Abstract
Purpose
In recent years, various imaging modalities have been developed to improve diagnosis, staging, and localization of early-stage prostate cancer (PCa).
Methods
A MEDLINE literature search of the time frame between 01/2007 and 06/2013 was performed on imaging of localized PCa.
Results
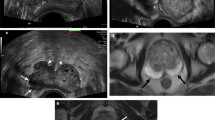
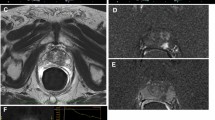
Conventional transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is mainly used to guide prostate biopsy. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound is based on the assumption that PCa tissue is hypervascularized and might be better identified after intravenous injection of a microbubble contrast agent. However, results on its additional value for cancer detection are controversial. Computer-based analysis of the transrectal ultrasound signal (C-TRUS) appears to detect cancer in a high rate of patients with previous biopsies. Real-time elastography seems to have higher sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value than conventional TRUS. However, the method still awaits prospective validation. The same is true for prostate histoscanning, an ultrasound-based method for tissue characterization. Currently, multiparametric MRI provides improved tissue visualization of the prostate, which may be helpful in the diagnosis and targeting of prostate lesions. However, most published series are small and suffer from variations in indication, methodology, quality, interpretation, and reporting.
Conclusions
Among ultrasound-based techniques, real-time elastography and C-TRUS seem the most promising techniques. Multiparametric MRI appears to have advantages over conventional T2-weighted MRI in the detection of PCa. Despite these promising results, currently, no recommendation for the routine use of these novel imaging techniques can be made. Prospective studies defining the value of various imaging modalities are urgently needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shepherd D, Keetch DW, Humphrey PA, Smith DS, Stahl D (1996) Repeat biopsy strategy in men with isolated prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on prostate needle biopsy. J Urol 156 (2 Pt 1):460–462; discussion 462–463
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, Mottet N, Schmid HP, van der Kwast T, Wiegel T, Zattoni F, European Association of U (2011) EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol 59(1):61–71. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.039
Holm HH, Gammelgaard J (1981) Ultrasonically guided precise needle placement in the prostate and the seminal vesicles. J Urol 125(3):385–387
Lee HY, Lee HJ, Byun SS, Lee SE, Hong SK, Kim SH (2009) Classification of focal prostatic lesions on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and the accuracy of TRUS to diagnose prostate cancer. Korean J Radiol 10(3):244–251. doi:10.3348/kjr.2009.10.3.244
Tamsel S, Killi R, Hekimgil M, Altay B, Soydan S, Demirpolat G (2008) Transrectal ultrasound in detecting prostate cancer compared with serum total prostate-specific antigen levels. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 52(1):24–28. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1673.2007.01906.x
Dahnert WF, Hamper UM, Eggleston JC, Walsh PC, Sanders RC (1986) Prostatic evaluation by transrectal sonography with histopathologic correlation: the echopenic appearance of early carcinoma. Radiology 158(1):97–102
Brock M, von Bodman C, Sommerer F, Loppenberg B, Klein T, Deix T, Palisaar JR, Noldus J, Eggert T (2011) Comparison of real-time elastography with grey-scale ultrasonography for detection of organ-confined prostate cancer and extra capsular extension: a prospective analysis using whole mount sections after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 108(8 Pt 2):E217–E222. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10209.x
Lee F, Siders DB, Torp-Pedersen ST, Kirscht JL, McHugh TA, Mitchell AE (1991) Prostate cancer: transrectal ultrasound and pathology comparison. A preliminary study of outer gland (peripheral and central zones) and inner gland (transition zone) cancer. Cancer 67(4 Suppl):1132–1142
Frauscher F, Klauser A, Halpern EJ, Horninger W, Bartsch G (2001) Detection of prostate cancer with a microbubble ultrasound contrast agent. Lancet 357(9271):1849–1850
Mitterberger M, Horninger W, Pelzer A, Strasser H, Bartsch G, Moser P, Halpern EJ, Gradl J, Aigner F, Pallwein L, Frauscher F (2007) A prospective randomized trial comparing contrast-enhanced targeted versus systematic ultrasound guided biopsies: impact on prostate cancer detection. Prostate 67(14):1537–1542. doi:10.1002/pros.20639
Mitterberger MJ, Aigner F, Horninger W, Ulmer H, Cavuto S, Halpern EJ, Frauscher F (2010) Comparative efficiency of contrast-enhanced colour Doppler ultrasound targeted versus systematic biopsy for prostate cancer detection. Eur Radiol 20(12):2791–2796. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1860-1
Uemura H, Sano F, Nomiya A, Yamamoto T, Nakamura M, Miyoshi Y, Miki K, Noguchi K, Egawa S, Homma Y, Kubota Y (2012) Usefulness of perflubutane microbubble-enhanced ultrasound in imaging and detection of prostate cancer: phase II multicenter clinical trial. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0833-1
Taverna G, Morandi G, Seveso M, Giusti G, Benetti A, Colombo P, Minuti F, Grizzi F, Graziotti P (2011) Colour Doppler and microbubble contrast agent ultrasonography do not improve cancer detection rate in transrectal systematic prostate biopsy sampling. BJU Int 108(11):1723–1727. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10199.x
Loch T (2007) Computerized transrectal ultrasound (C-TRUS) of the prostate: detection of cancer in patients with multiple negative systematic random biopsies. World J Urol 25(4):375–380. doi:10.1007/s00345-007-0181-8
Grabski B, Baeurle L, Loch A, Wefer B, Paul U, Loch T (2011) Computerized transrectal ultrasound of the prostate in a multicenter setup (C-TRUS-MS): detection of cancer after multiple negative systematic random and in primary biopsies. World J Urol 29(5):573–579. doi:10.1007/s00345-011-0713-0
Walz J, Loch T, Salomon G, Wijkstra H (2013) Imaging of the prostate. Urologe A 52(4):490–496. doi:10.1007/s00120-012-3103-3
Strunk T, Decker G, Willinek W, Mueller SC, Rogenhofer S (2012) Combination of C-TRUS with multiparametric MRI: potential for improving detection of prostate cancer. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0924-z
Walz J, Marcy M, Pianna JT, Brunelle S, Gravis G, Salem N, Bladou F (2011) Identification of the prostate cancer index lesion by real-time elastography: considerations for focal therapy of prostate cancer. World J Urol 29(5):589–594. doi:10.1007/s00345-011-0688-x
Zhu Y, Chen Y, Qi T, Jiang J, Qi J, Yu Y, Yao X, Guan W (2012) Prostate cancer detection with real-time elastography using a bi-plane transducer: comparison with step section radical prostatectomy pathology. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0922-1
Pallwein L, Mitterberger M, Pinggera G, Aigner F, Pedross F, Gradl J, Pelzer A, Bartsch G, Frauscher F (2008) Sonoelastography of the prostate: comparison with systematic biopsy findings in 492 patients. Eur J Radiol 65(2):304–310. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.03.032
Heinzelbecker J, Weiss C, Pelzer AE (2012) A learning curve assessment of real-time sonoelastography of the prostate. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0897-y
Brock M, Eggert T, Palisaar RJ, Roghmann F, Braun K, Loppenberg B, Sommerer F, Noldus J, von Bodman C (2013) Multiparametric ultrasound of the prostate: adding contrast enhanced ultrasound to real-time elastography to detect histopathologically confirmed cancer. J Urol 189(1):93–98. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.183
Simmons LA, Autier P, Zat’ura F, Braeckman J, Peltier A, Romic I, Stenzl A, Treurnicht K, Walker T, Nir D, Moore CM, Emberton M (2012) Detection, localisation and characterisation of prostate cancer by Prostate HistoScanning™. BJU Int 110(1):28–35. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10734.x
Hamann MF, Hamann C, Schenk E, Al-Najar A, Naumann CM, Junemann KP (2013) Computer-aided (HistoScanning) biopsies versus conventional transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsies: do targeted biopsy schemes improve the cancer detection rate? Urology 81(2):370–375. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.08.072
Javed S, Chadwick E, Beveridge S, Bott S, Eden C, Langley S (2013) Does Prostate HistoScanning™ accurately identify prostate cancer, measure tumour volume and assess pathological stage prior to radical prostatectomy? J Clin Urol. doi:10.1177/2051415813489682
Salomon G, Spethmann J, Beckmann A, Autier P, Moore C, Durner L, Sandmann M, Haese A, Schlomm T, Michl U, Heinzer H, Graefen M, Steuber T (2013) Accuracy of HistoScanning for the prediction of a negative surgical margin in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 111(1):60–66. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11396.x
Hovels AM, Heesakkers RA, Adang EM, Jager GJ, Strum S, Hoogeveen YL, Severens JL, Barentsz JO (2008) The diagnostic accuracy of CT and MRI in the staging of pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol 63(4):387–395. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2007.05.022
Probert JL, Glew D, Gillatt DA (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging in urology. BJU Int 83(3):201–214
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Hoeks C, Bouwense SA, Huisman H, Yakar D, van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Futterer JJ, Barentsz JO (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging guided prostate biopsy in men with repeat negative biopsies and increased prostate specific antigen. J Urol 183(2):520–527. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.10.022
Shimizu T, Nishie A, Ro T, Tajima T, Yamaguchi A, Kono S, Honda H (2009) Prostate cancer detection: the value of performing an MRI before a biopsy. Acta Radiol 50(9):1080–1088. doi:10.3109/02841850903216718
Graser A, Heuck A, Sommer B, Massmann J, Scheidler J, Reiser M, Mueller-Lisse U (2007) Per-sextant localization and staging of prostate cancer: correlation of imaging findings with whole-mount step section histopathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(1):84–90. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.0401
Haider MA, van der Kwast TH, Tanguay J, Evans AJ, Hashmi AT, Lockwood G, Trachtenberg J (2007) Combined T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI for localization of prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189(2):323–328. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2211
Roethke MC, Lichy MP, Kniess M, Werner MK, Claussen CD, Stenzl A, Schlemmer HP, Schilling D (2012) Accuracy of preoperative endorectal MRI in predicting extracapsular extension and influence on neurovascular bundle sparing in radical prostatectomy. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0826-0
Porcaro AB, Borsato A, Romano M, Sava T, Ghimenton C, Migliorini F, Monaco C, Rubilotta E, Antoniolli SZ, Lacola V, Montemezzi S (2012) Accuracy of preoperative endo-rectal coil magnetic resonance imaging in detecting clinical under-staging of localized prostate cancer. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0900-7
Xylinas E, Yates DR, Renard-Penna R, Seringe E, Bousquet JC, Comperat E, Bitker MO, Grenier P, Roupret M (2011) Role of pelvic phased array magnetic resonance imaging in staging of prostate cancer specifically in patients diagnosed with clinically locally advanced tumours by digital rectal examination. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-011-0811-z
Ellis JH, Tempany C, Sarin MS, Gatsonis C, Rifkin MD, McNeil BJ (1994) MR imaging and sonography of early prostatic cancer: pathologic and imaging features that influence identification and diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162(4):865–872. doi:10.2214/ajr.162.4.8141009
Girouin N, Mege-Lechevallier F, Tonina Senes A, Bissery A, Rabilloud M, Marechal JM, Colombel M, Lyonnet D, Rouviere O (2007) Prostate dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with simple visual diagnostic criteria: is it reasonable? Eur Radiol 17(6):1498–1509. doi:10.1007/s00330-006-0478-9
Delongchamps NB, Rouanne M, Flam T, Beuvon F, Liberatore M, Zerbib M, Cornud F (2011) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the detection and localization of prostate cancer: combination of T2-weighted, dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted imaging. BJU Int 107(9):1411–1418. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09808.x
Chesnais AL, Niaf E, Bratan F, Mege-Lechevallier F, Roche S, Rabilloud M, Colombel M, Rouviere O (2013) Differentiation of transitional zone prostate cancer from benign hyperplasia nodules: evaluation of discriminant criteria at multiparametric MRI. Clin Radiol. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2013.01.018
Sonn GA, Chang E, Natarajan S, Margolis DJ, Macairan M, Lieu P, Huang J, Dorey FJ, Reiter RE, Marks LS (2013) Value of targeted prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance-ultrasound fusion in men with prior negative biopsy and elevated prostate-specific antigen. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.03.025
Roethke M, Anastasiadis AG, Lichy M, Werner M, Wagner P, Kruck S, Claussen CD, Stenzl A, Schlemmer HP, Schilling D (2012) MRI-guided prostate biopsy detects clinically significant cancer: analysis of a cohort of 100 patients after previous negative TRUS biopsy. World J Urol 30(2):213–218. doi:10.1007/s00345-011-0675-2
Hoeks CM, Schouten MG, Bomers JG, Hoogendoorn SP, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Hambrock T, Vergunst H, Sedelaar JP, Futterer JJ, Barentsz JO (2012) Three-Tesla magnetic resonance-guided prostate biopsy in men with increased prostate-specific antigen and repeated, negative, random, systematic, transrectal ultrasound biopsies: detection of clinically significant prostate cancers. Eur Urol 62(5):902–909. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.01.047
Jin G, Su DK, Luo NB, Liu LD, Zhu X, Huang XY (2013) Meta-analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in detecting prostate cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr 37(2):195–202. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e3182801ae1
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Hricak H, Narayan P, Carroll P, Nelson SJ (1996) Three-dimensional H-1 MR spectroscopic imaging of the in situ human prostate with high (0.24–0.7-cm3) spatial resolution. Radiology 198(3):795–805
Zakian KL, Eberhardt S, Hricak H, Shukla-Dave A, Kleinman S, Muruganandham M, Sircar K, Kattan MW, Reuter VE, Scardino PT, Koutcher JA (2003) Transition zone prostate cancer: metabolic characteristics at 1H MR spectroscopic imaging—initial results. Radiology 229(1):241–247. doi:10.1148/radiol.2291021383
Umbehr M, Bachmann LM, Held U, Kessler TM, Sulser T, Weishaupt D, Kurhanewicz J, Steurer J (2009) Combined magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 55(3):575–590. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2008.10.019
Alcaraz A, Burgos FJ, Cozar JM, Gomez-Veiga F, Morote J, Solsona E, Unda M, Carballido J (2011) Prostate cancer in Spain: from guidelines to clinical practice. BJU Int 108(1):61–66. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09832.x
Picchio M, Briganti A, Fanti S, Heidenreich A, Krause BJ, Messa C, Montorsi F, Reske SN, Thalmann GN (2011) The role of choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the management of patients with prostate-specific antigen progression after radical treatment of prostate cancer. Eur Urol 59(1):51–60. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.09.004
Pucar D, Sella T, Schoder H (2008) The role of imaging in the detection of prostate cancer local recurrence after radiation therapy and surgery. Curr Opin Urol 18(1):87–97. doi:10.1097/MOU.0b013e3282f13ac3
Umbehr MH, Muntener M, Hany T, Sulser T, Bachmann LM (2013) The role of 11C-choline and 18F-fluorocholine positron emission tomography (PET) and PET/CT in prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 64(1):106–117. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.04.019
Kuru TH, Roethke MC, Seidenader J, Simpfendorfer T, Boxler S, Alammar K, Rieker P, Popeneciu VI, Roth W, Pahernik S, Schlemmer HP, Hohenfellner M, Hadaschik BA (2013) Critical evaluation of MRI-targeted TRUS-guided transperineal fusion biopsy for detection of prostate cancer. J Urol. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.04.043
Bomers JG, Yakar D, Overduin CG, Sedelaar JP, Vergunst H, Barentsz JO, de Lange F, Futterer JJ (2013) MR imaging-guided focal cryoablation in patients with recurrent prostate cancer. Radiology. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121291
Oto A, Sethi I, Karczmar G, McNichols R, Ivancevic MK, Stadler WM, Watson S, Eggener S (2013) MR imaging-guided focal laser ablation for prostate cancer: phase I trial. Radiology 267(3):932–940. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121652
Napoli A, Anzidei M, De Nunzio C, Cartocci G, Panebianco V, De Dominicis C, Catalano C, Petrucci F, Leonardo C (2013) Real-time magnetic resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound focal therapy for localised prostate cancer: preliminary experience. Eur Urol 63(2):395–398. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.002
Matsuoka Y, Numao N, Saito K, Tanaka H, Kumagai J, Yoshida S, Koga F, Masuda H, Kawakami S, Fujii Y, Kihara K (2012) Combination of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and extended prostate biopsy predicts lobes without significant cancer: application in patient selection for hemiablative focal therapy. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.10.010
Moore CM, Kasivisvanathan V, Eggener S, Emberton M, Futterer JJ, Gill IS, Grubb Iii RL, Hadaschik B, Klotz L, Margolis DJ, Marks LS, Melamed J, Oto A, Palmer SL, Pinto P, Puech P, Punwani S, Rosenkrantz AB, Schoots IG, Simon R, Taneja SS, Turkbey B, Ukimura O, van der Meulen J, Villers A, Watanabe Y, on behalf of the SC, (2013) Standards of reporting for MRI-targeted biopsy studies (START) of the prostate: recommendations from an international working group. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.03.030
Xie SW, Li HL, Du J, Xia JG, Guo YF, Xin M, Li FH (2012) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with contrast-tuned imaging technology for the detection of prostate cancer: comparison with conventional ultrasonography. BJU Int 109(11):1620–1626. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10577.x
Cirillo S, Petracchini M, Della Monica P, Gallo T, Tartaglia V, Vestita E, Ferrando U, Regge D (2008) Value of endorectal MRI and MRS in patients with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels and previous negative biopsies to localize peripheral zone tumours. Clin Radiol 63(8):871–879. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2007.10.020
Jung EM, Wiggermann P, Greis C, Eder F, Ehrich J, Jung W, Schreyer AG, Stroszczynski C, Ganzer R (2012) First results of endocavity evaluation of the microvascularization of malignant prostate tumors using contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) including perfusion analysis: first results. Clin Hemorheol Microcircul 52(2–4):167–177. doi:10.3233/CH-2012-1594
Testa C, Schiavina R, Lodi R, Salizzoni E, Corti B, Farsad M, Kurhanewicz J, Manferrari F, Brunocilla E, Tonon C, Monetti N, Castellucci P, Fanti S, Coe M, Grigioni WF, Martorana G, Canini R, Barbiroli B (2007) Prostate cancer: sextant localization with MR imaging, MR spectroscopy, and 11C-choline PET/CT. Radiology 244(3):797–806. doi:10.1148/radiol.2443061063
Acknowledgments
M. Rieken acknowledges support from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Conflict of interest
S. Shariat is a member of the advisory board for Ferring Pharmaceuticals. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pummer, K., Rieken, M., Augustin, H. et al. Innovations in diagnostic imaging of localized prostate cancer. World J Urol 32, 881–890 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1172-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1172-6