pathol 26(9):1161–1168
Szasz AM, Nyirady P, Majoros A, Szendroi A, Szucs M, Szekely E, Tokes AM, Romics I, Kulka J (2010) beta-catenin expression and claudin expression pattern as prognostic factors of prostatic cancer progression. BJU Int 105(5):716–722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08808.x
Colegio OR, Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2003) Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284(6):C1346–1354. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00547.2002
Capaldo CT, Nusrat A (2015) Claudin switching: physiological plasticity of the tight junction. Semin Cell Dev Biol 42:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.04.003
Koval M (2013) Claudin heterogeneity and control of lung tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 75:551–567. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183809
Kinugasa T, Akagi Y, Ochi T, Tanaka N, Kawahara A, Ishibashi Y, Gotanda Y, Yamaguchi K, Shiratuchi I, Oka Y, Kage M, Shirouzu K (2012) Increased claudin-1 protein expression in hepatic metastatic lesions of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 32(6):2309–2314
Brase JC, Johannes M, Mannsperger H, Falth M, Metzger J, Kacprzyk LA, Andrasiuk T, Gade S, Meister M, Sirma H, Sauter G, Simon R, Schlomm T, Beissbarth T, Korf U, Kuner R, Sultmann H (2011) TMPRSS2-ERG -specific transcriptional modulation is associated with prostate cancer biomarkers and TGF-beta signaling. BMC Cancer 11:507. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-507
Gupta S, Iljin K, Sara H, Mpindi JP, Mirtti T, Vainio P, Rantala J, Alanen K, Nees M, Kallioniemi O (2010) FZD4 as a mediator of ERG oncogene-induced WNT signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer cells. Can Res 70(17):6735–6745. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0244
Jhavar S, Brewer D, Edwards S, Kote-Jarai Z, Attard G, Clark J, Flohr P, Christmas T, Thompson A, Parker M, Shepherd C, Stenman UH, Marchbank T, Playford RJ, Woodhouse C, Ogden C, Fisher C, Kovacs G, Corbishley C, Jameson C, Norman A, De-Bono J, Bjartell A, Eeles R, Cooper CS (2009) Integration of ERG gene mapping and gene-expression profiling identifies distinct categories of human prostate cancer. BJU Int 103(9):1256–1269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08200.x
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva B, Antipin Y, Mitsiades N, Landers T, Dolgalev I, Major JE, Wilson M, Socci ND, Lash AE, Heguy A, Eastham JA, Scher HI, Reuter VE, Scardino PT, Sander C, Sawyers CL, Gerald WL (2010) Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 18(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026
Fishilevich S, Nudel R, Rappaport N, Hadar R, Plaschkes I, Iny Stein T, Rosen N, Kohn A, Twik M, Safran M, Lancet D, Cohen D (2017) GeneHancer: genome-wide integration of enhancers and target genes in GeneCards. Database (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bax028
Wu L, Zhao JC, Kim J, Jin HJ, Wang CY, Yu J (2013) ERG is a critical regulator of Wnt/LEF1 signaling in prostate cancer. Can Res 73(19):6068–6079. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0882
Muller J, Ehlers A, Burkhardt L, Sirma H, Steuber T, Graefen M, Sauter G, Minner S, Simon R, Schlomm T, Michl U (2013) Loss of pSer2448-mTOR expression is linked to adverse prognosis and tumor progression in ERG-fusion-positive cancers. Int J Cancer 132(6):1333–1340. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27768
Grupp K, Ospina-Klinck D, Tsourlakis MC, Koop C, Wilczak W, Adam M, Simon R, Sauter G, Izbicki JR, Graefen M, Huland H, Steurer S, Schlomm T, Minner S, Quaas A (2014) NY-ESO-1 expression is tightly linked to TMPRSS2-ERG fusion in prostate cancer. Prostate 74(10):1012–1022. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22816
Burdelski C, Bujupi E, Tsourlakis MC, Hube-Magg C, Kluth M, Melling N, Lebok P, Minner S, Koop C, Graefen M, Heinzer H, Wittmer C, Sauter G, Wilczak W, Simon R, Schlomm T, Steurer S, Krech T (2015) Loss of SOX9 expression is associated with PSA recurrence in ERG-positive and PTEN deleted prostate cancers. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0128525. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128525
Burdelski C, Dieckmann T, Heumann A, Hube-Magg C, Kluth M, Beyer B, Steuber T, Pompe R, Graefen M, Simon R, Minner S, Tsourlakis MC, Koop C, Izbicki J, Sauter G, Krech T, Schlomm T, Wilczak W, Lebok P (2016) p16 upregulation is linked to poor prognosis in ERG negative prostate cancer. Tumour Biol 37(9):12655–12663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5167-y
Stumm L, Burkhardt L, Steurer S, Simon R, Adam M, Becker A, Sauter G, Minner S, Schlomm T, Sirma H, Michl U (2013) Strong expression of the neuronal transcription factor FOXP2 is linked to an increased risk of early PSA recurrence in ERG fusion-negative cancers. J Clin Pathol 66(7):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201335
Grupp K, Boumesli R, Tsourlakis MC, Koop C, Wilczak W, Adam M, Sauter G, Simon R, Izbicki JR, Graefen M, Huland H, Steurer S, Schlomm T, Minner S, Quaas A (2014) The prognostic impact of high Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS1) gene expression in ERG-negative prostate cancers lacking PTEN deletion is driven by KPNA2 expression. Int J Cancer 135(6):1399–1407. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28778
Heumann A, Heinemann N, Hube-Magg C, Lang DS, Grupp K, Kluth M, Minner S, Moller-Koop C, Graefen M, Heinzer H, Tsourlakis MC, Wilczak W, Wittmer C, Jacobsen F, Huland H, Simon R, Schlomm T, Sauter G, Steurer S, Lebok P, Hinsch A (2018) High BCAR1 expression is associated with early PSA recurrence in ERG negative prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 18(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3956-3
Melling N, Rashed M, Schroeder C, Hube-Magg C, Kluth M, Lang D, Simon R, Moller-Koop C, Steurer S, Sauter G, Jacobsen F, Buscheck F, Wittmer C, Clauditz T, Krech T, Tsourlakis MC, Minner S, Huland H, Graefen M, Budaus L, Thederan I, Salomon G, Schlomm T, Wilczak W (2017) High-level gamma-glutamyl-hydrolase (ggh) expression is linked to poor prognosis in ERG negative prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci 18(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020286
Grupp K, Jedrzejewska K, Tsourlakis MC, Koop C, Wilczak W, Adam M, Quaas A, Sauter G, Simon R, Izbicki JR, Graefen M, Huland H, Schlomm T, Minner S, Steurer S (2013) High mitochondria content is associated with prostate cancer disease progression. Mol Cancer 12(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-145
Kluth M, Runte F, Barow P, Omari J, Abdelaziz ZM, Paustian L, Steurer S, Christina Tsourlakis M, Fisch M, Graefen M, Tennstedt P, Huland H, Michl U, Minner S, Sauter G, Simon R, Adam M, Schlomm T (2015) Concurrent deletion of 16q23 and PTEN is an independent prognostic feature in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 137(10):2354–2363. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29613
Semba S, Satake S, Matsushita M, Yokozaki H (2009) Phosphatase activity of nuclear PTEN is required for CDX2-mediated intestinal differentiation of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett 274(1):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.019
Egevad L, Ahmad AS, Algaba F, Berney DM, Boccon-Gibod L, Comperat E, Evans AJ, Griffiths D, Grobholz R, Kristiansen G, Langner C, Lopez-Beltran A, Montironi R, Moss S, Oliveira P, Vainer B, Varma M, Camparo P (2013) Standardization of Gleason grading among 337 European pathologists. Histopathology 62(2):247–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12008
Wilczak W, Wittmer C, Clauditz T, Minner S, Steurer S, Buscheck F, Krech T, Lennartz M, Harms L, Leleu D, Ahrens M, Ingwerth S, Gunther CT, Koop C, Simon R, Jacobsen F, Tsourlakis MC, Chirico V, Hoflmayer D, Vettorazzi E, Haese A, Steuber T, Salomon G, Michl U, Budaus L, Tilki D, Thederan I, Fraune C, Gobel C, Henrich MC, Juhnke M, Moller K, Bawahab AA, Uhlig R, Adam M, Weidemann S, Beyer B, Huland H, Graefen M, Sauter G, Schlomm T (2018) Marked prognostic impact of minimal lymphatic tumor spread in prostate cancer. Eur Urol 74(3):376–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.05.034
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Inge Brandt, Melanie Witt, Maren Eisenberg and Sünje Seekamp for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK, TE, RS, CHM, GS: contributed to conception, design, data collection, data analysis and manuscript writing. SW, MK, DD, FB, DH, TSC, AML, EB, WW, AH, MCT, SS: conception and design, collection of samples. SK, CF, SM: immunohistochemistry analysis. TS, BB, TSt, MG, RS: collection and data analysis. TE, GS, MF: study supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
The usage of archived diagnostic left-over tissues for manufacturing of TMAs and their analysis for research purposes as well as patient data analysis has been approved by local laws (HmbKHG, §12,1) and by the local ethics committee (Ethics commission Hamburg, WF-049/09). All work has been carried out in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kind, S., Büscheck, F., Höflmayer, D. et al. Claudin-1 upregulation is associated with favorable tumor features and a reduced risk for biochemical recurrence in ERG-positive prostate cancer. World J Urol 38, 2185–2196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-03017-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-03017-w