Abstract
Purpose
Bladder cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy in urinary system. The prognosis of metastatic BC is poor, but there remains no reliable marker to early detect metastasis. Dysregulated prenylated protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are commonly associated with cancer metastasis. From a published BC transcriptome, we identified that PTP IVA3 (PTP4A3) was the most significantly upregulated gene implicated in tumor progression among genes related to prenylated PTPs. We therefore analyzed PTP4A3 expression in our well-characterized cohort of BC.
Methods
By immunohistochemistry, PTP4A3 expression was determined using H-score. PTP4A3 expression of 295 BCs was compared with clinicopathological parameters, and the effect of PTP4A3 on cancer-specific survival (CSS) and metastasis-free survival (MFS) was also examined. Two independent sets of BCs were used to assess PTP4A3 protein and transcript expression in normal urothelium and different stage tumors.
Results
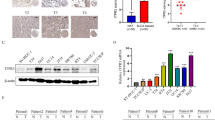
PTP4A3 overexpression was significantly associated with higher pT stage (P < 0.001), nodal metastasis (P < 0.001), vascular invasion (P < 0.001), and perineural invasion (P = 0.021). In multivariate analysis, PTP4A3 overexpression was an independent predictor for CSS (P < 0.001) and MFS (P = 0.007). Notably, the difference in CSS and MFS between high and low PTP4A3-expressing tumors was also significant in muscle-invasive BCs. PTP4A3 protein expression showed significant and stepwise increments from normal urothelium to noninvasive BC, invasive BC, and metastatic foci (P < 0.001). PTP4A3 transcript was also obviously upregulated in high-stage BC (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
PTP4A3 may play a role in BC oncogenesis and is a predictive marker of metastasis. PTP4A3 overexpression represents an independent prognosticator for BC, suggesting its potential theranostic value.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65(1):5–29
Lai MN, Wang SM, Chen PC, Chen YY, Wang JD (2010) Population-based case-control study of Chinese herbal products containing aristolochic acid and urinary tract cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(3):179–186
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW, Kurth K (2006) Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol 49(3):465–466
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU, Feldman AS (2009) Bladder cancer. Lancet 374(9685):239–249
Latini DM, Lerner SP, Wade SW, Lee DW, Quale DZ (2010) Bladder cancer detection, treatment and outcomes: opportunities and challenges. Urology 75(2):334–339
Ostman A, Hellberg C, Bohmer FD (2006) Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(4):307–320
Zeng Q, Si X, Horstmann H, Xu Y, Hong W, Pallen CJ (2000) Prenylation-dependent association of protein-tyrosine phosphatases PRL-1, -2, and -3 with the plasma membrane and the early endosome. J Biol Chem 275(28):21444–21452
Zeng Q, Dong JM, Guo K, Li J, Tan HX, Koh V, Pallen CJ, Manser E, Hong W (2003) PRL-3 and PRL-1 promote cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Res 63(11):2716–2722
Saha S, Bardelli A, Buckhaults P, Velculescu VE, Rago C, St Croix B, Romans KE, Choti MA, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2001) A phosphatase associated with metastasis of colorectal cancer. Science 294(5545):1343–1346
Hao RT, Zhang XH, Pan YF, Liu HG, Xiang YQ, Wan L, Wu XL (2010) Prognostic and metastatic value of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 in invasive breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(9):1349–1357
Ming J, Liu N, Gu Y, Qiu X, Wang EH (2009) PRL-3 facilitates angiogenesis and metastasis by increasing ERK phosphorylation and up-regulating the levels and activities of Rho-A/C in lung cancer. Pathology 41(2):118–126
Ooki A, Yamashita K, Kikuchi S, Sakuramoto S, Katada N, Watanabe M (2010) Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 as a convergent therapeutic target for lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer J 127(3):543–554
Wang Z, Cai SR, He YL, Zhan WH, Chen CQ, Cui J, Wu WH, Wu H, Song W, Zhang CH, Peng JJ, Huang XH (2009) High expression of PRL-3 can promote growth of gastric cancer and exhibits a poor prognostic impact on patients. Ann Surg Oncol 16(1):208–219
Xu Y, Zhu M, Zhang S, Liu H, Li T, Qin C (2010) Expression and prognostic value of PRL-3 in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 16(2):169–175
Liang PI, Wang YH, Wu TF, Wu WR, Liao AC, Shen KH, Hsing CH, Shiue YL, Huang HY, Hsu HP, Chen LT, Lin CY, Tai C, Wu JY, Li CF (2013) IGFBP-5 overexpression as a poor prognostic factor in patients with urothelial carcinomas of upper urinary tracts and urinary bladder. J Clin Pathol 66(7):573–582
McCarty KS Jr, Szabo E, Flowers JL, Cox EB, Leight GS, Miller L, Konrath J, Soper JT, Budwit DA, Creasman WT et al (1986) Use of a monoclonal anti-estrogen receptor antibody in the immunohistochemical evaluation of human tumors. Cancer Res 46(8 Suppl):4244s–4248s
Li CF, Fang FM, Lan J, Wang JW, Kung HJ, Chen LT, Chen TJ, Li SH, Wang YH, Tai HC, Yu SC, Huang HY (2014) AMACR amplification in myxofibrosarcomas: a mechanism of overexpression that promotes cell proliferation with therapeutic relevance. Clin Cancer Res 20(23):6141–6152
Basak S, Jacobs SB, Krieg AJ, Pathak N, Zeng Q, Kaldis P, Giaccia AJ, Attardi LD (2008) The metastasis-associated gene Prl-3 is a p53 target involved in cell-cycle regulation. Mol Cell 30(3):303–314
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang JP, Zeng Q (2007) PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals through PI3 K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 67(7):2922–2926
Fiordalisi JJ, Keller PJ, Cox AD (2006) PRL tyrosine phosphatases regulate rho family GTPases to promote invasion and motility. Cancer Res 66(6):3153–3161
Forte E, Orsatti L, Talamo F, Barbato G, De Francesco R, Tomei L (2008) Ezrin is a specific and direct target of protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL-3. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783(2):334–344
Peng L, Xing X, Li W, Qu L, Meng L, Lian S, Jiang B, Wu J, Shou C (2009) PRL-3 promotes the motility, invasion, and metastasis of LoVo colon cancer cells through PRL-3-integrin beta1-ERK1/2 and-MMP2 signaling. Mol Cancer 8:110
Liang F, Liang J, Wang WQ, Sun JP, Udho E, Zhang ZY (2007) PRL3 promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down-regulation of Csk leading to Src activation. J Biol Chem 282(8):5413–5419
Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell 14(6):818–829
Kato H, Semba S, Miskad UA, Seo Y, Kasuga M, Yokozaki H (2004) High expression of PRL-3 promotes cancer cell motility and liver metastasis in human colorectal cancer: a predictive molecular marker of metachronous liver and lung metastases. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7318–7328
Chan CH, Li CF, Yang WL, Gao Y, Lee SW, Feng Z, Huang HY, Tsai KK, Flores LG, Shao Y, Hazle JD, Yu D, Wei W, Sarbassov D, Hung MC, Nakayama KI, Lin HK (2012) The Skp2-SCF E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin sensitivity, and tumorigenesis. Cell 149(5):1098–1111
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Kaohsiung Medical University “Aim for the Top Universities (KMU-TP104E26, KMU-TP103G00, KMU-TP103G01, KMU-TP103G04, KMU-TP103G05)”, the health and welfare surcharge of tobacco products, Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW104-TDU-B-212-124-003), and Kaohsiung Municipal Ta-Tung Hospital (kmtth-102-014).
Authors’ contribution
HC Yeh contributed to data management, analyzed the data, and wrote and edited the manuscript. CN Huang contributed to data management and edited the manuscript. CC Li contributed to data collection and management. LL Chang edited the manuscript. HH Lin and HL Ke contributed to data management. AM Huang contributed to the project development. PI Liang involved in histopathological examination. CF Li involved in project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. WJ Wu contributed to data management and edited the manuscript.
Ethical standards
This research was approved by the Institute Review Board of the Chi Mei Medical Center (IRB10302015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All authors gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, HC., Huang, CN., Li, CC. et al. Overexpression of PTP4A3 is associated with metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in bladder cancer. World J Urol 34, 835–846 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1698-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1698-x