Abstract
Purpose
Local injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is postulated to work by delivering growth factors and cytokines that recruit healer cells and enhance recovery process at the injection site. As new scar formation leads to stricture recurrence after internal urethrotomy, we proposed to improve post-internal urethrotomy stricture recurrence rate by injecting local submucosal PRP at the time of urethrotomy.
Methods
From July 2015 to June 2018, 87 male patients with symptomatic bulbar urethral stricture (diagnosed by retrograde urethrography) randomized into two groups of internal urethrotomy and submucosal normal saline injection (control group, 43 patients), and internal urethrotomy with submucosal autologous platelet-rich plasma injection (PRP injection group, 44 patients). According to the endpoint, which happened sooner, each patient was followed at 3-month intervals for 2 years after internal urethrotomy or until urethral stricture recurrence.
Results
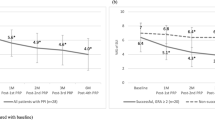
Twelve-month recurrence rates were 26.82 and 9.09% in the control and the PRP injection groups, respectively (p 0.032). After 2 years of follow-up, stricture recurrence was identified in 18 (43.90%) and 9 (21.95%) patients in the control and the PRP injection groups, respectively (p 0.34).
Conclusion
In our study, submucosal PRP injection at the site of internal urethrotomy decreased the rate of stricture recurrence a year after the intervention. This protective effect lasted for 24 months, at least. Submucosal PRP injection at the time of internal urethrotomy also decreased the length of stricture in case of recurrence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sievert KD, Selent-Stier C, Wiedemann J, Greiner TO, Amend B, Stenzl A, Feil G, Seibold J (2012) Introducing a large animal model to create urethral stricture similar to human stricture disease: a comparative experimental microscopic study. J Urol 187(3):1101–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.10.132
Santucci RA, Joyce GF, Wise M (2007) Male urethral stricture disease. J Urol 177(5):1667–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.01.041
Tritschler S, Roosen A, Fullhase C, Stief CG, Rubben H (2013) Urethral stricture: etiology, investigation and treatments. Dtsch Arztebl Int 110(13):220–226. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2013.0220
Albers P, Fichtner J, Bruhl P, Muller SC (1996) Long-term results of internal urethrotomy. J Urol 156(5):1611–1614
Pansadoro V, Emiliozzi P (1996) Internal urethrotomy in the management of anterior urethral strictures: long-term followup. J Urol 156(1):73–75
Steenkamp JW, Heyns CF, de Kock ML (1997) Internal urethrotomy versus dilation as treatment for male urethral strictures: a prospective, randomized comparison. J Urol 157(1):98–101
Wallace BJ, Cooper TP, Tremann JA, Ansell JS (1978) Results of large-caliber internal urethrotomy. Urology 11(4):366–368
Sampson S, Gerhardt M, Mandelbaum B (2008) Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries: a review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 1(3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-008-9032-5
Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W, den Oudsten BL (2011) Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 39(6):1200–1208. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546510397173
Hall MP, Band PA, Meislin RJ, Jazrawi LM, Cardone DA (2009) Platelet-rich plasma: current concepts and application in sports medicine. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 17(10):602–608
Mishra A, Pavelko T (2006) Treatment of chronic elbow tendinosis with buffered platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med 34(11):1774–1778. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546506288850
Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ, Gosens T (2010) Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 38(2):255–262. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546509355445
Sampson S, Gerhardt M, Mandelbaum B (2008) Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries: a review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 1(3–4):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-008-9032-5
Dragoo JL, Wasterlain AS, Braun HJ, Nead KT (2014) Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 42(3):610–618. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546513518416
Tavukcu H, AytaÇ O, Atug F, Alev B, Cevik O, Yarat A, Cetinel S, Sener G, Kulaksizoglu H (2017) Mp94-01 protective effect of platelet-rich plasma on urethral stricture model of male rats. J Urol 197(4):e1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.02.2904
Amable PR, Carias RBV, Teixeira MVT, da Cruz Pacheco I, Corrêa do Amaral RJF, Granjeiro JM, Borojevic R (2013) Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Ther 4(3):67–67. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt218
Gosain A, DiPietro LA (2004) Aging and wound healing. World J Surg 28(3):321–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-003-7397-6
Broughton G 2nd, Janis JE, Attinger CE (2006) The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(7 Suppl):12s–34s. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000225430.42531.c2
Campos AC, Groth AK, Branco AB (2008) Assessment and nutritional aspects of wound healing. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11(3):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e3282fbd35a
Guo S, Dipietro LA (2010) Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res 89(3):219–229. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509359125
Amable PR, Carias RBV, Teixeira MVT, da Cruz Pacheco Í, Corrêa do Amaral RJF, Granjeiro JM, Borojevic R (2013) Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Ther 4(3):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt218
Amable PR, Carias RBV, Teixeira MVT, da Cruz Pacheco Í, Corrêa do Amaral RJF, Granjeiro JM, Borojevic R (2013) Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Ther 4(3):67–67. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt218
Dawood AS, Salem HA (2018) Current clinical applications of platelet-rich plasma in various gynecological disorders: an appraisal of theory and practice. Clin Exp Reprod Med 45(2):67–74. https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2018.45.2.67
Albanese A, Licata ME, Polizzi B, Campisi G (2013) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in dental and oral surgery: from the wound healing to bone regeneration. Immun Ageing I A 10:23–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4933-10-23
Gkini MA, Kouskoukis AE, Tripsianis G, Rigopoulos D, Kouskoukis K (2014) Study of platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia through an one-year period. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 7(4):213–219. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.150743
Scarcia M, Maselli FP, Cardo G, Ludovico GM (2016) The use of autologous platelet rich plasma gel in bulbar and penile buccal mucosa urethroplasty: preliminary report of our first series. Arch Ital Urol Androl 88(4):274–278. https://doi.org/10.4081/aiua.2016.4.274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR: protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing. RB: protocol/project development, data collection or management. RB: data collection or management, data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors whose names are listed certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The protocol of this research was approved by the research ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran on April 7, 2015. All therapeutic and diagnostic interventions performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional (Shiraz University of Medical Sciences) and national (Iran) research committee, and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration of the World Medical Association and its later amendments. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before entering the study.
Data sharing statement
Data are available for bonafide researchers who request it from the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, M., Badiei, R. & Badiei, R. The effect of platelet-rich plasma injection on post-internal urethrotomy stricture recurrence. World J Urol 37, 1959–1964 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2597-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2597-8