Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of urgent percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL) for acute kidney injury secondary to bilateral upper urinary stones in infants.
Methods
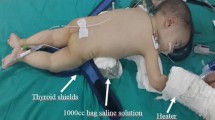
A total of seven infants (five boys and two girls), aged from 5 to 12 months, underwent urgent PNL for calculus anuria from September 2011 to March 2013. The initial blood test revealed acute renal injury in all infants. After correcting electrolyte imbalance and acid–base status through medical treatment in a short time without dialysis, all urgent PNL procedures were performed with 16F percutaneous access and small-diameter nephroscopes designed specifically for pediatric surgery on the side with the more dilated pelvis. Stones were fragmented with a pneumatic lithotripter.
Results
Stones were completely removed from the operative side kidneys. The operating time ranged from 35 to 57 min. Blood BUN, serum creatinine, and electrolyte levels returned to normal on postoperative 36 h. There were no major perioperative or postoperative complications and deaths.
Conclusions
When performed by experienced endourologists, urgent PNL is a safe and effective procedure in infants for acute kidney injury secondary to bilateral upper urinary stones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elgammal MA, Abdel-Kader MS, Kurkar A, Mohammed OA, Hammouda HM (2009) Management of calculus anuria in children: experience of 54 cases. J Pediatr Urol 5:462–465
Dogan HS, Kilicarslan H, Kordan Y, Celen S, Oktay B (2011) Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children: does age matter? World J Urol 29:725–729
Salah MA, Tóth C, Khan AM, Holman E (2004) Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children: experience with 138 cases in a developing country. World J Urol 22:277–280
Unsal A, Resorlu B, Kara C, Bozkurt OF, Ozyuvali E (2010) Safety and efficacy of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in infants, preschool age, and older children with different sizes of instruments. Urology 76:247–252
Bhageria A, Nayak B, Seth A, Dogra PN, Kumar R (2013) Paediatric percutaneous nephrolithotomy: single-centre 10-year experience. J Pediatr Urol 9:472–475
Salerno A, Nappo SG, Matarazzo E, De Dominicis M, Caione P (2013) Treatment of pediatric renal stones in a Western country: a changing pattern. J Pediatr Surg 48:835–839
Resorlu B, Unsal A, Tepeler A, Atis G, Tokatli Z, Oztuna D, Armagan A, Gurbuz C, Caskurlu T, Saglam R (2012) Comparison of retrograde intrarenal surgery and mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children with moderate-size kidney stones: results of multi-institutional analysis. Urology 80:519–523
Zeng G, Zhao Z, Wan S, Zhong W, Wu W (2013) Comparison of children versus adults undergoing mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy: large-scale analysis of a single institution. PLoS One 8:e66850
Zeng G, Jia J, Zhao Z, Wu W, Zhao Z, Zhong W (2012) Treatment of renal stones in infants: comparing extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urol Res 40:599–603
Onal B, Dogan HS, Satar N, Bilen CY, Güneş A, Ozden E, Ozturk A, Demirci D, Istanbulluoğlu O, Gurocak S, Nazli O, Tanriverdi O, Kefi A, Korgali E, Silay MS, Inci K, Izol V, Altintas R, Kilicarslan H, Sarikaya S, Yalcin V, Aygun C, Gevher F, Aridogan IA, Tekgul S (2014) Factors affecting complication rates of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children: results of multi-institutional retrospective analysis by Pediatric Stone Disease Study Group of Turkish Pediatric Urology Society. J Urol 191:777–782
Ozturk A, Guven S, Piskin M, Kilinc M, Celik J, Arslan M (2012) Management of multiple stones in a single session using minimally invasive methods in infants with renal failure: renal salvage. Int Urol Nephrol 44:3–6
Nalcacioglu H, Ozden E, Genc G, Yakupoglu YK, Sarikaya S, Ozkaya O (2013) An uncommon cause of acute kidney injury in young children: cystinuria. J Pediatr Urol 9:e58–e63
Gallego N, Gallego A, Pascual J, Liano F, Estepa R, Ortuno J (1993) Prognosis of children with acute renal failure: a study of 138 cases. Nephron 64:399–404
Gupta S, Gulati M, Shankar KU, Rungta U, Suri S (1997) Percutaneous nephrostomy with real-time sonographic guidance. Acta Radiol 38:454–457
Li CG, Fan ZL, Liu H, Sun WB, Liu YJ, Li ML (2008) A comparison of curative effects of percutaneous nephrostomy and open surgery in the management of postrenal acute renal failure. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 20:565–567 Chinese
Ziada AM, Sarhan OM, Habib EI, ElTabie N, El Sheemy M, Morsi HA, ElGhonemy MN, Helmy T, Dawaba M, Ghali A, Eissa MA (2011) Assessment of recoverability of kidney function in children with obstructive calcular anuria: multicenter study. J Pediatr Urol 7:252–256
Bogris S, Papatsoris AG (2010) Status quo of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children. Urol Res 38:1–5
Baştuğ F, Gündüz Z, Tülpar S, Poyrazoğlu H, Düşünsel R (2013) Urolithiasis in infants: evaluation of risk factors. World J Urol 31:1117–1122
Acar B, Arikan FI, Emeksiz S, Dallar Y (2008) Risk factors for nephrolithiasis in children. World J Urol 26:627–630
Kotb S, Elsheemy MS, Morsi HA, Zakaria T, Salah M, Eissa MA (2013) Renal recoverability in infants with obstructive calcular anuria: is it better than in older children? J Pediatr Urol 9:1178–1182
Woodside JR, Stevens GF, Stark GL, Borden TA, Ball WS (1985) Percutaneous stone removal in children. J Urol 134:1166–1167
Jackman SV, Hedican SP, Peters CA, Docimo SG (1998) Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in infants and preschool age children: experience with a new technique. Urology 52:697–701
Mahmud M, Zaidi Z (2004) Percutaneous nephrolithotomy in children before school age: experience of a Pakistani centre. BJU Int 94:1352–1354
Tander B, Baris S, Karakaya D, Ariturk E, Rizalar R, Bernay F (2005) Risk factors influencing inadvertent hypothermia in infants and neonates during anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth 15:574–579
Vorrakitpokatorn P, Permtongchuchai K, Raksamani EO, Phettongkam A (2006) Perioperative complications and risk factors of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Med Assoc Thai 89:826–833
Acknowledgments
Support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 81200504).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The study was approved by our ethics committee, and all infants’ parents were provided with an informed written consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Li, WH., Hasimu, S. et al. Urgent percutaneous nephrolithotomy for acute kidney injury secondary to bilateral stones: Is it safe and effective in infants?. World J Urol 33, 1345–1349 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1445-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1445-8