Abstract
Purpose
Prostate cancer chemoresistance is a major contributor to the poor survival of patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in regulating cancer resistance. Here we aim to explore the role and mechanism of miR-199a in regulating prostate cancer resistance.
Methods
MiR-199a expressions in human prostate cancer tissues and cell lines were investigated with real-time PCR (RT-PCR). MiR-199a was ectopically overexpressed in PC3 cells, and resistance to paclitaxel (PTX) was evaluated consequently. The interaction between miR-199a and the oncogene Yamaguchi sarcoma viral homolog 1 (YES1) was assessed after miR-199a overexpression. YES1 was ectopically overexpressed, followed by evaluation of PTX resistance. The efficacy of miR-199a as a therapeutic agent was also investigated in vivo.
Results
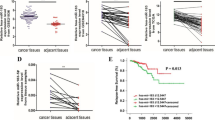
Downregulation of miR-199a was characteristic of prostate cancer, particularly recurrent cancers. MiR-199a was suppressed in PTX-resistant cell line. Overexpression of miR-199a inhibited PTX resistance. YES1 was a target of miR-199a, and overexpression of YES1 reversed the effect of miR-199a in suppressing PTX resistance. In vivo, miR-199a increased tumor PTX sensitivity.
Conclusions
The downregulation of miR-199a contributes to PTX resistance in prostate cancer. YES1 mediates the regulation of miR-199a in prostate cancer PTX resistance. This miR-199a replacement therapy has potential to overcome PTX resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pienta KJ, Smith DC (2005) Advances in prostate cancer chemotherapy: a new era begins. CA Cancer J Clin 55:300–318
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, Mason M, Matveev V, Wiegel T, Zattoni F (2014) EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol 65:467–479
Grünwald V, DeGraffenried L, Russel D, Friedrichs WE, Ray RB, Hidalgo M (2002) Inhibitors of mTOR reverse doxorubicin resistance conferred by PTEN status in prostate cancer cells. Can Res 62:6141–6145
Hu C-MJ, Zhang L (2012) Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 83:1104–1111
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao J-J, O’Donnell JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV (2008) MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res 68:425–433
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B, Roy S, Datta J, Shapiro CL, Jacob S, Majumder S (2008) MicroRNA-221/222 confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 283:29897–29903
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Kong D, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2010) Targeting miRNAs involved in cancer stem cell and EMT regulation: an emerging concept in overcoming drug resistance. Drug Resist updates 13:109–118
Fornari F, Milazzo M, Chieco P, Negrini M, Calin GA, Grazi GL, Pollutri D, Croce CM, Bolondi L, Gramantieri L (2010) MiR-199a-3p regulates mTOR and c-Met to influence the doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 70:5184–5193. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0145
Henry JC, Park JK, Jiang JM, Kim JH, Roberts LR, Nagorney DM, Banerjee S, Schmittgen TD (2011) miR-199a-3p targets CD44 and reduces proliferation of CD44 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2011-1183
Chen R, Alvero A, Silasi D, Kelly M, Fest S, Visintin I, Leiser A, Schwartz P, Rutherford T, Mor G (2008) Regulation of IKKβ by miR-199a affects NF-κB activity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 27:4712–4723
Yamamoto H, Takeda T, Kanzaki H, Suzawa K, Namba K, Sato H, Torigoe H, Watanabe M, Maki Y, Soh J (2016) Yes1 is the key molecule for the resistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer, and dasatinib overcomes the resistance. AACR. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2016-4392
Liu L, Yang J, Zhu X, Li D, Lv Z, Zhang X (2016) Long noncoding RNA H19 competitively binds miR-17-5p to regulate YES1 expression in thyroid cancer. FEBS J 283:2326–2339
Giannakakou P, Sackett DL, Kang YK, Zhan ZR, Buters JTM, Fojo T, Poruchynsky MS (1997) Paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian cancer cells have mutant beta-tubulins that exhibit impaired paclitaxel-driven polymerization. J Biol Chem 272:17118–17125. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.27.17118
Chen D, Guo WJ, Qiu ZP, Wang QF, Li Y, Liang LH, Liu L, Huang SL, Zhao YJ, He XH (2015) MicroRNA-30d-5p inhibits tumour cell proliferation and motility by directly targeting CCNE2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett 362:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.041
Carlsson S, Assel M, Sjoberg D, Ulmert D, Hugosson J, Lilja H, Vickers A (2014) Influence of blood prostate specific antigen levels at age 60 on benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening: population based cohort study. Bmj 348:g2296
Xu N, Zhang JJ, Shen CH, Luo Y, Xia L, Xue F, Xia Q (2012) Cisplatin-induced downregulation of miR-199a-5p increases drug resistance by activating autophagy in HCC cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423:826–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.048
Cheng W, Liu T, Wan X, Gao Y, Wang H (2012) MicroRNA-199a targets CD44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells. FEBS J 279:2047–2059
Pillai RS (2005) MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? Rna 11:1753–1761
Bader AG (2012) miR-34—a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet 3:120
Bouchie A (2013) First microRNA mimic enters clinic. Nat Res 31(7):577
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang H-W, Chang T-C, Vivekanandan P, Torbenson M, Clark KR (2009) Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137:1005–1017
Gandhi NS, Tekade RK, Chougule MB (2014) Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: current progress and advances. J Controll Release 194:238–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LC and HC contributed to data collection and manuscript writing. YF helped in project development and manuscript writing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by The Third Batch of young Chinese Name Training Program of LongHua Hospital Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Chen Lei). Subject number: RC-2017-01-14; Shanghai Municipal Health and Family Planning Commission Special Subject of Chinese Medicine Research: Inhibitory Effect of Indirubin on Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer DU145 cells. Subject number: 2016JP014.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors declare competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Cao, H. & Feng, Y. MiR-199a suppresses prostate cancer paclitaxel resistance by targeting YES1. World J Urol 36, 357–365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2143-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2143-0